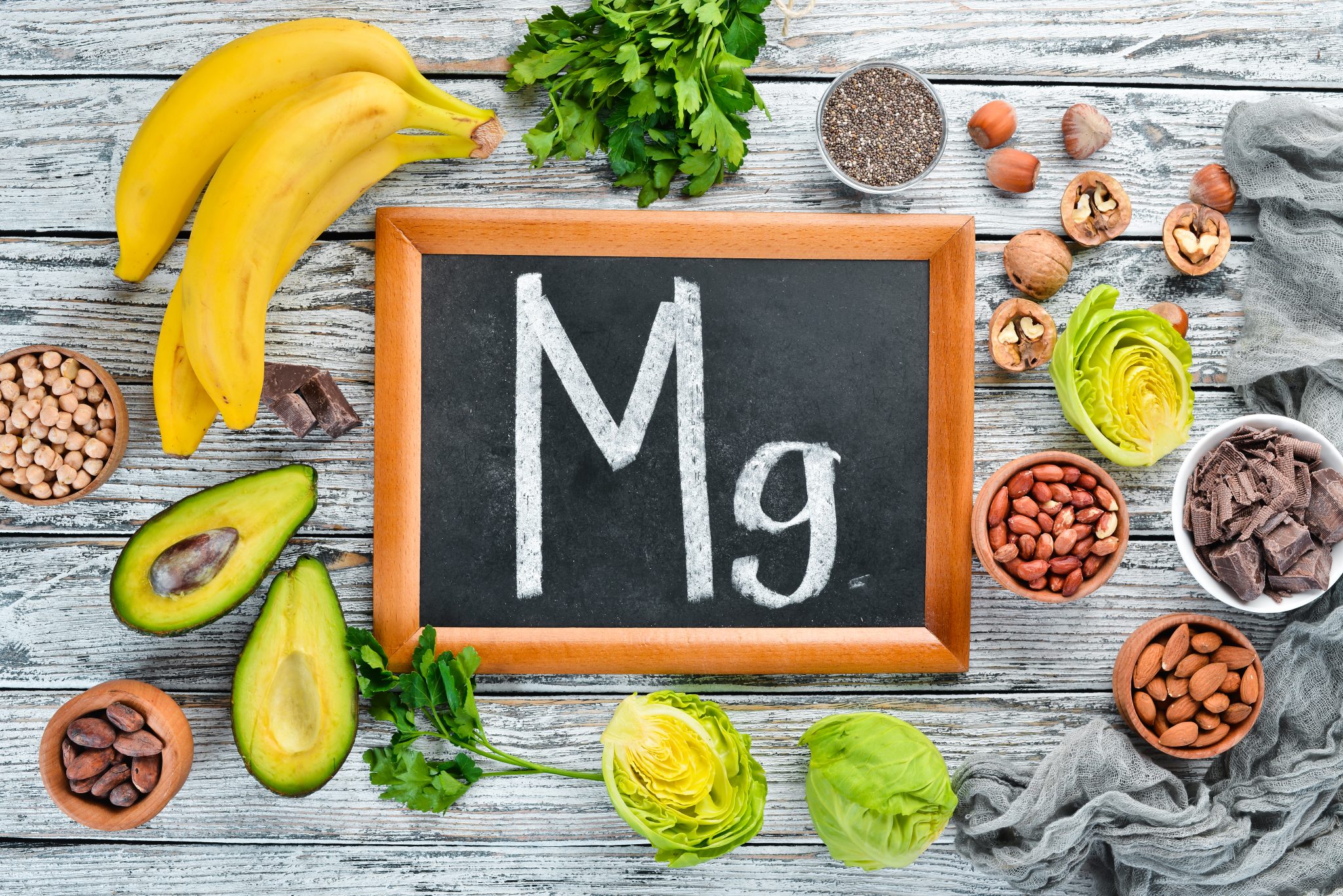Table of Contents
Introduction
Semaglutide is a medication that has gained a lot of attention recently for its benefits in managing diabetes and aiding in weight loss. It is a type of drug known as a GLP-1 receptor agonist, which means it works by mimicking a hormone in the body called glucagon-like peptide-1. This hormone helps to regulate blood sugar levels, making semaglutide an effective treatment for type 2 diabetes. Additionally, semaglutide has been found to help people lose weight, which is a significant benefit for those struggling with obesity.
Magnesium, on the other hand, is a mineral that is essential for many functions in the body. It plays a critical role in muscle and nerve function, blood sugar control, and bone health. Magnesium is found in many foods, including leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Despite its importance, many people do not get enough magnesium from their diet, leading to deficiency-related health issues such as muscle cramps, fatigue, and irregular heartbeats.
The purpose of this article is to explore how magnesium can enhance the effects of semaglutide. By understanding the relationship between these two substances, individuals can potentially improve their health outcomes. This article will answer common questions about how magnesium and semaglutide work together, the benefits and potential risks, and how to safely incorporate magnesium into a treatment plan that includes semaglutide.
