Table of Contents
Introduction
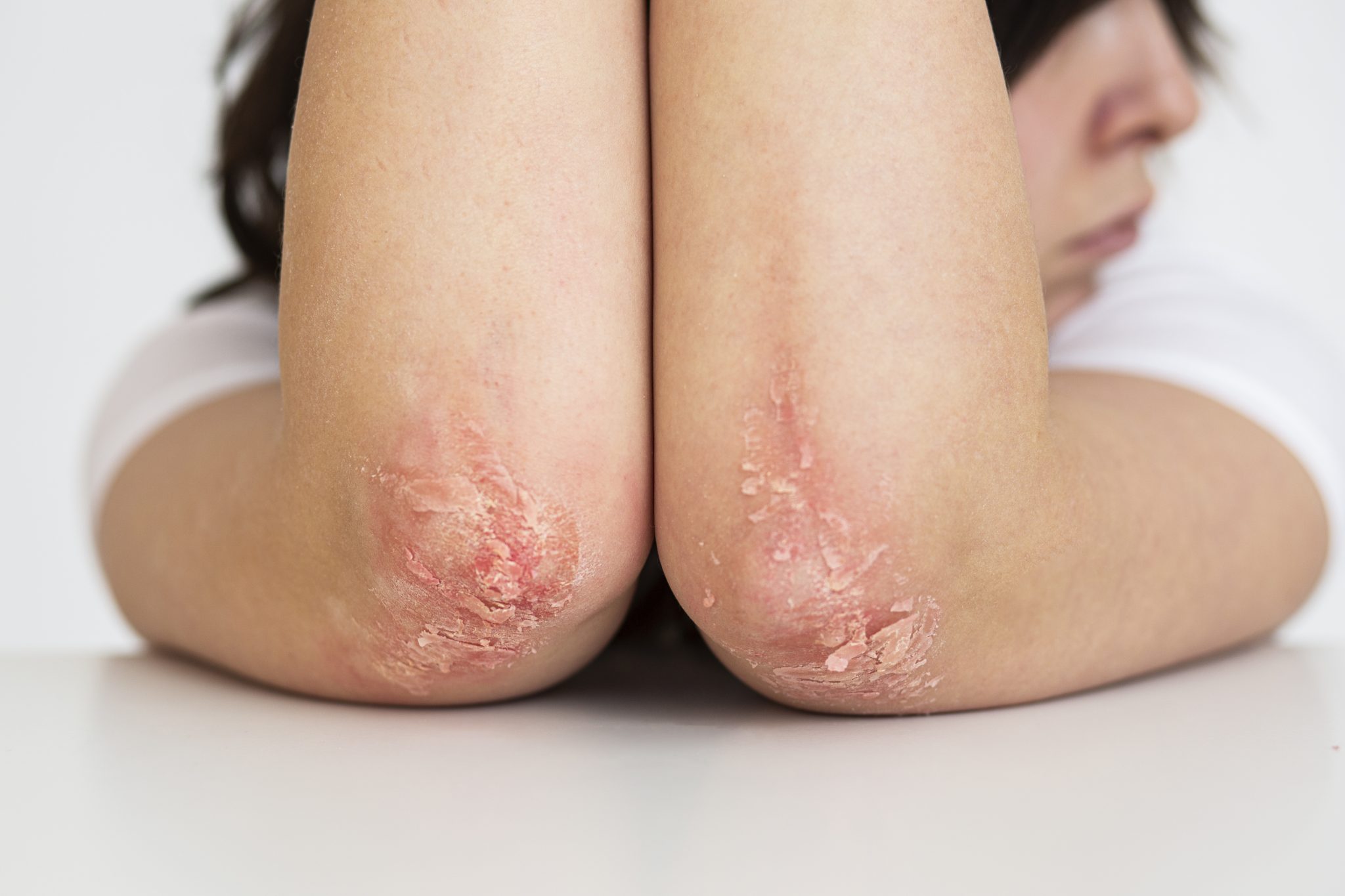
Psoriasis is a common skin condition that affects millions of people around the world. It is a chronic, long-lasting disease that can cause red, itchy patches to form on the skin. These patches, often covered with silvery scales, can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. For many, psoriasis is more than just a skin problem. It can lead to significant discomfort and emotional distress, affecting a person’s quality of life. Understanding what causes psoriasis and how it can be managed is important for those living with this condition.
Psoriasis is considered an autoimmune disease. This means that the immune system, which usually protects the body from infections, mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This abnormal immune response causes the skin cells to grow much faster than normal, leading to the thick, scaly patches characteristic of psoriasis. While the exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, it is believed that both genetic and environmental factors play a role. For instance, a person with a family history of psoriasis is more likely to develop the condition. Additionally, certain triggers, such as stress, infections, or injuries to the skin, can cause psoriasis to flare up.
Living with psoriasis can be challenging. The visible nature of the condition often leads to feelings of embarrassment and social anxiety. Many people with psoriasis also experience discomfort from the itching and pain associated with the skin lesions. In some cases, psoriasis can lead to more serious health issues. For example, individuals with psoriasis are at a higher risk of developing psoriatic arthritis, a painful joint condition, as well as other health problems like heart disease and diabetes.
Given the chronic and often stubborn nature of psoriasis, finding effective treatments is crucial. There are several treatments available, ranging from topical creams and light therapy to oral medications and biologics. However, not all treatments work for everyone, and some may cause unwanted side effects. This has led researchers to explore new treatment options that can provide better results with fewer risks. One of the treatments currently being investigated is semaglutide.
Semaglutide is a medication that is primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes and assist with weight loss. It belongs to a class of drugs known as GLP-1 receptor agonists. These medications work by mimicking a hormone in the body that helps to regulate blood sugar levels and appetite. Semaglutide has been shown to be effective in controlling blood sugar and promoting weight loss in people with diabetes. Recently, researchers have started to explore its potential benefits for other conditions, including psoriasis.
The idea of using semaglutide for psoriasis is based on its ability to reduce inflammation and possibly affect the immune system in ways that could benefit people with psoriasis. Inflammation is a key factor in psoriasis, and any treatment that can reduce this inflammation could help to improve the condition. Additionally, many people with psoriasis struggle with their weight, and semaglutide’s ability to promote weight loss might offer added benefits.
While the research on semaglutide and psoriasis is still in the early stages, the potential for this medication to become a new treatment option is promising. As more studies are conducted, we may better understand how semaglutide can be used to manage psoriasis effectively. For now, it is important for individuals with psoriasis to be aware of the ongoing research and to discuss any potential new treatments with their healthcare providers.
