Table of Contents
Introduction
Semaglutide is a medication that many people use to help manage type 2 diabetes and aid in weight loss. It works by mimicking a hormone in your body called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1). This hormone helps control your blood sugar levels and appetite. While semaglutide has proven to be effective for these purposes, some people have reported experiencing skin sensitivity as a side effect. This article aims to explore the link between semaglutide and skin sensitivity in detail.
The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of how semaglutide might cause skin sensitivity and what you can do about it. By answering the top 10 questions that people ask search engines about this topic, we aim to shed light on the potential side effects and help you make informed decisions about your health.
Firstly, we’ll discuss what semaglutide is and how it works. This will give you a foundation to understand why it might affect your skin. Then, we’ll explain what skin sensitivity is and what symptoms to look out for. This will help you identify if you might be experiencing skin sensitivity as a side effect of semaglutide.
Next, we will delve into whether semaglutide can cause skin sensitivity. We will look at the reported side effects and analyze data from clinical trials and studies. This will include expert insights from dermatologists and endocrinologists who specialize in skin and hormone-related issues.
Following this, we will examine the common types of skin reactions associated with semaglutide use. These reactions can include rashes, itching, and redness. We will discuss how often these reactions occur and how severe they can be. Understanding these reactions can help you better manage them if they happen to you.
We will also explore the mechanisms behind skin sensitivity caused by semaglutide. This means looking at how the medication interacts with your body to cause these reactions. We will discuss the role of your immune system and inflammation in these processes.
It’s important to identify who is at risk for developing skin sensitivity from semaglutide. We will highlight factors that might increase your risk, such as having pre-existing skin conditions or allergies. We will also discuss how the dosage and duration of semaglutide treatment might influence these risks.
Managing skin sensitivity while on semaglutide is crucial. We will provide practical tips and recommendations for skincare routines and products that can help mitigate skin reactions. Knowing when to seek medical advice is also important, and we will guide you on what to do if you experience severe or persistent skin issues.
For those who might consider alternatives, we will discuss other medications and treatments. This section will cover other GLP-1 receptor agonists and compare their pros and cons. Non-pharmacological alternatives for diabetes and weight management will also be explored.
Consulting your healthcare provider is key to managing any side effects effectively. We will emphasize the importance of open communication with your doctor. We will provide a list of questions you should ask your healthcare provider regarding semaglutide and skin sensitivity, and explain how to monitor and report side effects.
Finally, we will look at current research and future directions. Ongoing studies are continually providing new insights into the link between semaglutide and skin reactions. We will summarize these studies and discuss potential new formulations or adjunct therapies that might reduce skin sensitivity. Emerging trends in personalized medicine, which tailor treatments to individual patients, will also be highlighted.
In conclusion, we will recap the key findings and insights from this article. Understanding and managing skin sensitivity with semaglutide is important for your overall health and well-being. We will encourage further research and emphasize the importance of patient education in making informed healthcare decisions. By the end of this article, you should have a thorough understanding of semaglutide, its potential effects on your skin, and how to manage any side effects that may arise.
What is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is a medication that has gained a lot of attention in recent years, especially for its role in managing diabetes and aiding in weight loss. To understand how semaglutide works and its impact on health, it’s important to break down its key components and uses.
Definition and Medical Classification
Semaglutide is classified as a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. This means it mimics the action of a naturally occurring hormone in the body called GLP-1. GLP-1 plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. Medications like semaglutide are designed to help people with type 2 diabetes manage their blood sugar more effectively.
Mechanism of Action
Understanding how semaglutide works in the body can help explain its benefits and potential side effects. Semaglutide helps lower blood sugar levels by:
- Stimulating Insulin Secretion: When you eat, your blood sugar levels rise. Semaglutide helps your pancreas release insulin in response to this increase in blood sugar. Insulin is the hormone that allows your cells to take in glucose (sugar) from the blood and use it for energy.
- Reducing Glucagon Levels: Glucagon is another hormone that works opposite to insulin. It raises blood sugar levels by signaling the liver to release stored glucose. Semaglutide reduces the release of glucagon, which helps keep blood sugar levels from rising too high.
- Slowing Gastric Emptying: Semaglutide slows down the rate at which food leaves your stomach and enters your intestines. This helps prevent sharp spikes in blood sugar levels after meals and also helps you feel fuller for longer, which can aid in weight loss.
Common Uses
Semaglutide is primarily used for two main purposes:
- Managing Type 2 Diabetes: For people with type 2 diabetes, keeping blood sugar levels within a normal range is crucial. Semaglutide helps achieve this by the mechanisms described above. By improving insulin secretion, reducing glucagon levels, and slowing gastric emptying, semaglutide can significantly improve blood sugar control.
- Aiding in Weight Loss: In addition to its effects on blood sugar, semaglutide has been found to be effective in helping people lose weight. The feeling of fullness that semaglutide induces can lead to reduced calorie intake. Weight loss is an important factor in managing type 2 diabetes and can also improve overall health and reduce the risk of other conditions, such as heart disease.
How Semaglutide is Administered
Semaglutide is available in two main forms:
- Injectable Form: The injectable form of semaglutide is administered once a week. Patients can do this at home using a pre-filled pen. The weekly injection makes it convenient compared to other medications that require daily dosing.
- Oral Form: More recently, an oral form of semaglutide has been developed. This form is taken once daily and offers an alternative for those who prefer not to use injections.
Side Effects and Considerations
Like all medications, semaglutide can cause side effects. The most common ones include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These gastrointestinal issues are usually mild and tend to decrease over time as the body adjusts to the medication. However, there are some more serious side effects to be aware of, such as pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) and thyroid tumors, although these are rare.
Who Should Not Use Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is not suitable for everyone. It should not be used by individuals with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (a type of thyroid cancer) or those with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). Additionally, those with a history of pancreatitis should use semaglutide with caution and under close supervision by a healthcare provider.
Semaglutide is a powerful medication that offers significant benefits for managing type 2 diabetes and aiding in weight loss. By understanding its mechanism of action, common uses, and potential side effects, patients and healthcare providers can work together to use this medication effectively and safely.