To start, let’s look at what semaglutide is and how it works. Semaglutide is usually administered through an injection once a week. It helps to lower blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin release when blood sugar is high. It also slows down the movement of food through the stomach, which helps to reduce appetite and, consequently, leads to weight loss. For people with type 2 diabetes, controlling blood sugar levels is crucial because it helps to prevent complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems.
Now, let’s understand more about magnesium and its role in the body. Magnesium is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body. It helps to maintain normal nerve and muscle function, supports a healthy immune system, keeps the heartbeat steady, and helps bones remain strong. Magnesium also helps regulate blood glucose levels and aids in the production of energy and protein. Despite its importance, studies have shown that a significant portion of the population does not get the recommended daily amount of magnesium, which can lead to various health problems.
So, how do semaglutide and magnesium work together? Research suggests that magnesium might enhance the effectiveness of semaglutide in several ways. For one, magnesium is known to improve insulin sensitivity, which means it helps the body use insulin more efficiently. Since semaglutide also works to improve blood sugar control, taking magnesium might boost this effect, making blood sugar levels even more stable. Additionally, magnesium has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which can further benefit individuals with type 2 diabetes, as inflammation is a common issue in this condition.
Moreover, magnesium can help reduce some of the side effects associated with semaglutide. For example, semaglutide can sometimes cause gastrointestinal issues like nausea and constipation. Magnesium, particularly in the form of supplements like magnesium citrate, can help alleviate constipation by promoting bowel movements. This can make the overall treatment plan more comfortable and effective for the patient.
In conclusion, combining magnesium with semaglutide can offer enhanced benefits for those managing type 2 diabetes and obesity. This article will delve deeper into the science behind this interaction, discuss the best ways to incorporate magnesium into your diet or supplement routine, and provide practical tips for maximizing the health benefits of both semaglutide and magnesium. By the end of this comprehensive guide, readers will have a clear understanding of how to optimize their treatment plan and improve their health outcomes.
What is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is a medication that has become popular for treating type 2 diabetes and helping with weight loss. Understanding how semaglutide works and why it is effective can help people make informed decisions about their health.
Semaglutide belongs to a class of drugs called GLP-1 receptor agonists. GLP-1 stands for glucagon-like peptide-1, which is a hormone our bodies naturally produce. This hormone helps to regulate blood sugar levels by increasing insulin production when blood sugar is high and by reducing the amount of glucose (sugar) produced by the liver. Insulin is a hormone that allows cells to take in glucose from the blood, lowering blood sugar levels.
One of the key benefits of semaglutide is that it mimics the action of GLP-1. When a person with type 2 diabetes takes semaglutide, it helps their body manage blood sugar more effectively. Semaglutide is usually given as an injection under the skin once a week. This makes it easier for people to stick to their treatment compared to medications that need to be taken daily.
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for people with type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels over time can cause serious complications, such as damage to the eyes, kidneys, and nerves. It can also lead to heart disease and stroke. By helping to keep blood sugar levels in check, semaglutide helps to prevent these complications and improve overall health.
Another significant benefit of semaglutide is its role in weight loss. Many people with type 2 diabetes are also overweight or obese, which can make managing diabetes more difficult. Semaglutide helps with weight loss in several ways. First, it slows down the emptying of the stomach, which helps people feel full longer after eating. This can reduce overall food intake. Second, semaglutide acts on the brain to reduce appetite, making people less likely to overeat. In clinical trials, people taking semaglutide lost more weight compared to those taking a placebo (a dummy treatment).
The combination of better blood sugar control and weight loss makes semaglutide a powerful tool for managing type 2 diabetes. However, like all medications, semaglutide can have side effects. Some common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These side effects are usually mild and tend to decrease over time as the body gets used to the medication. More serious side effects are rare but can include pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) and allergic reactions. It is important for people taking semaglutide to be aware of these potential side effects and to talk to their healthcare provider if they experience any unusual symptoms.
Semaglutide has been extensively studied in clinical trials, and the results have been very promising. In addition to improving blood sugar control and promoting weight loss, semaglutide has also been shown to reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke, in people with type 2 diabetes. This is especially important because people with diabetes are at a higher risk for these events.
Another advantage of semaglutide is its convenient dosing schedule. Since it only needs to be taken once a week, it can be easier for people to remember and adhere to their treatment plan. This can lead to better overall management of diabetes and improved health outcomes.
Semaglutide is a highly effective medication for managing type 2 diabetes and aiding in weight loss. By mimicking the action of the GLP-1 hormone, it helps to regulate blood sugar levels, reduce appetite, and promote a feeling of fullness. While it can have some side effects, the benefits of semaglutide often outweigh these risks, especially when it comes to preventing serious complications of diabetes. Understanding how semaglutide works can help people make informed decisions about their treatment and work with their healthcare providers to achieve the best possible health outcomes.
The Role of Magnesium in the Body
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in many bodily functions. It is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions, which means it helps to trigger and speed up chemical processes in the body. Understanding the importance of magnesium can help you see why it’s so crucial to maintain adequate levels of this mineral, especially if you’re taking medications like semaglutide.
Importance of Magnesium in Physiological Functions
Magnesium is necessary for several key functions in the body:
- Energy Production: Magnesium helps convert food into energy. It is a co-factor in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the main energy carrier in cells.