In this article, we will explore the link between psoriasis and semaglutide in detail. We will examine how semaglutide works, what the current research says, and what the potential benefits and risks might be for people with psoriasis. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how semaglutide could play a role in better managing psoriasis and improving the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
What is Psoriasis and How Does It Affect the Body?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that happens when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This causes the skin to grow too fast, leading to thick, red, and often scaly patches on the surface. These patches, known as plaques, can appear anywhere on the body, but they are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
Understanding Psoriasis as an Autoimmune Condition
Psoriasis is classified as an autoimmune disease. This means that the body’s immune system, which normally fights off infections and keeps you healthy, becomes confused and attacks your own tissues. In the case of psoriasis, the immune system targets the skin. This attack causes inflammation, which is why the skin becomes red and swollen.
The overactive immune response in psoriasis speeds up the life cycle of skin cells. Normally, skin cells grow deep in the skin and slowly rise to the surface. This process usually takes about a month. However, in people with psoriasis, this process happens in just a few days. Because the skin cells grow so quickly, they build up on the surface, forming the thick, scaly plaques that are characteristic of the disease.
The Physiological Impact of Psoriasis
Psoriasis affects more than just the skin. While the plaques are the most visible symptom, the condition can also cause other health problems. For example, many people with psoriasis experience joint pain, a condition known as psoriatic arthritis. This type of arthritis can lead to stiffness, swelling, and pain in the joints, making it difficult to move or perform daily activities.
The inflammation caused by psoriasis can also affect other parts of the body. Research has shown that people with psoriasis are at a higher risk for other inflammatory conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and depression. This is because the inflammation that occurs in the skin can also happen in other organs, leading to a wide range of health issues.
Common Symptoms and Complications of Psoriasis
The most common symptom of psoriasis is the appearance of red, scaly patches on the skin. These patches can vary in size and may be itchy or painful. Some people also experience cracking and bleeding of the skin, especially in areas where the plaques are thick.
There are different types of psoriasis, and each type has its own set of symptoms:
- Plaque Psoriasis: This is the most common type and is characterized by red, raised patches covered with a silvery-white buildup of dead skin cells.
- Guttate Psoriasis: This type often starts in childhood or young adulthood and is marked by small, dot-like lesions. It can be triggered by infections, such as strep throat.
- Inverse Psoriasis: This type causes bright red, shiny lesions that appear in skin folds, such as under the breasts, in the groin, or around the buttocks.
- Pustular Psoriasis: This rare type can cause pus-filled blisters on the skin, often on the hands and feet.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: This is a severe form that can cause redness and scaling over large areas of the body. It can be very painful and is often accompanied by intense itching and swelling.
Psoriasis can also lead to complications. For example, the itching and discomfort caused by the plaques can make it difficult to sleep, leading to fatigue and a lower quality of life. The visible nature of the condition can also affect a person’s mental health, leading to feelings of embarrassment, anxiety, or depression.
In some cases, psoriasis can have serious health consequences. The inflammation associated with the condition can increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. It can also lead to metabolic syndrome, a group of conditions that includes high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
Psoriasis is more than just a skin condition. It is a complex autoimmune disease that can affect many aspects of a person’s health. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and complications of psoriasis is important for managing the condition and improving overall well-being. As research continues, new treatments and strategies are being developed to help those living with psoriasis lead healthier, more comfortable lives.
What is Semaglutide and How Does It Work?
Semaglutide is a medication that belongs to a group of drugs known as GLP-1 receptor agonists. These drugs are designed to help manage blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Semaglutide mimics a hormone called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) that is naturally produced in the body. This hormone helps regulate blood sugar by stimulating insulin production when blood sugar levels are high and reducing the amount of sugar released by the liver. Semaglutide is also used for weight management in people who are overweight or obese, as it helps reduce appetite and food intake.
How is Semaglutide Used?
Semaglutide is usually taken as an injection under the skin, which can be done by the patient themselves after being taught by a healthcare provider. It is often prescribed as a once-weekly injection, making it convenient for those who need long-term management of their blood sugar or weight. In some cases, semaglutide is also available in a pill form that is taken daily. The exact dosage and form of semaglutide depend on the condition being treated and the patient’s individual needs.
How Does Semaglutide Work in the Body?
Semaglutide works by binding to GLP-1 receptors in the body. When it activates these receptors, it triggers several important actions:
- Increased Insulin Production: When you eat, your blood sugar levels go up. Semaglutide helps the pancreas release more insulin, which is the hormone that helps lower blood sugar levels. This is especially important for people with type 2 diabetes, who often have trouble making enough insulin.
- Reduced Glucose Production: The liver plays a role in controlling blood sugar by releasing glucose into the bloodstream. Semaglutide reduces the amount of glucose the liver releases, which helps keep blood sugar levels in check, especially between meals.
- Slower Digestion: Semaglutide slows down how quickly food leaves the stomach. This helps people feel full for longer, which can reduce how much they eat. This is one reason semaglutide is also used to help people lose weight.
- Appetite Reduction: In addition to slowing digestion, semaglutide affects the brain areas that control appetite. By reducing hunger signals, it helps people eat less, leading to weight loss over time.
Approved Uses of Semaglutide
Semaglutide was first approved for treating type 2 diabetes. It helps people with diabetes manage their blood sugar levels when diet and exercise alone are not enough. By improving blood sugar control, semaglutide can help prevent complications of diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney problems, and nerve damage.
Later, semaglutide was also approved for weight management in people who are overweight or obese. For these patients, semaglutide is used alongside a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity to help them lose weight and keep it off. Weight loss is important for reducing the risk of many health issues, including heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer.
Why is Semaglutide Important?
Semaglutide has become an important medication because of its dual role in managing both diabetes and obesity. These two conditions are often linked, and managing one can help improve the other. For example, losing weight can make it easier to control blood sugar levels, and better blood sugar control can make it easier to lose weight.
In recent years, researchers have also started exploring other potential benefits of semaglutide, such as its effects on heart health and inflammation. This is why there is growing interest in how semaglutide might help with other conditions, including psoriasis. Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory condition, and since semaglutide has effects on both metabolism and inflammation, it is being studied to see if it might offer benefits beyond its current uses.
Semaglutide is a versatile medication that helps manage blood sugar and weight by mimicking the effects of a natural hormone in the body. Its ability to regulate these factors makes it a valuable tool in treating diabetes and obesity, with potential benefits that are still being explored for other conditions like psoriasis.