Understanding Skin Sensitivity
Skin sensitivity refers to a condition where the skin reacts more easily to stimuli that would not usually cause a reaction in other people. This can include reactions to certain chemicals, weather conditions, or even physical touch. People with sensitive skin often experience discomfort or irritation more quickly and intensely than those with normal skin.
Common symptoms of skin sensitivity include:
- Redness: The affected area may turn red and become warm to the touch.
- Itching: A persistent or intense urge to scratch the affected area.
- Dryness: The skin may feel rough, flaky, and tight.
- Burning or stinging: A sensation of heat or pain in the affected area.
- Rashes: Small bumps, blisters, or patches of irritated skin can appear.
- Swelling: The skin may become puffy or swollen, particularly around the eyes or lips.
Potential Causes of Skin Sensitivity
There are many potential causes of skin sensitivity. These can vary widely from person to person. Some common causes include:
- Genetics: Some people are born with more sensitive skin. This can be due to genetic factors passed down from their parents.
- Environmental Factors: Weather conditions like extreme cold, heat, or wind can trigger skin sensitivity. Pollution and exposure to the sun can also cause reactions.
- Skin Care Products: Certain ingredients in soaps, lotions, and cosmetics can irritate sensitive skin. Common culprits include fragrances, dyes, and preservatives.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like eczema, rosacea, and psoriasis can make the skin more sensitive. People with these conditions often have to take extra care of their skin.
- Diet and Lifestyle: A diet lacking in essential nutrients can affect skin health. Stress and lack of sleep can also make the skin more reactive.
General Impact on Daily Life and Health
Living with sensitive skin can be challenging. Everyday activities that others take for granted can become sources of discomfort or pain. Here are some ways skin sensitivity can impact daily life and overall health:
- Choosing Products: People with sensitive skin often have to be very careful about the products they use. This means spending extra time reading labels and sometimes paying more for products designed for sensitive skin.
- Emotional Well-being: Constant irritation and discomfort can take a toll on a person’s emotional well-being. It can lead to stress, anxiety, and even depression. Worrying about flare-ups can make social situations more stressful.
- Medical Visits: Managing skin sensitivity often requires regular visits to dermatologists or other healthcare providers. This can be time-consuming and costly.
- Clothing Choices: Certain fabrics can irritate sensitive skin. People with this condition might need to avoid materials like wool or synthetic fabrics and stick to soft, natural fibers like cotton.
- Sun Protection: Sensitive skin is more prone to sunburn and damage from UV rays. This means always needing to use sunscreen and wearing protective clothing, which can be inconvenient, especially during outdoor activities.
- Daily Discomfort: Persistent symptoms like itching, burning, and dryness can be distracting and uncomfortable. This can affect concentration and performance at work or school.
Taking Care of Sensitive Skin
Proper care and management can help reduce the impact of skin sensitivity. Here are some tips for managing sensitive skin:
- Patch Test New Products: Before using a new product, apply a small amount to a less visible area of your skin to see if there is any reaction.
- Choose Gentle Products: Use products labeled as hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, and designed for sensitive skin. Avoid harsh soaps and cleansers.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated can help reduce dryness and irritation. Choose a gentle, non-comedogenic moisturizer.
- Protect from the Sun: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30. Wear protective clothing and seek shade when outdoors.
- Stay Hydrated and Eat Well: Drink plenty of water and eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that promote skin health, such as vitamins A, C, and E.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-relieving activities like yoga, meditation, or exercise to help maintain overall skin health.
By understanding the causes and effects of skin sensitivity, people can take steps to manage their condition and improve their quality of life. This is especially important for individuals using medications like semaglutide, as they may need to be extra cautious about potential skin reactions.

Can Semaglutide Cause Skin Sensitivity?
Semaglutide is a medication primarily used to manage type 2 diabetes and support weight loss. Like all medications, it can have side effects. While most people tolerate semaglutide well, some do experience side effects, including skin reactions. These side effects are documented in clinical trials and patient reports. Understanding the range of possible side effects helps patients and healthcare providers manage them effectively.
Analysis of Skin-Related Side Effects from Clinical Trials and Studies
Clinical trials for semaglutide have provided valuable information about its safety profile. These trials involve thousands of participants and closely monitor all side effects, including those affecting the skin. Some common skin-related side effects reported in these trials include rashes, itching, and redness. While these reactions are not extremely common, they do occur in a notable number of cases.
In one large clinical trial, skin reactions were reported in approximately 5-10% of participants. These reactions varied in severity, with most being mild to moderate. Severe skin reactions were rare but did occur in a small percentage of users. The data from these trials are crucial for understanding the potential risks associated with semaglutide.
Types of Skin Reactions Observed
Patients taking semaglutide may experience various types of skin reactions. The most commonly reported ones include:
- Rashes: Red, inflamed areas on the skin that can be itchy or uncomfortable.
- Itching (Pruritus): An irritating sensation that makes one want to scratch the affected area.
- Redness (Erythema): A red appearance of the skin, often associated with inflammation.
These reactions can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly observed on the arms, legs, and torso. The severity of these reactions can range from mild, temporary discomfort to more severe, persistent symptoms.
Severity and Duration of Skin Reactions
The severity of skin reactions to semaglutide can vary widely among individuals. Most reactions are mild and resolve on their own within a few days to weeks. In some cases, patients may experience moderate discomfort, which might require treatment with over-the-counter or prescription creams and ointments.
Severe skin reactions, though rare, can be more troublesome and may necessitate discontinuation of the medication. These severe reactions could include extensive rashes, blistering, or intense itching that does not improve with standard treatments. It is crucial for patients experiencing severe reactions to seek medical advice promptly.
Statistical Prevalence Among Semaglutide Users
To put the prevalence of skin reactions in perspective, it is helpful to consider the statistics from clinical trials. In a typical study involving semaglutide, skin reactions were reported in about 5-10% of participants. This means that out of 100 people taking the medication, 5 to 10 might experience some form of skin issue.
While this percentage might seem small, it is significant enough to warrant attention. Healthcare providers should inform patients about this potential side effect and monitor them for any signs of skin sensitivity. Early detection and management can help prevent more serious complications and ensure a better overall experience with the medication.