- Protein Synthesis: Magnesium is involved in the creation of proteins from amino acids. This is important for muscle growth, repair, and overall cellular health.
- Muscle and Nerve Function: Magnesium plays a critical role in the contraction and relaxation of muscles. It also helps regulate the nervous system, ensuring that nerve impulses are transmitted correctly.
- Blood Sugar Control: Magnesium aids in regulating blood sugar levels by influencing the action of insulin. Proper magnesium levels can help maintain healthy blood glucose levels, which is particularly important for people with diabetes.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Magnesium helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels. It relaxes the blood vessels, which can help reduce hypertension (high blood pressure).
- Bone Health: About 60% of the body’s magnesium is stored in the bones. Magnesium is essential for bone formation and influences the activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, which are responsible for building and breaking down bone tissue.
Sources of Magnesium in Diet and Supplements
There are many dietary sources of magnesium. Eating a balanced diet can help you get enough of this important mineral. Here are some foods rich in magnesium:
- Green Leafy Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are excellent sources of magnesium.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, cashews, peanuts, and pumpkin seeds are high in magnesium.
- Whole Grains: Foods like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread provide good amounts of magnesium.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are also rich in magnesium.
- Fruits: Bananas, avocados, and dried fruits like figs and apricots contain magnesium.
- Fish: Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel have good magnesium content.
- Dark Chocolate: High in magnesium and a delicious treat, dark chocolate can contribute to your magnesium intake.
For those who may not get enough magnesium from their diet, supplements are available. Magnesium supplements come in various forms, including magnesium oxide, magnesium citrate, and magnesium chloride. Each type has different absorption rates and effects on the body. It’s important to choose the right supplement and dosage based on individual needs and health conditions.
Common Health Issues Related to Magnesium Deficiency
A deficiency in magnesium can lead to a variety of health problems. Some of the most common symptoms and issues include:
- Muscle Cramps and Spasms: Low magnesium levels can cause painful muscle contractions and spasms.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Since magnesium is vital for energy production, a deficiency can lead to fatigue and general weakness.
- Mental Health Issues: Magnesium deficiency has been linked to mood disorders like depression and anxiety.
- High Blood Pressure: Lack of magnesium can contribute to hypertension, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Osteoporosis: Inadequate magnesium can affect bone health, making bones more prone to fractures.
- Irregular Heartbeat: Magnesium is crucial for maintaining a steady heart rhythm. A deficiency can cause arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats.
To prevent these issues, it’s important to ensure adequate magnesium intake through diet or supplements, especially for individuals using medications like semaglutide that can affect nutrient absorption and overall metabolic health.
Magnesium is a vital mineral necessary for many bodily functions, from energy production to muscle and nerve function. Getting enough magnesium through diet and supplements is essential for maintaining good health and preventing deficiency-related issues. This becomes even more important when using medications like semaglutide, which can have interactions with magnesium levels in the body.

How Does Magnesium Interact with Semaglutide?
Magnesium is a mineral that is essential for many functions in the body. It helps with muscle function, nerve signaling, and maintaining a healthy immune system. On the other hand, semaglutide is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes and aid in weight loss by mimicking a hormone called GLP-1, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and appetite. Understanding how magnesium and semaglutide interact can help enhance the benefits of both.
Scientific Basis for Interaction
Magnesium plays a crucial role in several biochemical reactions in the body. One of its key functions is to act as a cofactor for enzymes involved in glucose metabolism. This means that magnesium helps enzymes do their job of breaking down sugar in the body. When magnesium levels are adequate, these enzymes work more efficiently, helping to keep blood sugar levels stable.
Semaglutide works by stimulating the release of insulin, a hormone that lowers blood sugar levels. It also slows down the emptying of the stomach, making you feel full longer and reducing the amount of food you eat. By keeping blood sugar levels stable, semaglutide helps prevent spikes and crashes that can lead to hunger and overeating.
When you combine magnesium with semaglutide, the magnesium can enhance the action of the enzymes that break down sugar. This can make semaglutide more effective at keeping blood sugar levels stable. Additionally, since magnesium is important for nerve function, it may help improve the way the nerves in your stomach and intestines respond to semaglutide, enhancing its effects on appetite control.
Potential Synergistic Effects
Synergy occurs when two substances work together to produce a combined effect that is greater than the sum of their individual effects. When magnesium and semaglutide are taken together, they may have a synergistic effect on blood sugar control and weight loss.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: Magnesium helps regulate blood sugar by assisting enzymes in breaking down glucose. Semaglutide enhances insulin release and delays stomach emptying. Together, they can provide a more stable blood sugar level, reducing the risk of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
- Enhanced Weight Loss: Semaglutide helps with weight loss by making you feel full longer and reducing food intake. Magnesium supports muscle function and energy production, which can help you stay active and burn more calories. By working together, magnesium and semaglutide can boost your metabolism and aid in weight loss efforts.
- Reduced Inflammation: Both magnesium and semaglutide have anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is linked to insulin resistance and obesity. By reducing inflammation, magnesium and semaglutide can improve insulin sensitivity and promote a healthier weight.