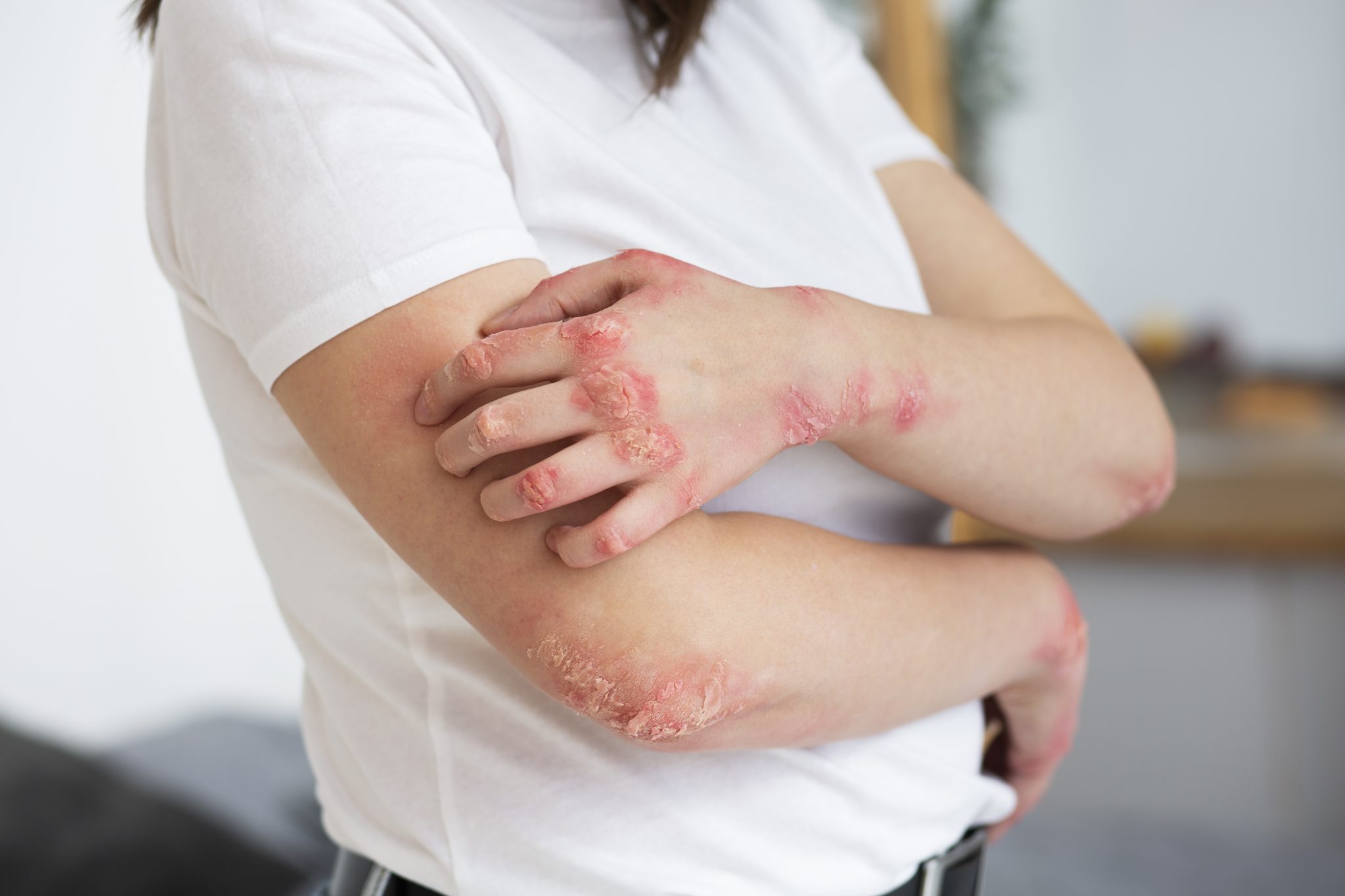

Can Semaglutide Be Used to Treat Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes red, scaly patches to appear on the skin. It is an autoimmune disease, which means that it occurs because the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. For years, doctors have been treating psoriasis with different medications, including topical creams, light therapy, and drugs that suppress the immune system. But recently, there has been interest in whether semaglutide, a medication primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes, could also help people with psoriasis.
Understanding Semaglutide
Semaglutide is a drug that belongs to a class of medications called GLP-1 receptor agonists. These drugs are designed to help manage blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Semaglutide works by mimicking a hormone in the body called GLP-1, which helps to regulate blood sugar, appetite, and digestion. In addition to lowering blood sugar levels, semaglutide has also been shown to help people lose weight, which can be a significant benefit for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Why Researchers Are Interested in Semaglutide for Psoriasis
The idea of using semaglutide to treat psoriasis comes from understanding how this medication works in the body. Since psoriasis is an inflammatory condition, and semaglutide has been shown to reduce inflammation in other conditions, researchers are curious to see if it could help with psoriasis as well.
There is also a link between obesity and psoriasis. People who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop psoriasis, and their symptoms can be more severe. Since semaglutide helps with weight loss, it might help to reduce the severity of psoriasis symptoms in overweight or obese patients. Additionally, losing weight can decrease inflammation in the body, which might also help improve psoriasis symptoms.
Current Research on Semaglutide for Psoriasis
Although semaglutide is not currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating psoriasis, some studies and clinical trials are exploring its potential benefits for this condition. Early research has provided mixed results, with some studies showing that semaglutide could help reduce the severity of psoriasis symptoms, while others have found little to no benefit.
One small study conducted on patients with both type 2 diabetes and psoriasis found that those who were treated with semaglutide experienced a reduction in the severity of their psoriasis. However, it is important to note that this study was small, and more extensive research is needed to determine whether semaglutide is truly effective for treating psoriasis.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
Currently, there are ongoing clinical trials that aim to provide more concrete answers about whether semaglutide can be used to treat psoriasis. These trials are crucial because they involve larger groups of patients and use rigorous scientific methods to evaluate the effectiveness of the drug. Researchers are particularly interested in seeing whether the anti-inflammatory and weight-loss benefits of semaglutide can translate into improved outcomes for psoriasis patients.
Limitations and Considerations
It is important to remember that semaglutide is not a cure for psoriasis. Even if research shows that it can help with symptoms, it may not work for everyone. Additionally, like any medication, semaglutide comes with potential side effects, and not all patients may be suitable candidates for this treatment. For instance, people with certain medical conditions or those who are pregnant may need to avoid using semaglutide.
Moreover, because semaglutide is not yet approved for psoriasis, using it for this purpose would be considered an “off-label” use. This means that a doctor would be prescribing the medication for something other than its officially approved use. Patients considering this option should have a thorough discussion with their healthcare provider to weigh the potential benefits and risks.
The Future of Semaglutide in Psoriasis Treatment
As research continues, we may see more evidence supporting the use of semaglutide for psoriasis. However, until more data is available and semaglutide is officially approved for this use, it should be approached cautiously. For now, semaglutide offers a promising but experimental option for those looking to manage their psoriasis, particularly for patients who also need to manage their weight or blood sugar levels. As always, it is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for managing psoriasis.
What Are the Potential Benefits of Semaglutide for Psoriasis Patients?
Semaglutide is a medication that has gained attention for its benefits in treating diabetes and obesity. However, researchers are now exploring how it might help people with psoriasis, a condition that causes red, scaly patches on the skin. Although semaglutide is not yet officially approved for psoriasis treatment, early research suggests there could be several benefits.