Semaglutide can cause skin sensitivity in some users, though it is not the most common side effect. Clinical trials and expert opinions provide valuable insights into the nature and prevalence of these reactions. By understanding the types, severity, and statistical likelihood of skin-related side effects, patients and healthcare providers can better manage and address any issues that arise. Communication with a healthcare provider is key to ensuring safe and effective use of semaglutide.
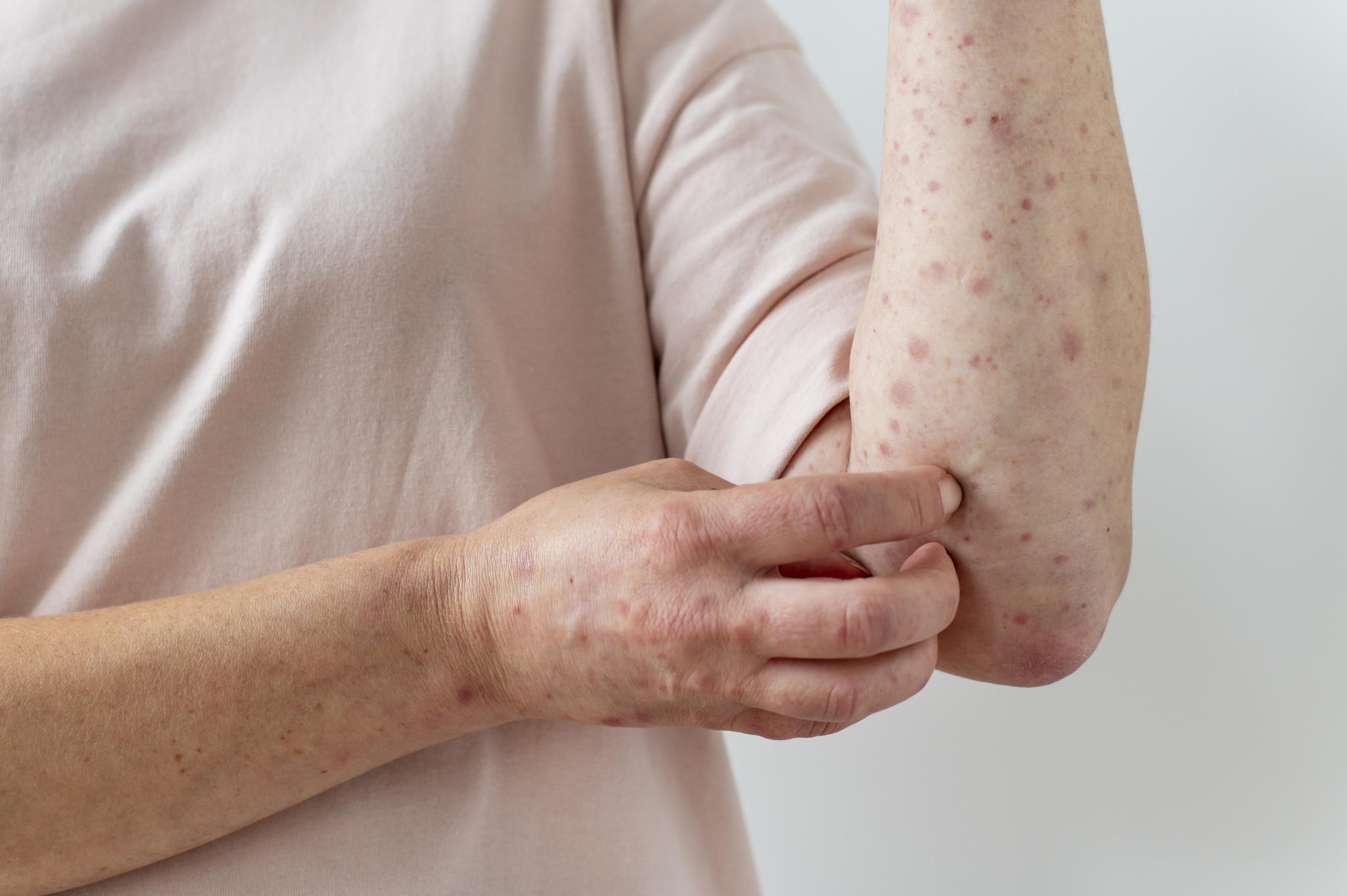
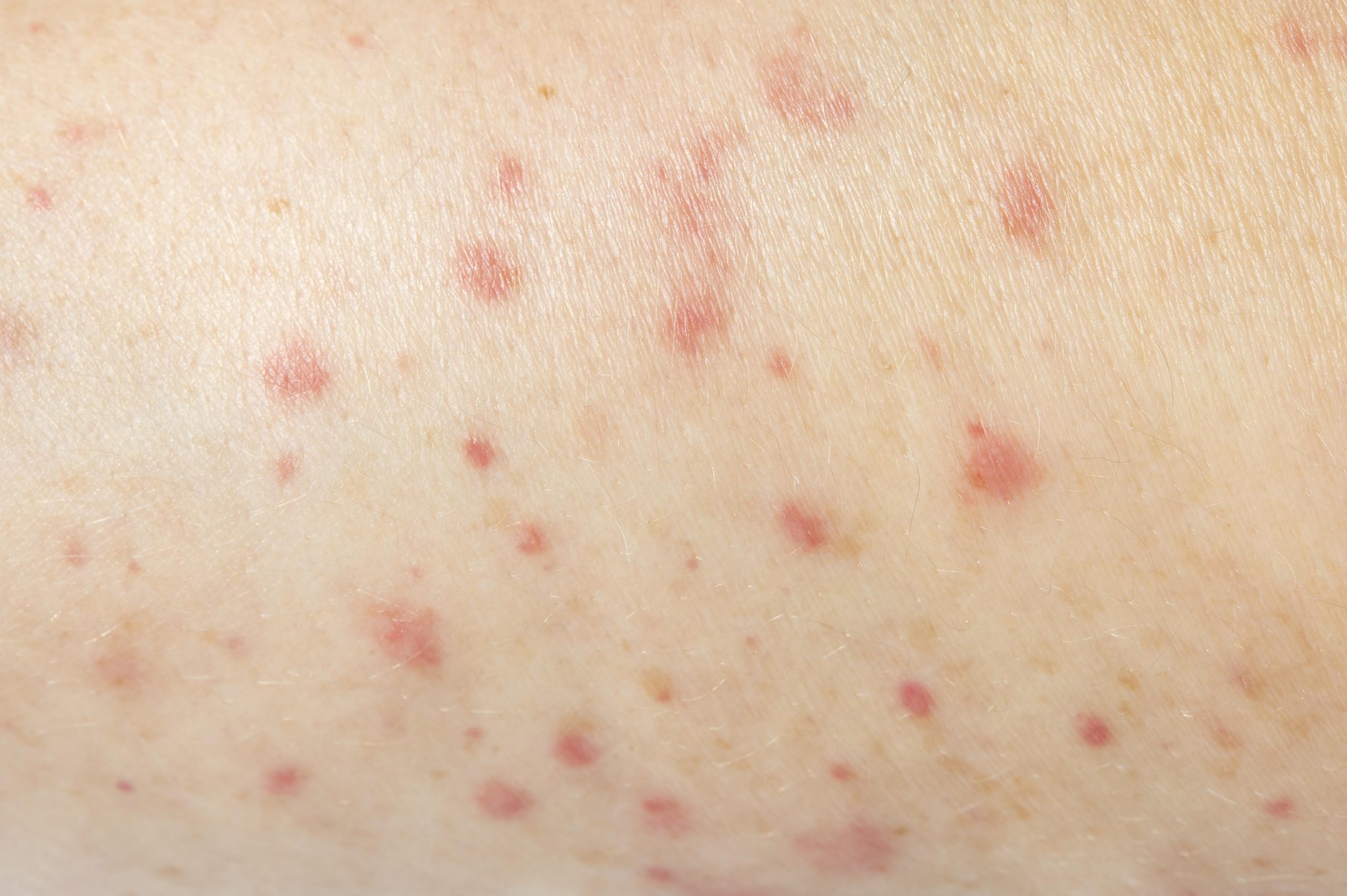
Common Skin Reactions Associated with Semaglutide
When taking semaglutide, some people may notice changes in their skin. These changes, or reactions, can vary in type and severity. Understanding these common skin reactions can help users recognize and manage them effectively.
Types of Skin Reactions
- Rashes
- Appearance: Rashes are a common skin reaction. They may appear as red, bumpy, or blotchy areas on the skin. These can be itchy and uncomfortable.
- Location: Rashes can occur anywhere on the body but are often found on the arms, legs, or stomach.
- Causes: Rashes can be caused by the body’s immune response to semaglutide. Sometimes, the skin reacts because it sees the medication as a foreign substance.
- Itching (Pruritus)
- Description: Itching is another common reaction. It may occur with or without a visible rash.
- Severity: The intensity of itching can vary from mild to severe. It can be a persistent annoyance that affects daily activities and sleep.
- Triggers: Itching can be triggered by dry skin, irritation from clothing, or an allergic reaction to semaglutide.
- Redness and Inflammation
- Symptoms: Redness and inflammation are often signs of irritation or allergic reaction. The affected areas may feel warm to the touch and appear swollen.
- Mechanism: These symptoms occur when blood vessels in the skin widen, allowing more blood to flow to the area. This is part of the body’s defense mechanism against what it perceives as a threat.
Severity and Duration of Skin Reactions
Mild Reactions
- Characteristics: Mild skin reactions may include slight redness or minor itching. These symptoms are usually manageable and may not require medical treatment.
- Duration: Mild reactions often resolve on their own within a few days to a week.
Moderate Reactions
- Characteristics: Moderate reactions might involve more noticeable rashes, persistent itching, and discomfort.
- Management: These reactions may need over-the-counter treatments like antihistamines or topical creams. Consulting a healthcare provider for advice can be beneficial.
Severe Reactions
- Characteristics: Severe reactions are rare but can be serious. They may include extensive rashes, severe itching, and significant swelling.
- Action: Immediate medical attention is necessary for severe reactions. A healthcare provider might suggest stopping the medication or switching to an alternative.
Statistical Prevalence Among Semaglutide Users