Studies and Clinical Trials
Several studies have looked at the effects of magnesium on blood sugar control and weight management. For example, research has shown that people with higher magnesium intake are less likely to develop type 2 diabetes. Other studies have found that magnesium supplements can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce fasting blood sugar levels.
Clinical trials on semaglutide have demonstrated its effectiveness in lowering blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss. While specific studies on the combination of magnesium and semaglutide are limited, the existing evidence suggests that adding magnesium to your diet could enhance the benefits of semaglutide.
Practical Implications
If you are taking semaglutide for diabetes or weight loss, consider discussing magnesium supplementation with your healthcare provider. They can help you determine the right dosage and form of magnesium to take. It’s important not to take too much magnesium, as excessive amounts can cause side effects like diarrhea and abdominal cramps.
In addition to supplements, you can increase your magnesium intake by eating more magnesium-rich foods. These include leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help ensure you get enough magnesium to support your body’s needs and enhance the effects of semaglutide.
Magnesium and semaglutide can work together to improve blood sugar control, aid in weight loss, and reduce inflammation. By understanding their interaction and incorporating magnesium into your diet or supplement regimen, you can maximize the benefits of semaglutide and support your overall health.
Benefits of Combining Magnesium with Semaglutide
Combining magnesium with semaglutide offers several potential benefits. Understanding these can help you make informed decisions about your health and treatment options. Let’s explore how this combination might enhance weight loss, improve blood sugar control, and reduce side effects.
Enhanced Efficacy in Weight Loss
Semaglutide is widely used to help with weight loss. It works by mimicking a hormone called GLP-1, which helps control appetite and blood sugar levels. However, adding magnesium to your routine may further boost these effects.
How Magnesium Helps with Weight Loss:
- Regulates Blood Sugar Levels: Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. Stable blood sugar can prevent spikes and crashes that often lead to cravings and overeating.
- Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Insulin is a hormone that helps your body use sugar for energy. Magnesium can improve how your body responds to insulin, making it easier to control weight.
- Reduces Inflammation: Chronic inflammation can make it harder to lose weight. Magnesium has anti-inflammatory properties that can support weight loss efforts.
Combining semaglutide and magnesium might lead to more significant weight loss results than using semaglutide alone.
Improved Glycemic Control
For people with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is crucial. Semaglutide helps by increasing insulin production and reducing the amount of sugar your liver releases into the blood. Magnesium can complement these effects, offering better overall glycemic control.
How Magnesium Supports Glycemic Control:
- Enhances Insulin Production: Magnesium helps your pancreas produce insulin more effectively. This can help lower blood sugar levels after meals.
- Improves Glucose Metabolism: Magnesium is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, many of which are related to glucose metabolism. This means your body can process sugar more efficiently.
- Prevents Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance occurs when cells in your body don’t respond well to insulin, leading to higher blood sugar levels. Magnesium can help prevent this condition, making it easier to control diabetes.
By improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, magnesium can make semaglutide more effective in managing diabetes.
Reduction in Side Effects
While semaglutide is effective, it can cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Magnesium might help reduce these side effects, making the treatment more tolerable.
How Magnesium Reduces Side Effects:
- Eases Digestive Issues: Magnesium can help relax muscles in the digestive tract, reducing symptoms like nausea and stomach cramps. This can be particularly helpful for people who experience gastrointestinal side effects from semaglutide.
- Supports Nerve Function: Proper nerve function is essential for a healthy digestive system. Magnesium supports nerve function, which can help mitigate some of the uncomfortable side effects of semaglutide.
- Maintains Electrolyte Balance: Vomiting and diarrhea can lead to electrolyte imbalances. Magnesium helps maintain this balance, ensuring your body functions properly even if you experience these side effects.
By addressing these side effects, magnesium can make it easier for people to stick to their semaglutide treatment plan.
Combining magnesium with semaglutide offers several benefits. It can enhance weight loss, improve glycemic control, and reduce side effects. Magnesium helps by regulating blood sugar, improving insulin sensitivity, and reducing inflammation. It also supports insulin production, glucose metabolism, and nerve function. Additionally, magnesium can ease digestive issues and maintain electrolyte balance.
If you’re considering this combination, talk to your healthcare provider. They can help you determine the right dosages and ensure that this combination is safe and effective for you. By working together, semaglutide and magnesium can help you achieve better health outcomes.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
When considering the combination of semaglutide and magnesium, it’s important to understand the potential side effects and risks. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions and manage your health more effectively.
Side Effects of Semaglutide Alone
Semaglutide, a medication commonly used for weight loss and diabetes management, can have side effects. These side effects vary from person to person. Some people may experience mild side effects, while others might have more serious ones.
Common side effects of semaglutide include:
- Nausea: Many people feel nauseous when they first start taking semaglutide. This usually gets better over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
- Vomiting: Along with nausea, some people might vomit, especially during the initial stages of treatment.
- Diarrhea: Semaglutide can cause loose stools or diarrhea. Staying hydrated and eating a balanced diet can help manage this.
- Constipation: While some experience diarrhea, others might have the opposite problem and become constipated.