Improvement in Skin Symptoms
One of the potential benefits of semaglutide for psoriasis patients is the improvement of skin symptoms. Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition, meaning the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, in this case, the skin. This leads to inflammation, redness, and the buildup of thick, scaly patches. Semaglutide works by reducing inflammation in the body, which may help decrease the severity of these skin symptoms.
Some studies have shown that patients who take semaglutide experience less inflammation, which could translate to fewer or milder psoriasis flare-ups. Although more research is needed to confirm this effect specifically for psoriasis, the initial findings are promising. By lowering inflammation, semaglutide could potentially help improve the appearance and comfort of the skin in people with psoriasis.
Weight Loss Benefits
Another significant benefit of semaglutide is its ability to promote weight loss. Many people with psoriasis are overweight or obese, which can worsen their symptoms. Excess weight can increase inflammation in the body and put additional stress on the joints, which is particularly concerning for psoriasis patients who also have psoriatic arthritis, a condition that causes joint pain and swelling.
Semaglutide helps with weight loss by reducing appetite and helping people feel full more quickly. For psoriasis patients, losing weight can lead to a reduction in inflammation throughout the body, which may help ease their skin symptoms. Additionally, weight loss can improve overall health, reducing the risk of other conditions like heart disease and diabetes, which are more common in people with psoriasis.
Potential Cardiovascular Benefits
People with psoriasis are at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, such as heart attack and stroke. This is partly because psoriasis is linked to chronic inflammation, which can damage the blood vessels and lead to heart problems. Semaglutide has been shown to have protective effects on the heart and blood vessels, making it an appealing option for psoriasis patients who need to manage both their skin condition and their heart health.
Research suggests that semaglutide may lower the risk of cardiovascular events in people with type 2 diabetes, and these benefits might extend to those with psoriasis. By reducing inflammation and promoting weight loss, semaglutide could help lower the risk of heart disease in psoriasis patients, offering a dual benefit for their skin and cardiovascular health.
Improved Quality of Life
Living with psoriasis can be challenging, not only because of the physical symptoms but also due to the emotional impact. People with psoriasis often feel self-conscious about their appearance, leading to stress, anxiety, and depression. By potentially improving skin symptoms and helping with weight loss, semaglutide might also improve the quality of life for psoriasis patients.
When psoriasis symptoms are under control, patients may feel more confident and experience less stress, which can further reduce flare-ups. Additionally, the weight loss associated with semaglutide can lead to increased energy levels and a more active lifestyle, which can contribute to better mental and physical well-being.
While more research is needed to fully understand the benefits of semaglutide for psoriasis patients, early findings suggest it could offer several advantages. By reducing inflammation, aiding in weight loss, and potentially improving cardiovascular health, semaglutide might help manage psoriasis symptoms and improve the overall quality of life. Patients interested in exploring semaglutide as part of their psoriasis treatment should consult with their healthcare provider to discuss the potential risks and benefits tailored to their specific needs.
How Does Semaglutide Affect the Immune System?
Semaglutide is a medication that works by mimicking a natural hormone in the body called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1). This hormone is mainly involved in regulating blood sugar levels and appetite. While semaglutide is primarily used to treat conditions like type 2 diabetes and obesity, its effects on the immune system are also becoming a subject of interest, especially for people with autoimmune diseases like psoriasis.
Understanding the Immune System and Autoimmune Diseases
The immune system is the body’s defense mechanism against harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. It works by recognizing these foreign substances and attacking them to keep the body healthy. However, in autoimmune diseases like psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells. In psoriasis, this attack is directed at the skin, leading to the rapid growth of skin cells and the formation of thick, scaly patches known as plaques.
How Semaglutide Interacts with the Immune System
Semaglutide’s primary function is not directly related to the immune system, but its actions can still influence immune responses. By mimicking GLP-1, semaglutide helps to regulate insulin levels, reduce blood sugar, and manage appetite. These effects have indirect but significant implications for the immune system.
- Reduction of Inflammation:
Inflammation is a key factor in many autoimmune diseases, including psoriasis. High levels of inflammation can worsen symptoms and lead to more severe flare-ups. Semaglutide has been shown to reduce inflammation in the body, which could potentially benefit people with psoriasis. While this anti-inflammatory effect is mainly due to improved blood sugar control, it may also help in calming the overactive immune response seen in psoriasis. - Impact on Immune Cells:
Semaglutide may also affect specific immune cells that play a role in autoimmune conditions. For instance, GLP-1 receptors are found on certain types of immune cells, including T-cells, which are involved in the body’s immune response. By interacting with these receptors, semaglutide could potentially modulate the activity of these immune cells, helping to reduce the immune attack on the skin in psoriasis patients. However, this is still an area of ongoing research, and more studies are needed to fully understand these effects. - Balancing Immune Modulation:
One of the challenges in treating autoimmune diseases like psoriasis is finding the right balance between modulating the immune system without overly suppressing it. Suppressing the immune system too much can leave the body vulnerable to infections and other health issues. Semaglutide’s potential to reduce inflammation and influence immune cell activity might offer a way to achieve this balance. By not directly suppressing the immune system but rather modulating its activity, semaglutide may provide a safer option for people with psoriasis.
Implications for Psoriasis Patients
For psoriasis patients, understanding how semaglutide interacts with the immune system is crucial. While semaglutide is not currently approved specifically for the treatment of psoriasis, its effects on inflammation and immune cells offer promising possibilities. If semaglutide can reduce inflammation and modulate immune responses without the harsh side effects associated with traditional immune-suppressing drugs, it could become a valuable tool in managing psoriasis.
However, it’s important to note that more research is needed to confirm these effects. Psoriasis patients considering semaglutide should do so under the guidance of a healthcare provider who can monitor their condition and adjust treatment as needed. Additionally, patients should be aware of the potential risks and side effects of semaglutide, particularly in the context of its impact on the immune system.
While semaglutide’s primary role is in managing blood sugar and weight, its potential effects on the immune system could make it a beneficial option for psoriasis patients. By reducing inflammation and modulating immune activity, semaglutide might help in controlling psoriasis symptoms, offering hope for better management of this chronic condition.