Clinical Trial Data
- Incidence: Clinical trials provide data on how often skin reactions occur among semaglutide users. According to studies, a small percentage of users experience skin-related side effects.
- Details: For example, in one study, about 5-10% of participants reported skin reactions like rashes or itching. These statistics help understand the likelihood of experiencing such side effects.
Real-World Data
- Reports: Real-world data from patients who use semaglutide outside of clinical trials also contribute to understanding skin reactions.
- Findings: Reports from these patients often align with clinical trial findings, showing a consistent percentage of users experiencing skin issues.
Impact on Quality of Life
Daily Activities
- Disruption: Skin reactions can disrupt daily activities. Itching and rashes can make it uncomfortable to wear certain clothes, engage in physical activities, or concentrate on tasks.
- Sleep: Persistent itching can also affect sleep quality, leading to fatigue and decreased productivity.
Emotional Well-Being
- Stress: Dealing with skin reactions can cause stress and anxiety. Concerns about appearance and discomfort can affect self-esteem and mental health.
- Support: Seeking support from healthcare providers and discussing concerns can help manage the emotional impact of these side effects.
While semaglutide is effective for managing diabetes and aiding weight loss, it can cause skin reactions in some users. Understanding the types, severity, and prevalence of these reactions helps in early recognition and effective management. If you experience skin issues while taking semaglutide, consult your healthcare provider for appropriate guidance and treatment options.
Mechanisms Behind Skin Sensitivity from Semaglutide
Skin sensitivity can occur for many reasons, and when taking a medication like semaglutide, it is essential to understand how it might affect the skin. Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, primarily used to manage diabetes and support weight loss. However, like any medication, it can have side effects, including skin reactions. In this section, we will explore how semaglutide might lead to skin sensitivity.
Biological and Chemical Pathways
Semaglutide works by mimicking a hormone called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1), which is naturally produced in the gut. This hormone helps to regulate blood sugar levels by increasing insulin release and reducing glucagon secretion. While this process is beneficial for managing diabetes, it can sometimes trigger unwanted effects on the skin.
One of the ways semaglutide can cause skin reactions is through the immune system. When you take semaglutide, it can sometimes be recognized by your body as a foreign substance. This recognition can cause your immune system to react, leading to inflammation. Inflammation is a common cause of skin sensitivity, resulting in symptoms like redness, itching, and rashes.