- Stomach Pain: Abdominal discomfort is another common complaint. It can be mild or severe.
- Headaches: Some people report headaches when taking semaglutide.
More serious but less common side effects include:
- Pancreatitis: This is inflammation of the pancreas, which can cause severe stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. If you experience these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
- Gallbladder Problems: Some people develop gallstones or inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Kidney Issues: Semaglutide can affect kidney function, especially in people with pre-existing kidney conditions.
- Thyroid Tumors: There is a potential risk of thyroid tumors, including cancer, although this is rare.
Potential Risks of Combining Semaglutide with Magnesium
Adding magnesium to your routine while taking semaglutide can have several benefits, but it also comes with its own set of risks. Understanding these risks can help you use both substances safely.
- Digestive Issues: Both semaglutide and magnesium can affect your digestive system. Semaglutide can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, while magnesium, especially in large doses, can also cause diarrhea and stomach cramps. Combining the two might increase the risk of these digestive issues. To manage this, start with lower doses and increase gradually under medical supervision.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Magnesium plays a key role in maintaining electrolyte balance in the body. Taking too much magnesium, especially in supplement form, can cause an imbalance. Symptoms of too much magnesium include diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. In severe cases, it can lead to more serious issues like low blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, and confusion.
- Kidney Strain: Both semaglutide and magnesium are processed by the kidneys. If you have existing kidney problems, adding magnesium supplements could put additional strain on your kidneys. This can potentially lead to kidney damage or worsen existing kidney conditions. It’s crucial to have your kidney function monitored regularly by your doctor.
- Drug Interactions: Magnesium can interact with other medications you might be taking. For example, magnesium can affect how your body absorbs certain medications, including antibiotics and bisphosphonates (used for osteoporosis). This interaction can reduce the effectiveness of these medications. Always inform your doctor about all the supplements and medications you are taking to avoid harmful interactions.
How to Mitigate These Risks
To safely combine semaglutide and magnesium, consider the following tips:
- Consult Your Doctor: Before starting magnesium supplements, talk to your doctor. They can help determine the right dosage and monitor your health for any adverse effects.
- Start Low, Go Slow: Begin with a low dose of magnesium and gradually increase it. This approach allows your body to adjust and helps identify the appropriate dose that doesn’t cause side effects.
- Monitor Your Health: Keep track of any new symptoms or changes in your health. Regular check-ups with your doctor can help catch potential problems early.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help your kidneys process both semaglutide and magnesium. Proper hydration can also alleviate some digestive side effects.
- Balanced Diet: Try to get magnesium from natural food sources like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. A balanced diet can provide necessary nutrients without the risk of over-supplementation.
By understanding the potential side effects and risks of combining semaglutide with magnesium, and by taking steps to mitigate these risks, you can safely enhance the effectiveness of your treatment plan. Always work closely with your healthcare provider to ensure the best outcomes for your health.

How to Supplement Magnesium Safely
Supplementing magnesium safely involves understanding the different forms of magnesium, following dosage guidelines, and monitoring and adjusting magnesium levels as needed. This section will explain these points in detail, making it clear and easy to understand.
Different Forms of Magnesium Supplements
Magnesium supplements come in various forms, each with its benefits and potential side effects. Some common types of magnesium supplements include:
- Magnesium Citrate: This form is easily absorbed by the body and is often used to treat constipation. It can sometimes cause loose stools, so it is important to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it.
- Magnesium Oxide: This form contains a higher amount of elemental magnesium but is not as easily absorbed. It is often used for treating magnesium deficiency and can also help with digestive issues.
- Magnesium Glycinate: Known for its high absorption rate, this form is gentle on the stomach and less likely to cause diarrhea. It is commonly used for improving overall magnesium levels and can be helpful for those with a sensitive digestive system.
- Magnesium Chloride: This form is well absorbed and can be used both orally and topically. It is often used to treat magnesium deficiency and can also help with muscle relaxation and skin health.
- Magnesium Sulfate: Commonly known as Epsom salt, this form is often used in baths to soothe sore muscles. It can also be taken orally in small doses for a quick increase in magnesium levels, but it is essential to follow dosing instructions carefully to avoid side effects.
Choosing the right form of magnesium supplement depends on your specific needs and how your body responds to different types. It is always best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
Dosage Guidelines
Determining the correct dosage of magnesium is crucial for safety and effectiveness. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for magnesium varies by age, sex, and life stage. For most adults, the RDA is around 310-420 mg per day. However, if you are taking magnesium to enhance the effects of semaglutide, your doctor may recommend a specific dosage tailored to your needs.
Here are some general dosage guidelines to consider:
- Start Low and Go Slow: Begin with a lower dose of magnesium, such as 100-200 mg per day, to see how your body reacts. Gradually increase the dosage as needed, based on your doctor’s advice and your body’s response.
- Avoid Over-Supplementation: Taking too much magnesium can lead to adverse effects such as diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and nausea. It is important not to exceed the upper intake level (UL) of 350 mg per day from supplements, unless directed by a healthcare provider.
- Consider Total Magnesium Intake: Remember to account for magnesium from all sources, including food and supplements, to avoid exceeding the recommended limits.
