
How to Inject Semaglutide Video and Instructions
What is a subcutaneous injection?
A subcutaneous injection is a way of administering medication, fluids, or blood that is injected into the tissue just below the skin. This can be done by a needle, depending on the situation and type of medication you are administering.
Subcutaneous injections are given outside the veins (IV). They administer fluid or medication that travels slowly through the body. This is a great option for patients who may be frightened by a needle going into their vein or muscle.
Subcutaneous injections are often used to administer vaccines, medications, or fluids as part of chemotherapy that cannot be taken orally, or when an individual has an allergy or sensitivity to the ingredients in the medication.
What Are the Benefits of Subcutaneous Injections?
- Easier and painless: If you are afraid of needles, subcutaneous injections may be the best option as they are easier to administer and far painless compared to an intra-muscular injection.
- Multiple injections: If you have to undergo multiple injections, subcutaneous injections may be advantageous to you.
- Easier with allergies: Subcutaneous injections are often preferred by patients with severe allergies to medications, as they allow the patient to receive treatment without having to deal with the allergic reaction.
- No inflatable needle: The subcutaneous injection method uses a special syringe that has a smaller needle that is more comfortable when injected into the skin.
What Are the Side Effects of Subcutaneous Injections?
- Bruising: One side effect of subcutaneous injections is bruising at the injection site. This can often be avoided by applying a warm compress to the injection site for up to 10 minutes after the injection.