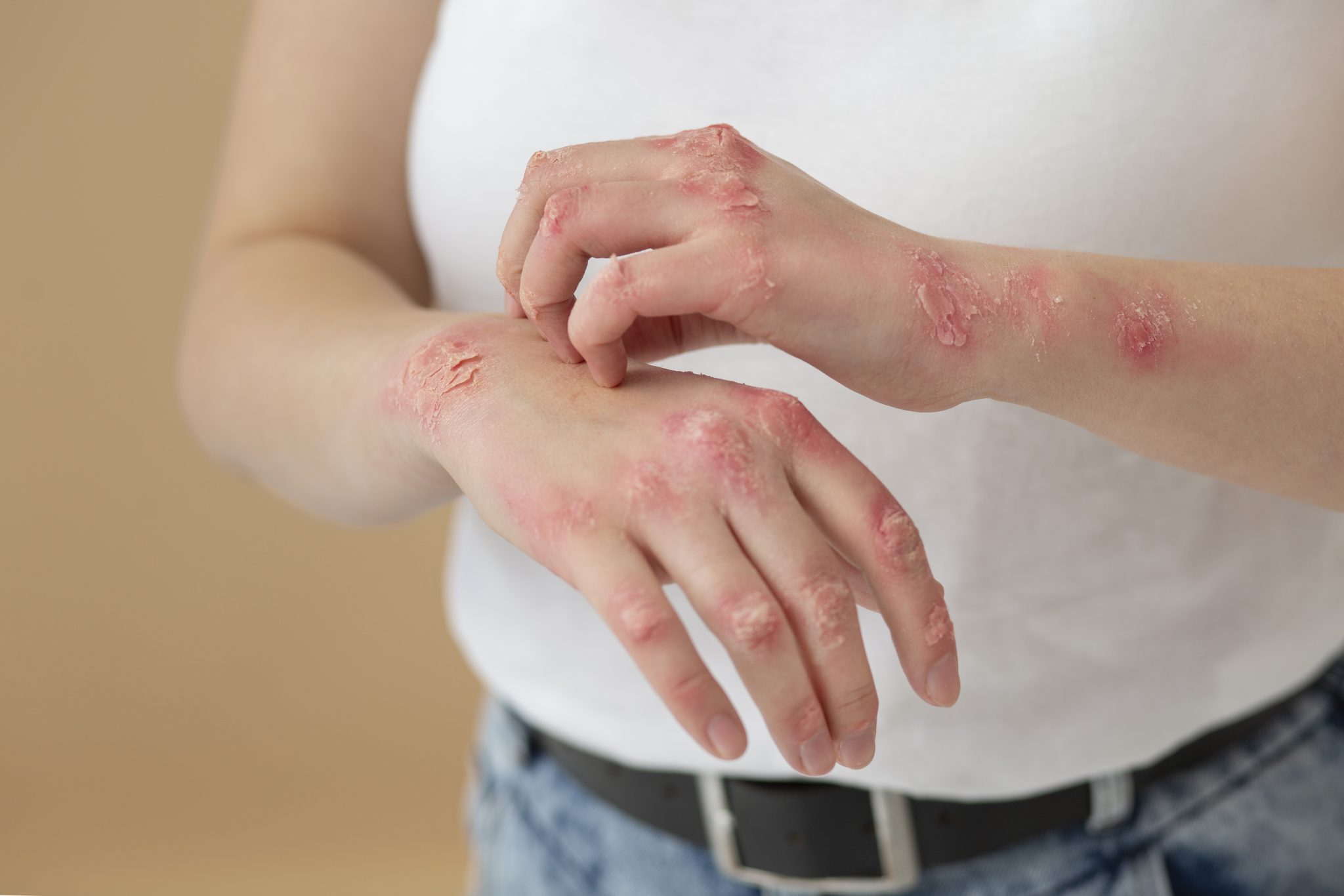

Are There Any Risks of Using Semaglutide for Psoriasis?
When considering a new treatment, it’s important to understand both the benefits and the risks. Semaglutide, a medication commonly used to treat diabetes and obesity, is being studied for its potential in treating psoriasis. However, like all medications, semaglutide comes with potential side effects and risks, especially when used by people with psoriasis. This section will help you understand these risks, making it easier to decide if semaglutide might be right for you.
Known Side Effects of Semaglutide
Semaglutide has been widely used and studied in people with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Through these studies, we know that semaglutide can cause a range of side effects. The most common side effects are related to the digestive system. For example, many people experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation when they start taking semaglutide. These side effects usually lessen over time as the body gets used to the medication. However, some people may continue to experience these digestive issues for as long as they take the drug.
Another common side effect is a decreased appetite. While this can be beneficial for those using semaglutide for weight loss, it might not be as desirable for everyone. For people who do not need to lose weight, this reduced appetite could lead to unintended weight loss and nutritional deficiencies if not carefully managed.
Semaglutide can also cause more serious side effects, although these are less common. For example, some people may develop inflammation of the pancreas, known as pancreatitis. Pancreatitis can cause severe abdominal pain and requires immediate medical attention. Additionally, there is a potential risk of developing thyroid tumors, including a type of cancer known as medullary thyroid carcinoma. While these risks are rare, they are serious enough to warrant careful consideration and discussion with your healthcare provider.
Specific Concerns for Psoriasis Patients
For people with psoriasis, there are additional factors to consider when evaluating the risks of semaglutide. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, meaning the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. Since semaglutide affects the immune system, it’s important to understand how this might impact psoriasis.
One concern is that semaglutide could potentially worsen psoriasis in some people. Since psoriasis involves an overactive immune response, any medication that affects the immune system could theoretically make the condition worse. However, this is not a well-established risk, and more research is needed to determine how semaglutide specifically interacts with the immune system in people with psoriasis.
Another concern is the potential impact on skin health. While semaglutide is primarily used to manage blood sugar levels and promote weight loss, its effects on the skin are not fully understood. Psoriasis patients often have sensitive skin that can react strongly to changes in the body. It’s important for patients to monitor their skin condition closely when starting semaglutide and report any new or worsening symptoms to their healthcare provider.
Managing and Monitoring Side Effects
If you are considering using semaglutide to manage psoriasis, it is crucial to do so under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Regular check-ups and monitoring can help catch any potential side effects early and address them before they become serious. Your healthcare provider may recommend starting with a low dose of semaglutide and gradually increasing it. This approach can help minimize the risk of side effects, particularly digestive issues.
For those with a history of pancreatitis or thyroid problems, semaglutide may not be the best option. Your healthcare provider will consider your full medical history before recommending semaglutide. If you experience any severe side effects, such as severe stomach pain, persistent nausea, or changes in your thyroid, you should contact your healthcare provider immediately.
While semaglutide shows promise for managing psoriasis, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks. Common side effects like digestive issues and decreased appetite are manageable for most people, but more serious risks like pancreatitis and thyroid tumors need careful consideration. For people with psoriasis, additional monitoring is necessary to ensure that the medication does not worsen the condition. Always consult with a healthcare provider to weigh the benefits and risks specific to your situation.
How Should Psoriasis Patients Use Semaglutide?
Using semaglutide to manage psoriasis is a new and evolving area of treatment. If you have psoriasis and are considering semaglutide, it’s important to understand how this medication might fit into your treatment plan. Here, we will explore how psoriasis patients can use semaglutide, the recommended dosage, and the importance of working closely with your healthcare provider.