Monitoring and Adjusting Magnesium Levels
Regular monitoring of magnesium levels can help ensure you are getting the right amount without overdoing it. Here are some tips for effective monitoring and adjustment:
- Blood Tests: Your doctor can order blood tests to check your magnesium levels. These tests can help determine if you are getting enough magnesium or if adjustments are needed.
- Track Symptoms: Pay attention to any changes in your symptoms, such as muscle cramps, fatigue, or digestive issues. These can be signs that your magnesium levels are too low or too high.
- Adjust Dosage as Needed: Based on your symptoms and test results, your doctor may recommend adjusting your magnesium dosage. This may involve increasing or decreasing the amount you take or switching to a different form of magnesium.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help your body absorb magnesium more effectively and reduce the risk of side effects like diarrhea.
- Regular Check-Ins with Your Doctor: Keep in touch with your healthcare provider to discuss your progress and any concerns you may have. Regular check-ins can help ensure you are supplementing magnesium safely and effectively.
By understanding the different forms of magnesium supplements, following dosage guidelines, and monitoring your levels, you can safely supplement magnesium to enhance the effects of semaglutide. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement to ensure it is right for you and to get personalized advice on the best approach for your health needs.
Dietary Sources of Magnesium
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in many of our body’s functions, such as muscle and nerve function, blood sugar control, and bone health. If you’re taking semaglutide, getting enough magnesium from your diet can help enhance its effects. Here’s a detailed look at how you can add more magnesium-rich foods to your meals.
Foods Rich in Magnesium
There are many foods that are naturally high in magnesium. Including these in your diet can help you meet your daily magnesium needs. Here are some of the best sources:
- Leafy Green Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are all excellent sources of magnesium. You can add these to salads, smoothies, or cook them as side dishes.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds are high in magnesium. They make great snacks or can be added to yogurt, oatmeal, or salads for extra crunch.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are rich in magnesium. These can be used in soups, stews, salads, or as side dishes.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread are good sources of magnesium. Switching from refined grains to whole grains can significantly boost your magnesium intake.
- Fish: Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel contain good amounts of magnesium. Including fish in your diet two to three times a week can contribute to your magnesium needs.
- Avocados: This popular fruit is not only high in healthy fats but also a good source of magnesium. You can add avocado to salads, sandwiches, or enjoy it as a spread.
- Dark Chocolate: Dark chocolate with a high cocoa content (70% or more) is rich in magnesium. Eating a small piece as a treat can help increase your magnesium levels.
Dietary Recommendations for Individuals on Semaglutide
If you are taking semaglutide, ensuring you have enough magnesium in your diet can be beneficial. Here are some tips:
- Balance Your Meals: Aim to include a variety of magnesium-rich foods in your daily meals. For example, you can have oatmeal with nuts for breakfast, a spinach salad with chickpeas for lunch, and grilled salmon with quinoa for dinner.
- Snack Wisely: Choose snacks that are high in magnesium, such as a handful of almonds, a piece of dark chocolate, or a smoothie made with spinach and avocado.
- Cook at Home: Preparing meals at home allows you to control the ingredients and ensure that your diet is rich in magnesium. Incorporate leafy greens, whole grains, and legumes into your recipes.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps your body absorb magnesium. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day.
Tips for Integrating Magnesium-Rich Foods into Daily Meals
Here are some practical ways to add more magnesium to your diet:
- Breakfast: Start your day with a magnesium-rich breakfast. Make a smoothie with spinach, banana, and almond milk, or have a bowl of whole grain cereal with milk and a handful of pumpkin seeds.
- Lunch: For lunch, consider a salad with leafy greens, avocado, and beans. Add a side of whole grain bread to further boost your magnesium intake.
- Dinner: Include a serving of fatty fish like salmon, paired with quinoa and a side of steamed broccoli or kale.
- Snacks: Keep magnesium-rich snacks on hand. Nuts, seeds, and dark chocolate are easy to carry and can help you meet your magnesium needs throughout the day.
- Cooking Tips: Use magnesium-rich herbs and spices like basil and coriander in your cooking. These can add flavor and extra nutrients to your meals.
By incorporating more magnesium-rich foods into your diet, you can support your body’s functions and potentially enhance the effects of semaglutide. Remember to balance your meals, choose healthy snacks, and stay hydrated. Making these changes can help you get the most out of your treatment and improve your overall health. If you have any questions or need personalized advice, don’t hesitate to consult with your healthcare provider.
Magnesium and Lifestyle Factors
Magnesium plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, and its levels can be influenced by various lifestyle factors. Understanding these factors can help you maximize the benefits of combining magnesium with semaglutide.
The Role of Physical Activity
Physical activity is essential for overall health and well-being. It helps maintain a healthy weight, improves cardiovascular health, and boosts mood. For individuals taking semaglutide, regular exercise can enhance the medication’s effectiveness in weight loss and glycemic control. Here’s how:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Exercise increases insulin sensitivity, which means your body uses insulin more effectively. This can be particularly beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes, who often struggle with insulin resistance.