- Inability to properly use a long-term pump: A subcutaneous injection may interfere with the proper use of a long-term pump that is used to deliver medication directly into the bloodstream. This is rare, however, and subcutaneous injections are generally safe for long-term use.
How to do a Semaglutide Injection: The Correct Angles and Ways to Hold the Syringe
A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. Syringes for subcutaneous injections will use smaller needles than those used for injections into a muscle. The typical Insulin or TB syringes will have a 1/2 inch or less needle length because it only needs to go slightly below the skin level. Only certain types of injections can be given through this route.
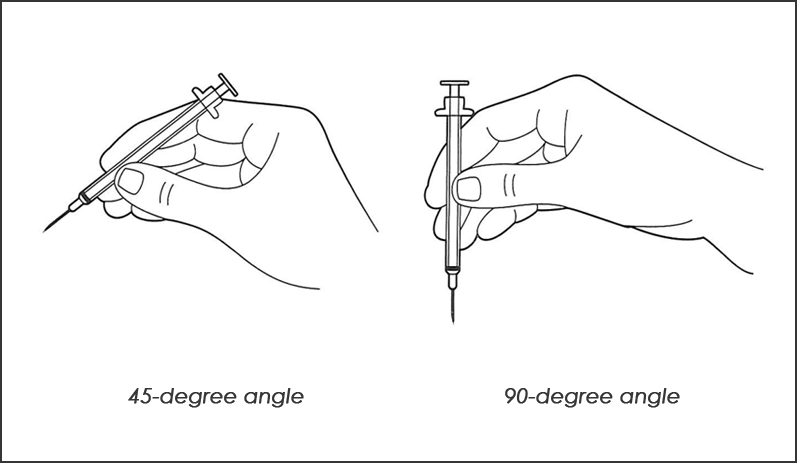
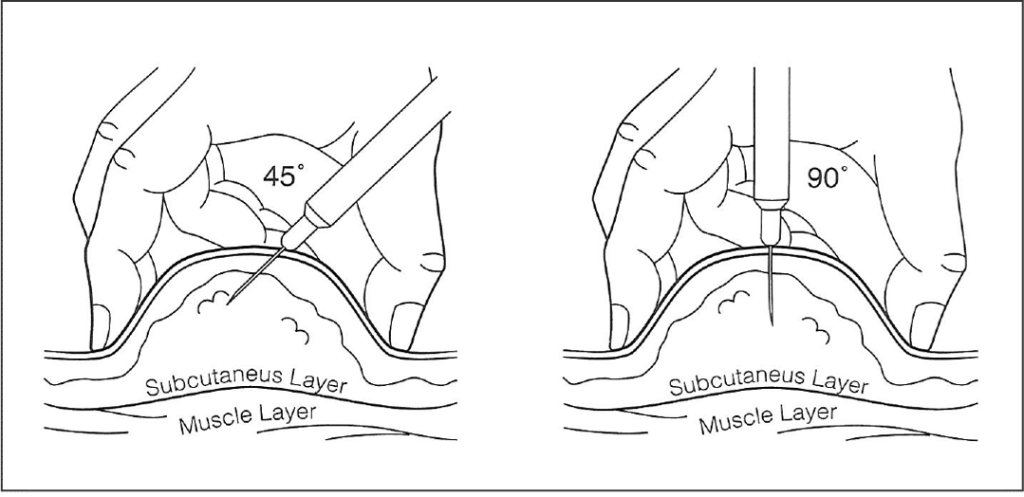
Subcutaneous injections can be given straight and at a 90-degree angle, or at a 45-degree angle. You can give the shot at a 90-degree angle if 2 inches of skin can be grasped between your thumb and first (index) finger. If only skin can be grasped, give the shot at a 45-degree angle.
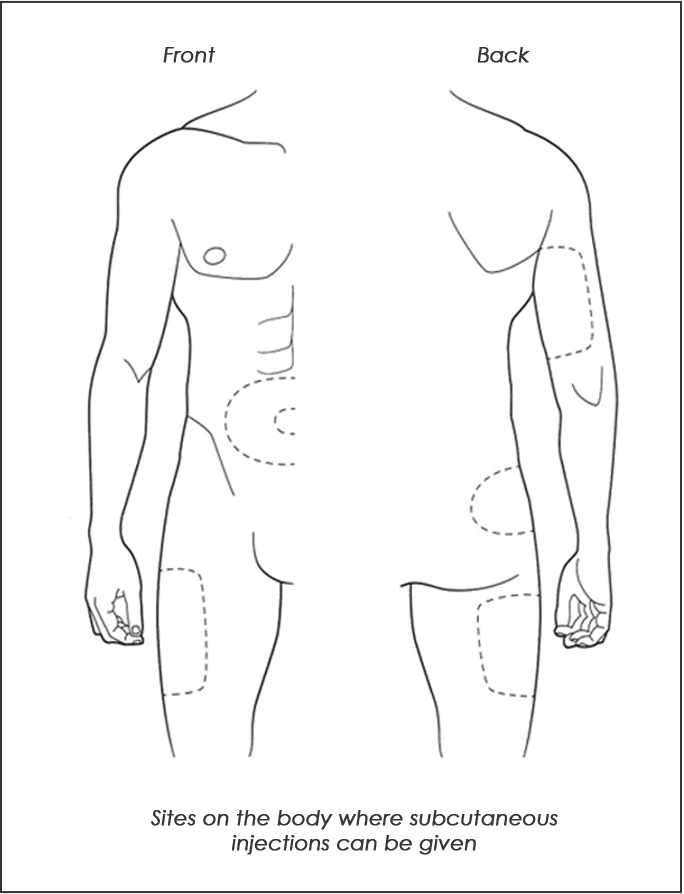
Semaglutide Injection Sites on the Body
Upper Arm:
Uncover the arm to the shoulder to see the whole arm. Have the person receiving the subcutaneous injection stand with a hand on the hip.
Stand next to and a little behind the person. Find the area in the middle part of the arm, halfway between the elbow and shoulder. Gently grasp the skin at the back of the arm between your thumb and first 2 fingers. You should have 1-2 inches of skin.
Abdomen:
Uncover the abdomen to see the whole area. Find the waist area. You may give a shot bounded by these landmarks below the waist, to just above the hip bone, and from where the body curves at the side to about 2 inches from the middle of the abdomen.