Immune Response and Inflammation
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, but it can also be triggered by certain medications. When your immune system detects something it considers harmful, it releases chemicals called cytokines. These cytokines help to fight off the perceived threat but can also cause inflammation. In the case of semaglutide, the immune system’s response might mistakenly target the medication, leading to skin inflammation.
This immune response can vary from person to person. Some people may have a mild reaction, while others might experience more severe skin sensitivity. Factors such as genetics, overall health, and the presence of other skin conditions can influence the severity of the reaction.
Comparison with Other Medications
It is helpful to compare semaglutide with other medications to understand its potential skin effects better. Many drugs, especially those that affect the immune system or hormone levels, can cause skin reactions. For example, other GLP-1 receptor agonists like liraglutide and exenatide have also been reported to cause similar skin issues. Understanding these comparisons can provide a clearer picture of why semaglutide might cause skin sensitivity.
The Role of Dosage and Duration
The dosage and duration of semaglutide use can also impact the likelihood of skin sensitivity. Higher doses of the medication can increase the risk of side effects, including skin reactions. Similarly, the longer you take semaglutide, the more time there is for potential side effects to develop.
It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s dosage recommendations and report any skin issues as soon as they arise. Early detection can help manage and minimize the impact of these reactions.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Your genetic makeup can influence how your body responds to semaglutide. Some people have genetic predispositions that make them more likely to experience adverse reactions to certain medications. These genetic factors can affect how your immune system reacts to semaglutide, increasing the likelihood of skin sensitivity.
Environmental factors also play a role. Exposure to allergens, pollutants, or harsh weather conditions can exacerbate skin sensitivity. If you already have sensitive skin, these environmental factors, combined with the effects of semaglutide, can lead to more pronounced reactions.
Understanding the mechanisms behind skin sensitivity from semaglutide involves looking at how the drug interacts with your body on multiple levels. From the immune response and inflammation to genetic and environmental factors, several pathways can lead to skin reactions. By knowing these mechanisms, you can better manage and mitigate skin sensitivity while using semaglutide. Always consult with your healthcare provider if you experience any skin issues while on this medication, and follow their guidance for the best outcomes.
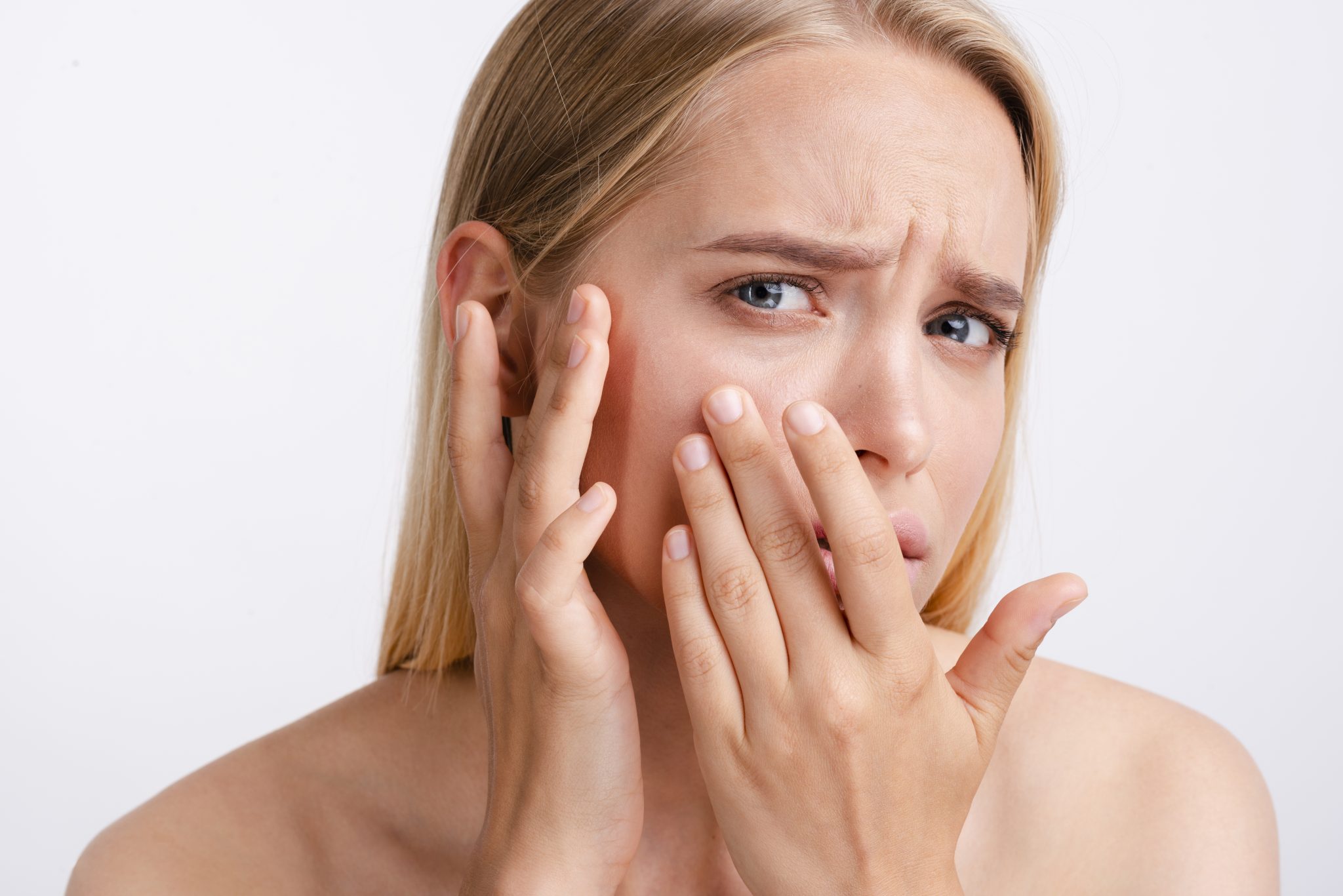
Risk Factors for Developing Skin Sensitivity on Semaglutide
When taking semaglutide, some people might develop skin sensitivity. Understanding the risk factors can help you and your doctor make better decisions about your treatment. In this section, we’ll look at who is more likely to develop skin sensitivity, the influence of dosage and treatment duration, and the role of genetic and environmental factors.