- Enhanced Weight Loss: Combining physical activity with semaglutide can lead to more significant weight loss. Exercise burns calories and builds muscle, which can help you shed pounds faster and maintain a healthy weight.
- Better Cardiovascular Health: Regular exercise strengthens your heart and improves circulation, reducing the risk of heart disease. This is especially important for people with diabetes, who are at higher risk of cardiovascular issues.
To get the most out of your exercise routine, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week. This can include activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Additionally, incorporate muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week.
Stress Management and Its Impact on Magnesium Levels
Stress is a common part of life, but chronic stress can negatively impact your health, including your magnesium levels. Here’s how stress affects magnesium and what you can do about it:
- Magnesium Depletion: Stress triggers the release of stress hormones like cortisol. These hormones can deplete magnesium levels in the body. Low magnesium levels can, in turn, increase your susceptibility to stress, creating a vicious cycle.
- Increased Risk of Deficiency: If you are under constant stress, your body’s need for magnesium increases. Without adequate magnesium intake, you may experience symptoms like fatigue, muscle cramps, and anxiety.
To manage stress and support healthy magnesium levels, consider incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine. These might include:
- Mindfulness Meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help you stay present and reduce anxiety. Even a few minutes of meditation each day can make a difference.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing can calm your nervous system and reduce stress. Try taking slow, deep breaths for a few minutes whenever you feel stressed.
- Physical Activity: Exercise is a natural stress reliever. As mentioned earlier, regular physical activity can improve your mood and reduce anxiety.
Overall Lifestyle Recommendations for Maximizing Health Outcomes
To get the best results from combining magnesium with semaglutide, consider the following lifestyle recommendations:
- Balanced Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in whole foods can provide the nutrients your body needs to function optimally. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Foods high in magnesium, such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, should be a staple in your diet.
- Adequate Hydration: Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and can help prevent side effects associated with semaglutide. Aim to drink at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water daily, more if you are physically active.
- Regular Sleep: Getting enough sleep is crucial for your body to repair and rejuvenate. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Poor sleep can affect your hormone levels, appetite, and stress levels, which can interfere with weight loss and diabetes management.
- Routine Health Check-ups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider can help you monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed. Your doctor can check your magnesium levels and ensure that you are not experiencing any adverse effects from the combination of semaglutide and magnesium.
By integrating these lifestyle factors into your daily routine, you can enhance the benefits of magnesium and semaglutide, leading to better health outcomes. Remember, making small, consistent changes can have a significant impact over time. Consult with your healthcare provider before making any major changes to your lifestyle or treatment plan to ensure it is safe and effective for your specific needs.

Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored how magnesium can enhance the effects of semaglutide, a medication primarily used for managing type 2 diabetes and aiding in weight loss. Semaglutide works by mimicking the hormone GLP-1, which helps control blood sugar levels, slow stomach emptying, and reduce appetite. On the other hand, magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, blood sugar control, and bone health. Combining these two can offer a range of benefits, but it is important to understand the interaction and how to manage it safely.
Firstly, semaglutide is effective in managing blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss, making it a popular choice for people with type 2 diabetes and those looking to lose weight. However, like any medication, it has its side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and sometimes low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). On its own, magnesium is vital for overall health, contributing to muscle function, nerve signaling, and maintaining a healthy immune system. It is found naturally in foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, and can also be taken as a supplement.
When combined, magnesium can potentially enhance the benefits of semaglutide. Magnesium is known to improve insulin sensitivity, which can help in better blood sugar control. This is particularly beneficial for those taking semaglutide for diabetes management. Moreover, magnesium helps in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, which are common issues in people with diabetes. By addressing these underlying problems, magnesium can aid in improving the overall effectiveness of semaglutide.
Additionally, magnesium can help reduce some of the side effects associated with semaglutide. For instance, since magnesium plays a role in digestive health, it may help alleviate gastrointestinal side effects like nausea and diarrhea. Magnesium also supports muscle function, which can be beneficial since some people on semaglutide experience muscle cramps or weakness. By ensuring adequate magnesium levels, patients may experience fewer side effects and better overall outcomes.
However, combining magnesium with semaglutide should be done carefully. It is essential to avoid excessive magnesium intake, which can lead to its own set of problems, such as diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and, in severe cases, heart issues. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for magnesium varies by age and gender but generally ranges from 310 to 420 milligrams per day for adults. It is best to get magnesium from dietary sources as much as possible, and if supplements are needed, they should be taken under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Dietary sources of magnesium include green leafy vegetables like spinach and kale, nuts and seeds, whole grains, and legumes. Including these foods in your diet can help maintain adequate magnesium levels. For individuals on semaglutide, focusing on a balanced diet rich in these foods can support the medication’s effectiveness and overall health. It’s also important to consider lifestyle factors. Regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep can all contribute to better health outcomes when using semaglutide and magnesium together.
Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and aids in weight loss, complementing the effects of semaglutide. Managing stress is crucial as stress can negatively impact blood sugar levels and overall health. Techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can be helpful. Lastly, ensuring adequate sleep is important as poor sleep can interfere with insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic health.