Use the natural line in the middle of the body as a marker. It may be hard to see, but it is there unless it’s been covered by surgery. Avoid the surrounding area 2 inches from the belly button.
Thigh:
Uncover the entire leg and the area between the knee and hip. The middle of the thigh, from mid-front to mid-side, on the outside part of the thigh, is a safe site. Gently grasp the area to make sure you can pinch 1-2 inches of skin.
How To Inject Semaglutide With a Syringe
1. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and dry them completely.
2. Open the foil covering the alcohol wipe.
3. Wipe the area where you plan to give the shot. Let the area dry.
4. Take the cover off the needle. Hold the syringe with your writing hand and pull the cover off with your other hand, like taking a cap off a pen.
5. If you will give the shot at a 45-degree angle, hold the syringe with your writing hand. Place the syringe between your thumb and your index and second fingers. The bevel of the needle should be pointing upwards at the 45-degree angle you plan to use.
6. If you will give the shot at a 90-degree angle, hold the syringe with your writing hand. Hold the syringe under your thumb and first finger.
Let the barrel of the syringe rest on your second finger. (Many people hold a pen this way when they write).
7. Grasp the skin with the hand not holding the syringe. Holding the syringe barrel tightly with your writing hand, use your wrist to insert the needle through the skin. Sometimes the needle goes in easily. Some people have tougher skin and a little more pressure or quickness will be required.
8. Once the needle is all the way in, push the plunger down slowly to inject the syringe’s contents.
9. Remove the needle at the same angle you put it in.
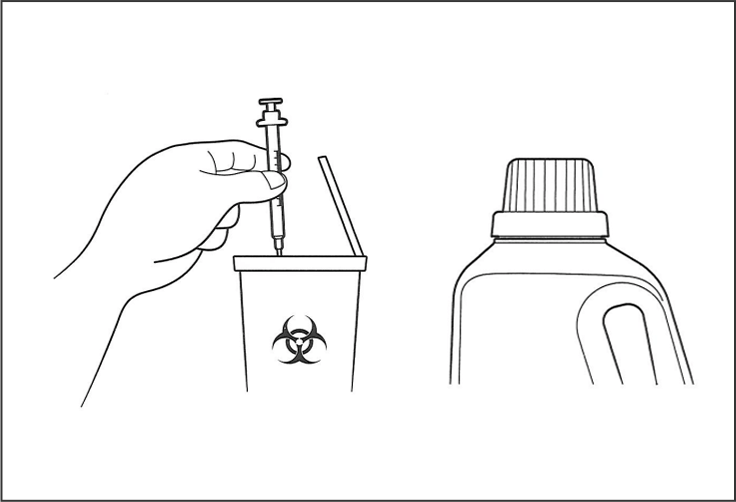
10. Dispose of the syringe and needle in a Sharps Container.
The correct size needle and syringe
Vial containing the medication
One alcohol wipe
You may want to use gloves for your protection or the protection of the person receiving the subcutaneous injection
How Can I Get Rid of Used Syringes and Needles?
You can purchase a Sharps Container, which is a hard plastic container made especially for used syringes and needles, at your local pharmacy. If you did not purchase this container with your medication, you can use a hard-plastic container with a screw-on top such as a clothing softener or hard plastic detergent bottle. Make sure you can easily put both the syringe and the needle into the container.
Whatever container you choose, make sure that other needles cannot break through the sides, bottom, or top.
Call your primary care physician or your local pharmacy to find out what your state or local requirements are for disposing of used syringes and needles.
BMI Doctors Semaglutide Injection for Weight Loss
Name brands such as Ozempic and Wegovy Semaglutide injections provide fixed dosages in prefilled pens, but our pens offer a game-changing advantage. You have the power to precisely tailor your dosage, catering to your unique needs.