Identifying Individuals at Higher Risk
Certain individuals are more likely to experience skin sensitivity when taking semaglutide. Here are some key risk factors:
- Pre-existing Skin Conditions: If you already have skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or chronic rashes, you might be more prone to developing skin sensitivity with semaglutide. These conditions can make your skin more reactive to new medications.
- Allergies: People with a history of allergies, especially those related to medications, are at a higher risk. If you have experienced allergic reactions to other drugs in the past, it’s important to inform your doctor.
- Immune System Issues: If your immune system is compromised or if you have autoimmune diseases, your skin might react more strongly to semaglutide. This can be due to an overactive immune response that affects your skin.
Influence of Dosage and Duration of Treatment
The amount of semaglutide you take and how long you take it can impact the likelihood of developing skin sensitivity:
- Higher Dosages: Taking higher doses of semaglutide can increase the risk of side effects, including skin sensitivity. Your body might react more strongly to larger amounts of the medication.
- Long-term Use: The longer you use semaglutide, the more likely it is for side effects to appear. This is because prolonged exposure to the drug can lead to cumulative effects on your skin.
- Initial Phase of Treatment: Skin sensitivity might be more noticeable when you first start taking semaglutide. Your body is adjusting to the new medication, and this adjustment period can sometimes trigger skin reactions.
Role of Genetic and Environmental Factors
Your genes and environment also play a significant role in determining how your skin might react to semaglutide:
- Genetic Predisposition: Some people are genetically predisposed to having sensitive skin. If your family has a history of skin reactions to medications, you might be more likely to experience the same.
- Environmental Factors: External factors like climate, pollution, and exposure to harsh chemicals can affect your skin’s sensitivity. For instance, living in an area with high pollution can make your skin more reactive to medications.
- Lifestyle Choices: Your lifestyle can influence your skin’s health. Poor diet, lack of hydration, and excessive use of skincare products with harsh ingredients can make your skin more susceptible to reactions.
Combining Risk Factors
It’s important to note that these risk factors can combine and increase your likelihood of developing skin sensitivity. For example, if you have a pre-existing skin condition and also live in a polluted area, your risk is higher than if you only had one of these factors.
Mitigating the Risk
Knowing these risk factors can help you take steps to reduce the chance of developing skin sensitivity while on semaglutide:
- Consult Your Doctor: Before starting semaglutide, discuss your medical history and any pre-existing conditions with your doctor. They can adjust your dosage or suggest additional precautions to minimize risk.
- Monitor Your Skin: Keep an eye on any changes in your skin condition, especially during the first few weeks of treatment. Report any unusual reactions to your healthcare provider immediately.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding harsh skincare products. This can help keep your skin resilient and less prone to sensitivity.
Understanding the risk factors for developing skin sensitivity when taking semaglutide can help you manage and possibly prevent these side effects. By recognizing if you’re at higher risk, monitoring your skin, and taking proactive steps, you can ensure a safer and more comfortable experience with semaglutide. Always work closely with your healthcare provider to tailor your treatment plan to your specific needs and risks.
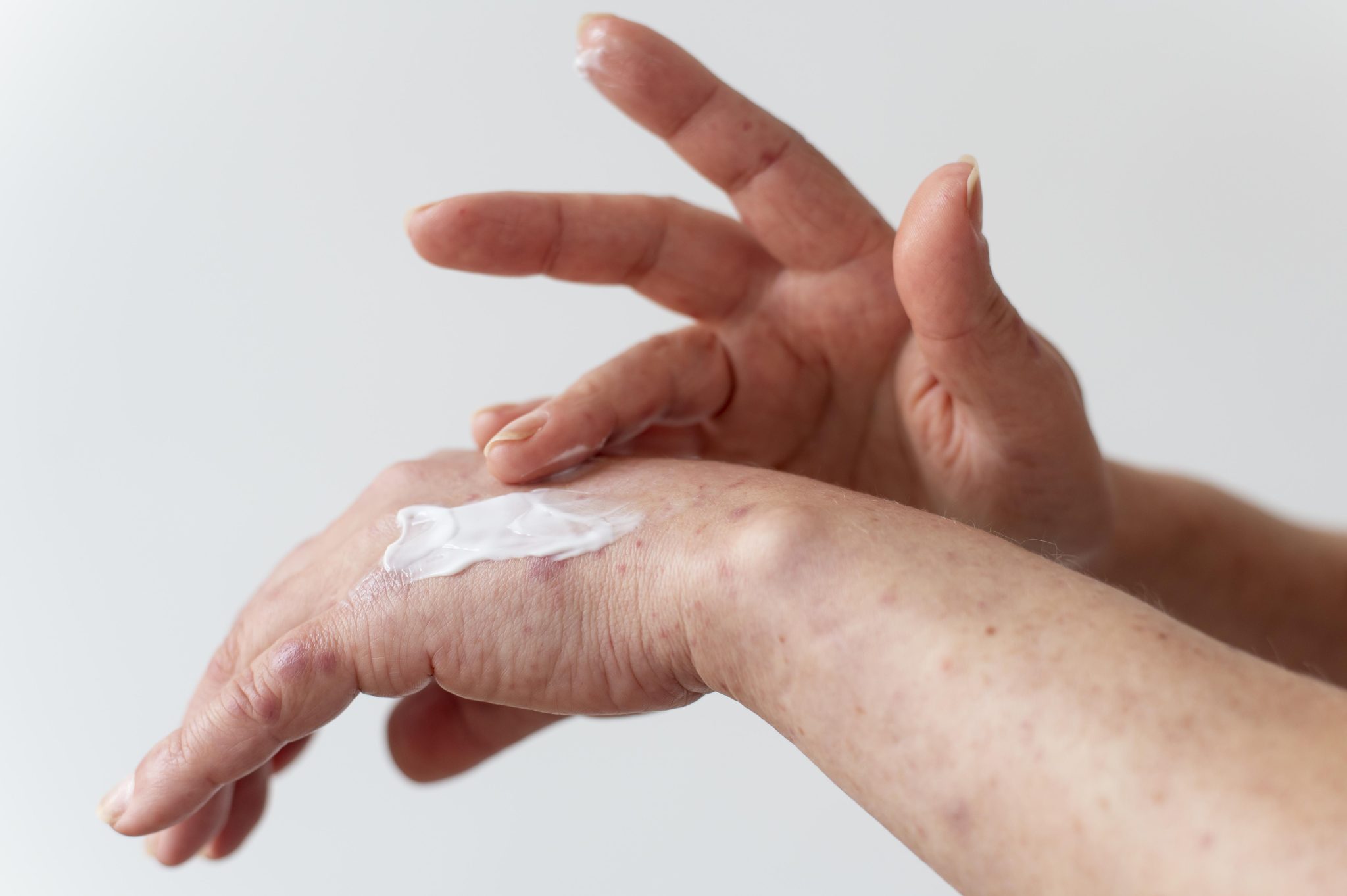
Managing Skin Sensitivity While on Semaglutide
If you experience skin sensitivity while taking semaglutide, there are several ways to manage it effectively. Skin sensitivity can be uncomfortable, but with the right approach, you can reduce its impact on your daily life. Here are some practical tips and recommendations:
Practical Tips for Mitigating Skin Reactions
Hydrate Your Skin
- Keeping your skin well-hydrated can help reduce dryness and irritation. Use a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer daily. Moisturizers create a barrier that protects the skin and helps it retain moisture.