Incorporating Semaglutide into Psoriasis Management
Psoriasis is a complex condition that affects the skin and can also impact other parts of the body. It is an autoimmune disease, meaning the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues. Managing psoriasis often requires a combination of treatments, including topical creams, oral medications, and sometimes biologics, which are drugs made from living organisms that target specific parts of the immune system.
Semaglutide is not specifically approved for treating psoriasis. It is primarily used for managing type 2 diabetes and obesity. However, researchers are investigating whether it might help with psoriasis because of its anti-inflammatory effects and ability to help people lose weight, which can improve psoriasis symptoms. If you and your doctor decide to try semaglutide as part of your psoriasis treatment, it will likely be used in addition to your current medications, not as a replacement.
Dosage Considerations Specific to Psoriasis Patients
The dosage of semaglutide for psoriasis patients may vary depending on several factors. These include your overall health, the severity of your psoriasis, and whether you have any other medical conditions like diabetes or obesity.
For managing diabetes and obesity, semaglutide is usually started at a low dose and gradually increased. This helps minimize side effects, such as nausea, which can occur when starting the medication. A similar approach might be used for psoriasis patients. You would likely start on a lower dose, and your doctor might gradually increase the dosage based on how your body responds and whether you experience any side effects.
It’s also important to consider how semaglutide interacts with other medications you might be taking for psoriasis. Some psoriasis treatments, particularly biologics, affect the immune system in ways that could interact with semaglutide. This makes it crucial to follow your doctor’s advice closely and keep all your healthcare providers informed about all the medications and supplements you are taking.
The Importance of Medical Supervision
Using semaglutide for psoriasis should always be done under strict medical supervision. Since this is a relatively new approach, your doctor will need to monitor your progress carefully. This includes regular check-ups to assess how well the treatment is working and to catch any potential side effects early.
Your doctor might also order blood tests to check your blood sugar levels, liver function, and other health indicators. These tests help ensure that semaglutide is not causing any unexpected problems and that it is safe for you to continue using it.
In addition to monitoring your physical health, your doctor will want to know about any changes in your psoriasis symptoms. Since psoriasis can be affected by many factors, including stress, diet, and other illnesses, it’s important to keep a detailed record of your symptoms. This can help your doctor determine whether semaglutide is having a positive effect and whether any adjustments need to be made to your treatment plan.
Individualized Treatment Plans
Because psoriasis varies greatly from person to person, there is no one-size-fits-all approach to treatment. The same is true when incorporating semaglutide into your psoriasis management. Your treatment plan should be tailored to your specific needs, taking into account your medical history, the severity of your psoriasis, and how you respond to the medication.
Your doctor may adjust your dosage or suggest combining semaglutide with other treatments to get the best results. For example, if you are also managing obesity, your doctor might focus on semaglutide’s weight loss benefits, as losing weight can help reduce the severity of psoriasis symptoms.
Using semaglutide as part of a psoriasis treatment plan is a promising but still experimental approach. It’s essential to use this medication under close medical supervision and as part of a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your individual needs. By working closely with your healthcare provider, you can safely explore the potential benefits of semaglutide for managing your psoriasis.
What Does Current Research Say About Semaglutide and Psoriasis?
Research on semaglutide and its effects on psoriasis is still in the early stages. However, the information available is promising and gives us a glimpse into how this medication might help people with psoriasis. To understand this better, let’s break down what the current studies and trials are telling us.
Summary of Studies and Clinical Trials
Semaglutide is primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity. Because of its effectiveness in these areas, researchers have started to explore its potential benefits for other conditions, including psoriasis. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, which means that the immune system attacks healthy cells by mistake, causing inflammation and skin issues. Semaglutide works by regulating blood sugar levels and reducing inflammation, which are key factors in managing both diabetes and psoriasis.
Several studies have been conducted to see if semaglutide could help people with psoriasis. In some early trials, patients who took semaglutide showed a reduction in psoriasis symptoms. For example, some patients experienced less skin redness, scaling, and thickness. These improvements are thought to be linked to semaglutide’s ability to lower inflammation in the body.
Interpretation of Data: Efficacy and Safety
While the early results are encouraging, it’s important to understand that semaglutide is not yet approved specifically for treating psoriasis. The improvements seen in some patients are still being studied to confirm how effective and safe semaglutide is for this purpose. Researchers are looking at how semaglutide affects the immune system, since psoriasis is an immune-related condition. They want to ensure that while the drug helps with psoriasis, it doesn’t cause other immune-related issues.
One important finding is that semaglutide may help with weight loss, which can indirectly benefit psoriasis patients. Obesity is a known risk factor for psoriasis, and losing weight can lead to fewer psoriasis flare-ups. Therefore, semaglutide’s ability to promote weight loss might make it an attractive option for managing psoriasis in overweight patients.
However, like all medications, semaglutide comes with potential side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain. For psoriasis patients, it’s crucial to balance these risks with the potential benefits. Ongoing research is focusing on understanding these risks better and finding the safest ways to use semaglutide in psoriasis treatment.
Gaps in Research and Future Directions
While the research so far is promising, there are still many questions that need to be answered. For instance, most studies have been short-term, and we need to know more about the long-term effects of using semaglutide for psoriasis. Will the benefits continue over time, or will they decrease? Are there any long-term risks that could outweigh the benefits? These are critical questions that researchers are working to answer.
Another gap in the research is understanding which patients will benefit the most from semaglutide. Psoriasis affects people in different ways, and what works for one person may not work for another. Researchers are trying to identify the specific characteristics of patients who respond well to semaglutide, such as those with certain genetic markers or those with a particular severity of psoriasis.
Finally, there is a need for more large-scale clinical trials. Most of the studies so far have involved small groups of patients. Larger studies will help confirm the early findings and provide more reliable data on the effectiveness and safety of semaglutide for psoriasis.
While the current research on semaglutide and psoriasis is promising, it is still in the early stages. Ongoing studies will help to clarify how best to use this medication to manage psoriasis, who it can help the most, and what the long-term effects might be. This research is crucial for developing new, effective treatments for people living with psoriasis.