In conclusion, the combination of magnesium and semaglutide holds promise for enhancing health outcomes, particularly for those managing type 2 diabetes and looking to lose weight. Magnesium supports many of the body’s functions that can help mitigate some of the side effects of semaglutide and improve its effectiveness. However, it is essential to approach this combination carefully, ensuring that magnesium intake is adequate but not excessive. Consulting with a healthcare provider before making any changes to your treatment plan is crucial. By understanding the interaction between these two substances and making informed choices, patients can achieve better health outcomes and improve their quality of life.
Research Citations
Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016 Nov 10;375(19):1834-1844. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1607141. PMID: 27633186.
Tuttle KR, Lakshmanan MC, Rayner B, et al. Dulaglutide versus insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate-to-severe chronic kidney disease (AWARD-7): a multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Feb;6(2):605-617. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30002-4. Epub 2018 Jan 8. PMID: 29326031.
Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016 Jul 28;375(4):311-22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1603827. Epub 2016 Jun 13. PMID: 27295427.
Khanderia U, Townsend RR. Magnesium: cardiovascular benefits and research challenges. Open Heart. 2018 May 24;5(1)
. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2018-000775. PMID: 29942572; PMCID: PMC5993535.
Stone M, Tao L, Tan X, et al. Magnesium intake, plasma C-peptide, and risk of pancreatic cancer: results from two large cohort studies. Diabetes Care. 2015 Mar;38(3):620-6. doi: 10.2337/dc14-1942. Epub 2015 Jan 12. PMID: 25583751; PMCID: PMC4338327.
Han H, Fang X, Wei X, et al. Dose-response relationship between dietary magnesium intake, serum magnesium concentration and risk of hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nutr J. 2017 Mar 2;16(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12937-017-0240-6. PMID: 28249576; PMCID: PMC5338263.
Bertoia ML, Triche EW, Michaud DS, et al. Long-term dietary flavonoid intake and risk of epithelial ovarian cancer. Am J Epidemiol. 2014 Oct 1;179(7):1471-8. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwu062. Epub 2014 Jun 6. PMID: 24907753; PMCID: PMC4166708.
Guasch-Ferré M, Bulló M, Estruch R, et al. Dietary magnesium intake is inversely associated with mortality in adults at high cardiovascular disease risk. J Nutr. 2014 Jan;144(1):55-60. doi: 10.3945/jn.113.183012. Epub 2013 Nov 20. PMID: 24259554.
Fang X, Han H, Li M, et al. Dose-response relationship between dietary magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nutrients. 2016 Nov 10;8(11):739. doi: 10.3390/nu8110739. PMID: 27834959; PMCID: PMC5133066.
Hruby A, Meigs JB, O’Donnell CJ, et al. Higher magnesium intake reduces risk of impaired glucose and insulin metabolism and progression from prediabetes to diabetes in middle-aged Americans. Diabetes Care. 2014 Jan;37(2):419-27. doi: 10.2337/dc13-1397. Epub 2013 Aug 14. PMID: 23948537; PMCID: PMC3898748.
Questions and Answers: Semaglutide and Magnesium
Yes, you can take magnesium supplements while on semaglutide. However, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements to ensure they won’t interfere with your medication or health condition.
There is no direct evidence that semaglutide affects magnesium levels in the body. However, maintaining adequate magnesium levels is important for overall health, especially when managing conditions like diabetes.
Magnesium is crucial for many bodily functions, including glucose metabolism and muscle function. For people with diabetes or those taking semaglutide, maintaining adequate magnesium levels can help support overall metabolic health and potentially improve medication effectiveness.
Magnesium may help alleviate some side effects of semaglutide, such as muscle cramps or gastrointestinal discomfort. However, this should be discussed with your healthcare provider to ensure it is appropriate for your situation.
There are no known significant interactions between semaglutide and magnesium supplements. Nevertheless, it’s always best to check with your healthcare provider before combining any medications or supplements.
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for magnesium varies by age and sex. Generally, adult men should aim for 400-420 mg per day, and adult women should aim for 310-320 mg per day. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice, especially if you are taking semaglutide.
While magnesium itself is not a weight loss aid, maintaining adequate magnesium levels is important for overall metabolic health, which can indirectly support weight loss efforts when combined with semaglutide.
It is not typically required to monitor magnesium levels specifically while taking semaglutide. However, if you have a condition that affects magnesium levels or are experiencing symptoms of magnesium deficiency, your healthcare provider may recommend monitoring.
Magnesium plays a role in glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Adequate magnesium levels can support blood sugar control, complementing the effects of semaglutide in managing diabetes.
Good dietary sources of magnesium include green leafy vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help maintain adequate magnesium levels while taking semaglutide.

Dr. Melissa VanSickle
Dr. Melissa Vansickle, MD is a family medicine specialist in Onsted, MI and has over 24 years of experience in the medical field. She graduated from University of Michigan Medical School in 1998. She is affiliated with medical facilities Henry Ford Allegiance Health and Promedica Charles And Virginia Hickman Hospital. Her subspecialties include General Family Medicine, Urgent Care, Complementary and Integrative Medicine in Rural Health.