Avoid Harsh Chemicals
- Products containing alcohol, fragrances, and other harsh chemicals can exacerbate skin sensitivity. Opt for skincare products labeled as “hypoallergenic” and “for sensitive skin.” These products are formulated to be gentle and less likely to cause irritation.
Wear Sun Protection
- Sun exposure can worsen skin sensitivity. Always apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 before going outdoors. Choose sunscreens that are designed for sensitive skin to avoid additional irritation.
Use Gentle Cleansers
- Harsh soaps and cleansers can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and sensitivity. Use mild, soap-free cleansers that are pH-balanced and designed for sensitive skin.
Avoid Hot Water
- Hot water can irritate sensitive skin. Use lukewarm water for bathing and washing your face. After washing, gently pat your skin dry with a soft towel instead of rubbing it.
Recommended Skincare Routines and Products
Morning Routine
- Cleanse your face with a gentle cleanser.
- Apply a hydrating, fragrance-free moisturizer.
- Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen.
Evening Routine
- Remove makeup with a gentle, non-irritating remover.
- Cleanse your face with a mild cleanser.
- Apply a soothing, hydrating moisturizer.
Weekly Routine
- Exfoliate gently once a week with a mild exfoliant. Avoid harsh scrubs that can cause micro-tears and irritation.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It’s important to know when to consult a healthcare professional about skin sensitivity. Here are some signs that you should seek medical advice:
Persistent Symptoms
- If your skin sensitivity persists despite following the recommended skincare routine, it’s time to see a doctor. Persistent symptoms may indicate an underlying issue that needs medical attention.
Severe Reactions
- If you experience severe skin reactions such as blistering, severe itching, or extensive redness, seek medical help immediately. These symptoms could indicate a more serious reaction that requires professional treatment.
Signs of Infection
- If you notice signs of infection, such as increased pain, swelling, warmth, or pus, contact your healthcare provider. Skin infections can complicate skin sensitivity and need prompt treatment.
Allergic Reactions
- If you suspect an allergic reaction, stop using the suspected product and consult a doctor. Allergic reactions can escalate quickly and may require medication to manage.
Skincare Products to Consider
Moisturizers
- Look for moisturizers with ingredients like ceramides, hyaluronic acid, and glycerin. These ingredients help to lock in moisture and strengthen the skin barrier.
Cleansers
- Choose soap-free, fragrance-free cleansers. Products like Cetaphil Gentle Skin Cleanser or Vanicream Gentle Facial Cleanser are good options.
Sunscreens
- Mineral-based sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are less likely to irritate sensitive skin. Examples include La Roche-Posay Anthelios Mineral Sunscreen and Neutrogena Sensitive Skin Sunscreen.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Stress Management
- Stress can exacerbate skin sensitivity. Practice stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Healthy Diet
- A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can support skin health. Avoid foods that trigger inflammation, such as processed foods and sugary snacks.
Hydration
- Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated from the inside out. Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day.
Managing skin sensitivity while on semaglutide requires a proactive approach. By following these practical tips, using gentle skincare products, and knowing when to seek medical advice, you can minimize discomfort and maintain healthy skin. Always communicate with your healthcare provider about any side effects you experience to ensure the best possible outcome.
Alternative Medications and Treatments
If you experience skin sensitivity while using semaglutide, you might wonder about other medication options or treatments. It’s essential to know there are alternatives. Let’s explore some of these options, including other medications and non-drug treatments that can help manage diabetes and weight loss effectively.
Other GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, but it’s not the only one available. Here are a few others:
- Liraglutide (Victoza® and Saxenda®): Like semaglutide, liraglutide helps control blood sugar levels and promotes weight loss. It works in a similar way but may have different side effects. Some people who react to semaglutide may not have the same reactions to liraglutide.
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity®): This medication is another GLP-1 receptor agonist. It’s used once a week, similar to semaglutide. Dulaglutide also helps with blood sugar control and weight loss. It’s worth discussing with your doctor if you have skin reactions with semaglutide.
- Exenatide (Byetta® and Bydureon®): Exenatide is another option in this class. It comes in both daily (Byetta®) and weekly (Bydureon®) forms. Some patients find they tolerate exenatide better than semaglutide.
Pros and Cons of Switching Medications
Switching to a different GLP-1 receptor agonist or another type of diabetes medication has its benefits and challenges. Here’s what to consider:
Pros:
- Reduced Side Effects: Switching medications might help reduce skin sensitivity or other side effects you’re experiencing with semaglutide.
- Different Formulations: Some medications come in different forms, such as daily or weekly injections, which might be more convenient for you.
- Personalized Treatment: Finding the right medication can be a trial-and-error process. Switching can help you find the most effective and tolerable option.
Cons:
- Adjustment Period: Your body may need time to adjust to a new medication. This can involve temporary side effects or changes in blood sugar control.
- Monitoring: Switching medications will require regular monitoring to ensure the new treatment is working effectively and safely.