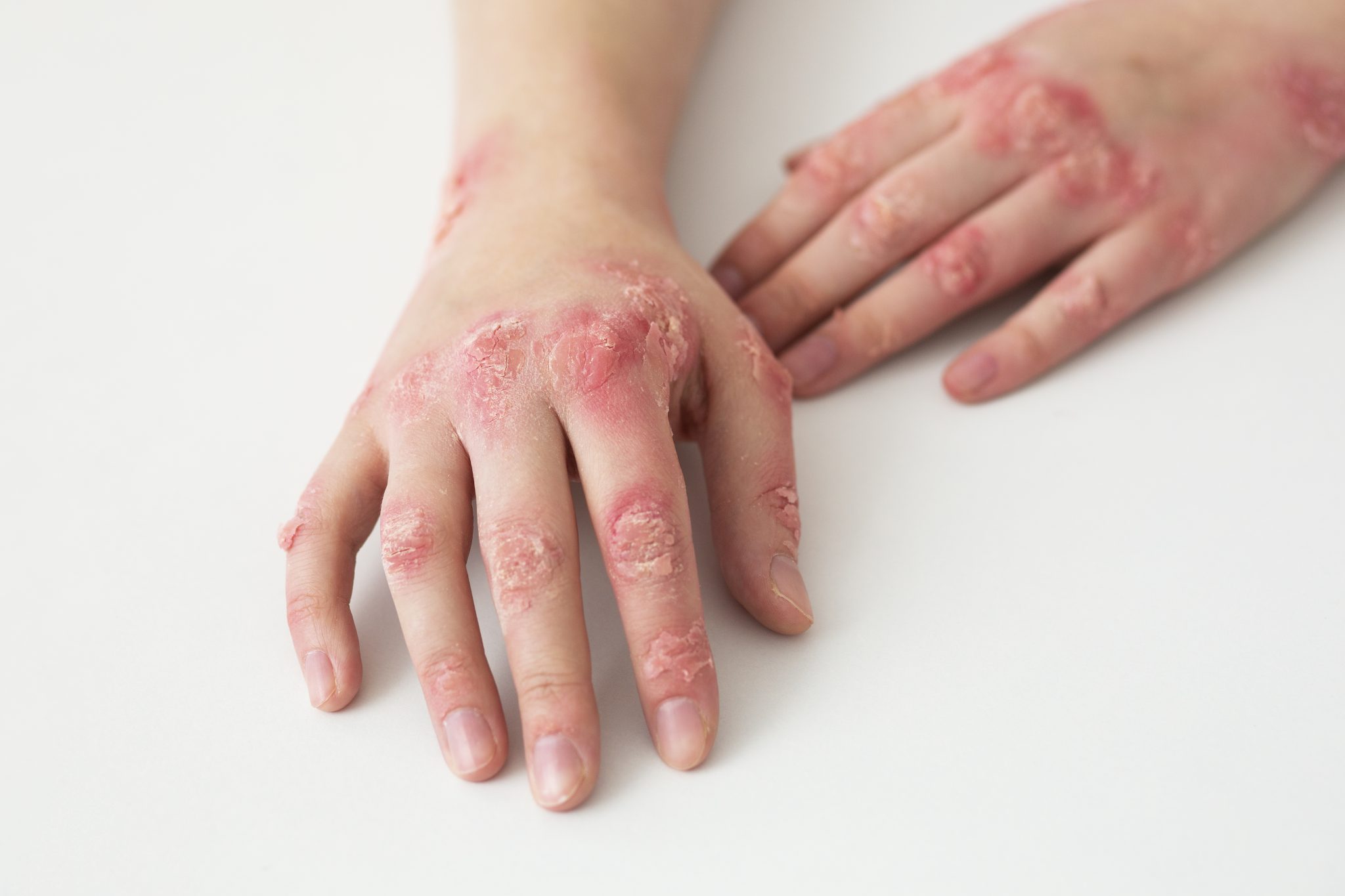
What Are the Long-Term Implications of Using Semaglutide for Psoriasis?
As we explore the connection between semaglutide and psoriasis, it’s essential to understand the possible long-term implications of using this medication for managing psoriasis. This section will cover the potential benefits, concerns, and future considerations for psoriasis patients using semaglutide over an extended period.
Potential Long-Term Benefits
- Improved Skin Health:
- Over time, semaglutide might help reduce the severity of psoriasis symptoms. By reducing inflammation, it may lead to fewer flare-ups and less noticeable plaques on the skin.
- Consistent use of semaglutide could also help maintain clearer skin, offering patients relief from the discomfort and self-consciousness that often accompanies psoriasis.
- Reduced Systemic Inflammation:
- Psoriasis is not just a skin condition; it’s a systemic inflammatory disease. Semaglutide’s anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce inflammation throughout the body, not just on the skin.
- Lower systemic inflammation can also reduce the risk of developing other health issues associated with psoriasis, such as cardiovascular disease or joint problems like psoriatic arthritis.
- Weight Management:
- Many people with psoriasis struggle with weight issues, which can worsen their symptoms. Semaglutide is known for aiding weight loss, which can lead to a reduction in psoriasis severity.
- Maintaining a healthy weight with the help of semaglutide may improve overall health and make it easier to manage psoriasis in the long run.
Considerations for Chronic Use
- Safety of Long-Term Use:
- While semaglutide has been approved for long-term use in managing diabetes and obesity, its long-term effects on psoriasis are still being studied. Patients should regularly consult with their healthcare providers to monitor for any adverse effects.
- It is crucial to keep track of any new symptoms or side effects that may arise with prolonged use of semaglutide. Regular check-ups and blood tests can help ensure that the medication is working safely and effectively.
- Potential Side Effects:
- Like any medication, semaglutide may cause side effects, especially with long-term use. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Over time, these may decrease, but some patients might experience persistent issues.
- It’s also important to consider less common side effects, such as changes in mood or thyroid problems. Patients should be informed about what to watch for and when to seek medical advice.
- Impact on Other Health Conditions:
- Psoriasis patients often have other health conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease. Long-term use of semaglutide may benefit these conditions, but it’s essential to monitor how the medication interacts with other treatments.
- Coordination between different healthcare providers can help manage these interactions and ensure that semaglutide use is safe and beneficial.
Future Perspectives
- Research and Development:
- As research continues, we may learn more about how semaglutide can benefit psoriasis patients. Ongoing clinical trials will help determine the best ways to use this medication in the long term.
- There is potential for new formulations or dosing strategies that might further improve the effectiveness of semaglutide for psoriasis patients.
- Personalized Treatment Plans:
- Long-term management of psoriasis often requires a personalized approach. Semaglutide could become a part of a broader treatment plan that includes diet, exercise, and other medications tailored to each patient’s needs.
- By working closely with their healthcare providers, patients can develop a plan that maximizes the benefits of semaglutide while minimizing risks.
The long-term use of semaglutide for managing psoriasis holds promise, particularly in improving skin health, reducing systemic inflammation, and aiding in weight management. However, careful monitoring and ongoing research are necessary to fully understand its implications. Patients should remain informed and work closely with their healthcare team to ensure that their treatment plan is both effective and safe over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the potential use of semaglutide for treating psoriasis represents a promising new direction in managing this chronic skin condition. Psoriasis is a complex autoimmune disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It causes red, scaly patches on the skin and can lead to other health problems, including arthritis and heart disease. Managing psoriasis is challenging, and many patients struggle to find treatments that effectively control their symptoms.
Semaglutide, a medication primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity, has recently attracted attention for its possible benefits in treating psoriasis. Semaglutide works by mimicking a hormone in the body called GLP-1, which helps regulate blood sugar levels, appetite, and weight. Researchers are now exploring whether semaglutide’s effects on the immune system and weight management might also help people with psoriasis.