Also, with BMI Doctors, you won’t face the inconvenience of global shortages that can disrupt your treatment plan and it will be affordable.
Unlike Wegovy and Ozempic Semaglutide injections, our solution is the thinnest and shortest needles for optimal comfort and convenience. Since you draw medicine from a vial, you get full control over your medication. Whether starting at 0.10 or tapering down to 0.05, we offer flexibility and support to help you comfortably and effectively achieve your body weight goals.
Support and Guidance for Your Weight Loss Injection
If you happen to miss a scheduled injection due to unforeseen circumstances, simply take it as soon as you can. For example, if you’re going on vacation from Sunday until Tuesday, inject on Tuesday to maintain the necessary 7-day interval.
We’re all about making your injection process as comfortable as possible. Remember to properly cleanse your skin before injecting. Pro tip: if you do your injection after a shower, you’ll experience less of a pinch on your soft skin.
Over time, patients who were initially nervous about needles have gained confidence in their ability to self-administer Semaglutide injections. However, if you have any concerns or questions, feel free to reach out to our helpline. Our dedicated team will be there to guide you through every step.
Now that you’re informed about our Semaglutide injections, take the first step on your weight loss journey today.
Before & After Photos of BMI Patients
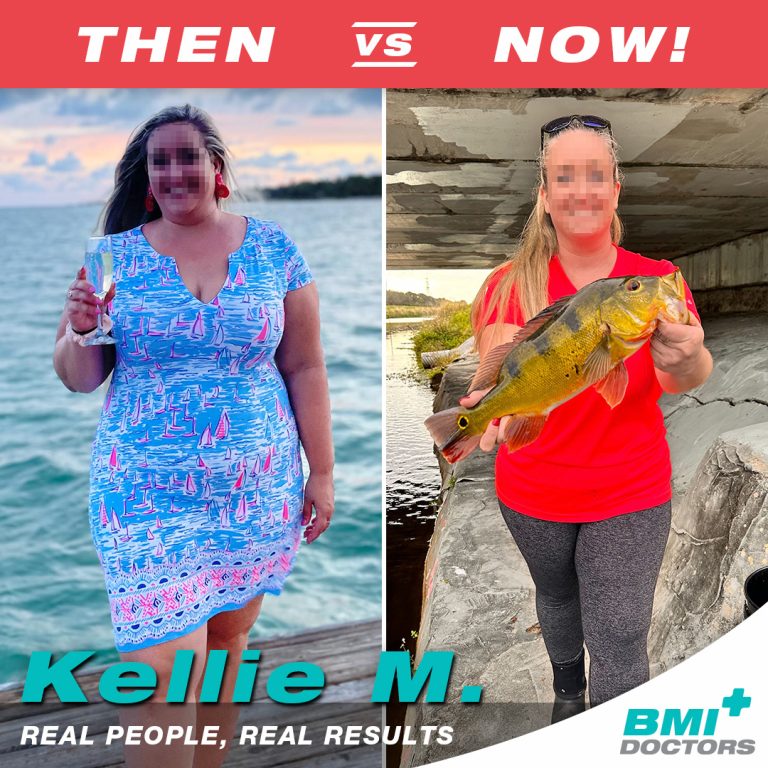
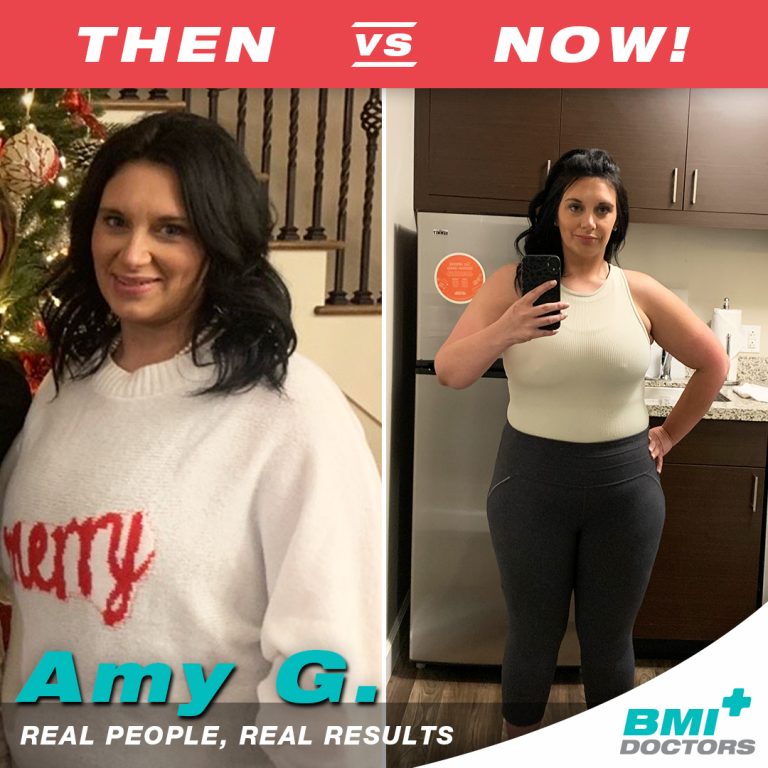
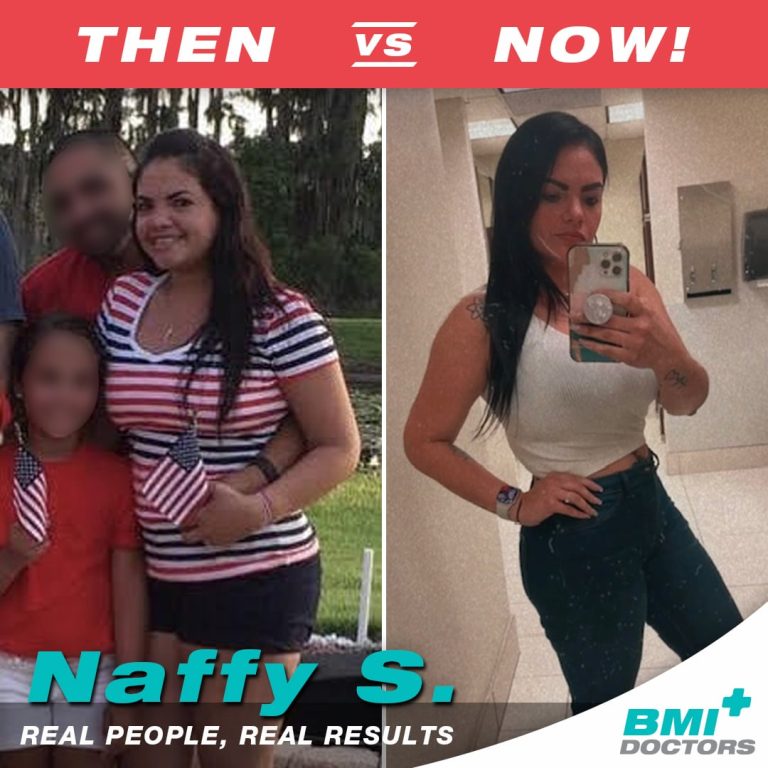