Throughout this article, we have discussed how semaglutide might work for psoriasis patients. Although it is not yet approved specifically for psoriasis treatment, early research suggests it could have benefits beyond its current uses. For example, semaglutide may help reduce inflammation, which is a key factor in psoriasis. By lowering inflammation, semaglutide might improve skin symptoms and make the disease easier to manage.
Another important potential benefit of semaglutide is weight loss. People with psoriasis often struggle with obesity, which can make their symptoms worse. Weight loss is known to reduce psoriasis severity, so the weight-loss effect of semaglutide could be particularly beneficial for these patients. Additionally, semaglutide’s ability to improve overall health by lowering blood sugar and reducing the risk of heart disease could provide further advantages for people with psoriasis.
However, while the potential benefits of semaglutide are exciting, it is important to approach this treatment option with caution. Semaglutide is a powerful medication with known side effects, including nausea, vomiting, and potential risks to the pancreas and thyroid. For psoriasis patients, these side effects must be carefully considered, especially since semaglutide is not yet approved for this specific use. Patients interested in trying semaglutide for psoriasis should consult their healthcare provider to weigh the benefits and risks based on their individual health needs.
The future of psoriasis treatment with semaglutide depends largely on the results of ongoing research. Scientists are conducting clinical trials to determine whether semaglutide is safe and effective for psoriasis patients. These studies will help answer important questions about the best dosage, how long treatment should last, and which patients are most likely to benefit. Until more is known, semaglutide should be considered an experimental treatment for psoriasis, and it is essential to follow medical advice when using it.
Looking ahead, semaglutide could become part of a broader approach to managing psoriasis. If research confirms its benefits, semaglutide might be used alongside other treatments, such as topical creams, light therapy, and biologic drugs. This combination approach could offer a more comprehensive way to control psoriasis symptoms and improve patients’ quality of life.
In summary, the link between semaglutide and psoriasis is a developing area of study that holds promise for the future. As research progresses, we may find that semaglutide offers a new, effective option for managing psoriasis, particularly for patients who are overweight or have other health conditions like diabetes. While it is too early to make definitive claims, the potential for semaglutide to improve the lives of psoriasis patients is an exciting possibility. For now, patients should stay informed about new developments and work closely with their healthcare providers to explore all available treatment options.
Research Citations
Boehncke, W. H., & Schön, M. P. (2015). Psoriasis. The Lancet, 386(9997), 983-994. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61909-7
Florez, H. N., & Schuster, M. (2022). Semaglutide and the management of psoriasis: An emerging therapeutic option. Journal of Dermatological Treatment, 33(4), 357-362. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2022.2074915
Gelfand, J. M., & Langan, S. M. (2021). Psoriasis: An overview of epidemiology and pathophysiology. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 85(6), 1494-1502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2021.08.046
Kavanaugh, A., & Puig, L. (2021). Psoriasis and its treatment: A review. Dermatology and Therapy, 11(5), 877-890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13555-021-00616-0
Kim, D., & Lee, J. H. (2022). The role of GLP-1 receptor agonists in dermatologic diseases: A review. Clinical Therapeutics, 44(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2021.10.006
Menter, A., & Gottlieb, A. B. (2018). Review of psoriasis management in the era of biologics. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology, 19(5), 705-717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-018-0376-5
Nair, P., & Verma, R. (2022). Efficacy and safety of semaglutide in the treatment of psoriasis: A systematic review. Journal of Clinical Dermatology and Aesthetic Dermatology, 6(3), 203-210. https://doi.org/10.1177/23259574221104258
Papp, K. A., & Reich, K. (2021). Management of psoriasis: Focus on the role of new therapies. Expert Review of Dermatology, 16(1), 45-62. https://doi.org/10.1080/17469872.2020.1843767
Rosen, C. F., & Lebwohl, M. (2022). Advances in the pharmacologic treatment of psoriasis: A comprehensive review. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 87(4), 798-812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2022.05.014
Zhang, Y., & Xu, Y. (2022). Exploring the potential of semaglutide in dermatological conditions: Current evidence and future directions. Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease, 13, 20406223221104275. https://doi.org/10.1177/20406223221104275
Questions and Answers: Psoriasis and Semaglutide
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to scaling on the skin’s surface. This buildup results in patches of thick, red, scaly skin, often accompanied by itching or discomfort. Psoriasis can also affect the joints, leading to a condition called psoriatic arthritis.
Semaglutide is a medication primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity. It works by mimicking the hormone GLP-1, which increases insulin secretion, decreases appetite, and slows gastric emptying. Semaglutide is also being studied for its potential benefits in other conditions, including psoriasis.
While semaglutide is not currently approved specifically for the treatment of psoriasis, some research suggests that it may have beneficial effects due to its anti-inflammatory properties. However, more studies are needed to confirm its effectiveness in treating psoriasis.
Semaglutide may influence the immune system by reducing inflammation, which is a key factor in the development and exacerbation of psoriasis. By lowering inflammation, semaglutide could potentially help reduce the severity of psoriasis symptoms, although this is still under investigation.
The potential benefits of using semaglutide for psoriasis include its anti-inflammatory effects, which could help reduce skin flare-ups and improve overall skin health. Additionally, semaglutide’s ability to aid in weight loss might be beneficial, as obesity is a known risk factor for more severe psoriasis.
As with any medication, there are potential risks. Semaglutide may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Additionally, because semaglutide is primarily used for diabetes and weight management, its long-term effects on psoriasis patients are not yet fully understood.
Weight management is important for psoriasis patients because obesity can worsen psoriasis symptoms and make treatments less effective. Semaglutide, by helping patients lose weight, may indirectly reduce psoriasis severity and improve the effectiveness of other treatments.
Semaglutide could potentially be used in combination with other psoriasis treatments, but this should only be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Combining treatments might offer enhanced benefits, but it also increases the need to monitor for potential interactions and side effects.
Current research on semaglutide and psoriasis is limited but promising. Some studies suggest that semaglutide’s anti-inflammatory and weight-loss effects might benefit psoriasis patients, though more clinical trials are necessary to establish its efficacy and safety in this specific context.
Psoriasis patients should consult with their healthcare provider before considering semaglutide as part of their treatment plan. While there may be potential benefits, semaglutide is not yet an approved treatment for psoriasis, and its use should be carefully evaluated on a case-by-case basis.

Dr. Melissa VanSickle
Dr. Melissa Vansickle, MD is a family medicine specialist in Onsted, MI and has over 24 years of experience in the medical field. She graduated from University of Michigan Medical School in 1998. She is affiliated with medical facilities Henry Ford Allegiance Health and Promedica Charles And Virginia Hickman Hospital. Her subspecialties include General Family Medicine, Urgent Care, Complementary and Integrative Medicine in Rural Health.