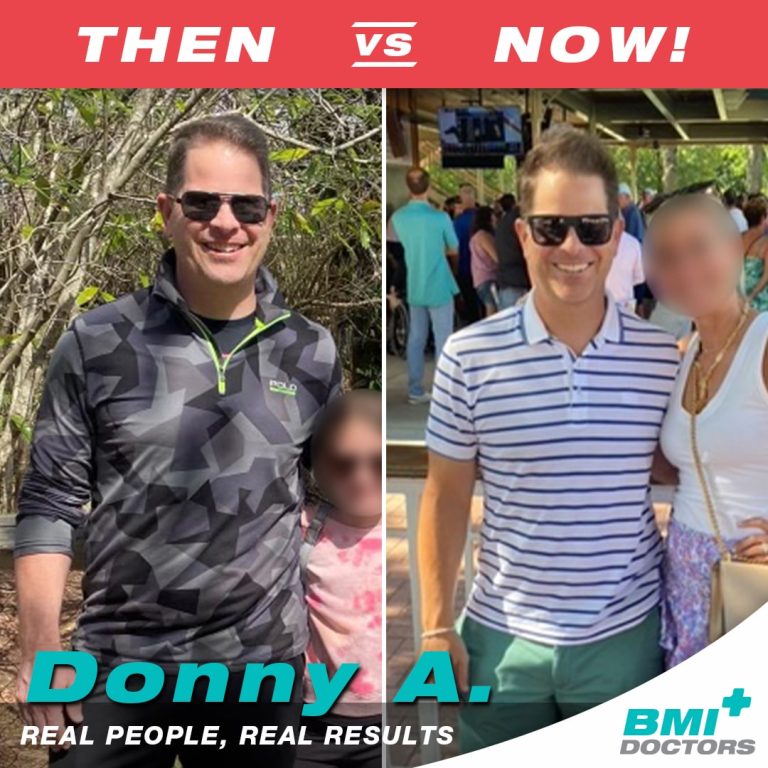





What Makes Us Different
Comprehensive Lab Testing:
Every plan includes a Quest Diagnostics blood test to ensure safe and effective treatment tailored to your health. Most other practices do NOT offer lab testing.
Real Consultations with Board-Certified Doctors:
Unlike others, we provide one-on-one consultations—not just a questionnaire. That means you will actually meet with one of our Doctors. This does NOT happen with most high-volume practices.
Personalized, High-Quality Care:
Our Doctors make sure that GLP-1 medications are right for you. We prioritize safety and sustainable results over speed or volume.
Questions and Answers: Semaglutide Injections
Semaglutide injections are primarily used for improving blood sugar control in adults with type 2 diabetes and for weight management.
Semaglutide injections are typically administered once a week.
The injection can be administered in the thigh, abdomen, or upper arm.
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, decreased appetite, and constipation.
Yes, one of the effects of Semaglutide injections can be significant weight loss, especially when combined with diet and exercise.
Semaglutide has shown cardiovascular benefits in some studies, but individual assessment is necessary, especially for those with existing heart conditions.
Yes, they can be used with insulin, but blood sugar levels need to be closely monitored to avoid hypoglycemia.
Some effects can be noticed within a few days to weeks, but it may take longer for significant changes in blood sugar levels or weight.
If a dose is missed, take it as soon as possible if it’s within a certain timeframe before the next dose. Otherwise, skip it and resume your regular schedule.
There is a risk of pancreatitis, and patients should be aware of the symptoms and seek medical attention if they occur.
There are no specific dietary restrictions, but a balanced diet may enhance the effectiveness of the treatment.
It’s not recommended to stop the injections abruptly without consulting a healthcare provider.
No, it’s a GLP-1 receptor agonist, not insulin, but it helps in insulin secretion.
While less common than with other diabetes medications, they can cause hypoglycemia, especially when used with other drugs that lower blood sugar.
They should be stored in the refrigerator, and once in use, they can be kept at room temperature for a certain period as specified in the product instructions.
There have been reports of kidney problems, so individuals with kidney issues should use it cautiously.
The safety of Semaglutide during pregnancy is not well established, and it should be used only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
They can interact with certain medications, so it’s important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new medications.
Although rare, severe allergic reactions can occur, and immediate medical attention is necessary if symptoms of an allergic reaction appear.
Semaglutide works by mimicking GLP-1, a hormone that regulates insulin secretion, which is different from how many other diabetes medications work. It also aids in weight loss, which is not a common feature of most diabetes medications.