- Insurance Coverage: Some medications may not be covered by your insurance, or they might require a higher co-pay. It’s important to check with your insurance provider.
Non-Pharmacological Alternatives
Medications are not the only way to manage diabetes and support weight loss. Here are some non-drug treatments that can help:
- Dietary Changes: Following a healthy diet is crucial for managing diabetes. Focus on eating balanced meals with plenty of vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Reducing sugar and processed foods can also help control blood sugar levels.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps manage weight and blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week. This can include activities like walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Behavioral Therapy: Working with a therapist can help address behaviors and habits related to eating and exercise. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly effective for making lasting changes.
- Weight Management Programs: Structured programs that include diet, exercise, and behavioral support can be very effective. Programs like Weight Watchers or medically supervised weight loss programs provide comprehensive support.
Holistic Approaches
Some people find relief through holistic or complementary therapies. These approaches can be used alongside traditional treatments but should be discussed with your doctor:
- Acupuncture: Some studies suggest acupuncture can help manage diabetes symptoms and improve overall well-being.
- Herbal Supplements: Certain herbs, like berberine and cinnamon, may help with blood sugar control. Always consult with your doctor before adding supplements, as they can interact with medications.
- Mindfulness and Stress Reduction: Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress, which can improve blood sugar control and overall health.
If you experience skin sensitivity with semaglutide, it’s important to know you have options. Other GLP-1 receptor agonists, different medications, and non-drug treatments can all play a role in managing diabetes and supporting weight loss. Work closely with your healthcare provider to find the best approach for you. Remember, managing diabetes is a personal journey, and finding the right treatment can make all the difference in your health and well-being.
Consulting Your Healthcare Provider
When taking a medication like semaglutide, it’s essential to have an open line of communication with your healthcare provider. Semaglutide is a powerful drug used to manage diabetes and assist with weight loss. However, like any medication, it can have side effects, including skin sensitivity. Talking to your doctor about any changes you notice in your skin is important. This open communication helps ensure that any potential problems are addressed quickly and effectively.
Monitoring and Reporting Side Effects Effectively
Keeping track of your symptoms and sharing this information with your doctor is crucial. Here are some tips on how to monitor and report side effects effectively:
- Keep a Symptom Diary: Write down any skin changes you notice, including when they occur, how long they last, and any factors that might have triggered them. This information can help your doctor understand your situation better.
- Take Photos: If you notice any unusual skin reactions, taking photos can be helpful. This visual record can provide your doctor with a clearer picture of what you’re experiencing.
- Be Honest and Detailed: When discussing your symptoms with your doctor, be as detailed as possible. Explain how the skin reactions affect your daily life and whether they seem to be getting better or worse.
- Follow Up Regularly: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your condition. Even if your symptoms improve, it’s important to keep your doctor informed.
Understanding the Role of Your Healthcare Provider
Your healthcare provider is your partner in managing your health. They have the expertise to guide you through any challenges you might face while taking semaglutide. Here are some ways your doctor can help:
- Adjusting Your Treatment Plan: If you experience significant skin sensitivity, your doctor might adjust your dosage or recommend a different medication. They can also suggest additional treatments to help manage your symptoms.
- Providing Resources and Support: Your doctor can provide resources such as pamphlets, websites, and support groups where you can learn more about managing skin sensitivity.
- Referring to Specialists: In some cases, your doctor might refer you to a dermatologist, a specialist in skin conditions, for further evaluation and treatment.
The Importance of Being Proactive
Being proactive about your health means taking an active role in your treatment. Here are some steps you can take:
- Educate Yourself: Learn about semaglutide and its potential side effects. The more you know, the better prepared you’ll be to manage any issues that arise.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest research and recommendations related to semaglutide and skin sensitivity. This can help you stay ahead of any potential problems.
- Advocate for Yourself: Don’t be afraid to speak up if you have concerns or if something doesn’t seem right. Your health is important, and your healthcare provider is there to help you.
Consulting your healthcare provider about semaglutide and skin sensitivity is a crucial step in ensuring your treatment is both safe and effective. By maintaining open communication, asking the right questions, and being proactive about your health, you can manage any potential side effects and continue to benefit from your medication. Remember, your healthcare provider is your partner in this journey, and working together will help you achieve the best possible outcomes.
Current Research and Future Directions
Semaglutide is a medication that has shown great promise for managing type 2 diabetes and aiding weight loss. However, some users have reported skin sensitivity and reactions as side effects. Researchers are actively studying these reactions to better understand why they happen and how to prevent them.
One of the main areas of research focuses on identifying the exact cause of skin reactions in people using semaglutide. Scientists are looking at different biological processes, such as the immune system’s response to the drug. They are also studying the chemical composition of semaglutide to see if certain ingredients might be causing skin problems. These studies often involve both human trials and laboratory tests.
Potential for New Formulations or Adjunct Therapies
Another exciting area of research is the development of new formulations of semaglutide. Researchers are exploring ways to modify the drug to reduce the risk of skin reactions. For example, they are testing different delivery methods, such as patches or inhalers, which might be less likely to cause skin problems than injections.
In addition to new formulations, scientists are also investigating adjunct therapies. These are treatments that can be used alongside semaglutide to minimize side effects. For example, certain anti-inflammatory creams or antihistamines might help reduce skin reactions. Researchers are conducting clinical trials to determine the effectiveness of these adjunct therapies.
Emerging Trends in Personalized Medicine for Managing Side Effects
Personalized medicine is an exciting trend in healthcare that tailors treatment to the individual patient. This approach can be particularly useful in managing side effects like skin sensitivity. By understanding a patient’s unique genetic makeup, doctors can predict how they might react to certain medications, including semaglutide.
Researchers are developing genetic tests that can identify patients who are more likely to experience skin reactions from semaglutide. These tests can help doctors decide whether semaglutide is the best option for a particular patient or if another medication might be more suitable. Personalized medicine also involves adjusting the dosage and treatment plan based on the patient’s specific needs, which can help minimize side effects.
Future Directions in Research
Looking ahead, there are several promising directions for future research on semaglutide and skin sensitivity. One area of focus is long-term studies that follow patients over several years. These studies can provide valuable insights into how skin reactions develop over time and whether they persist or subside with continued use of the medication.
Another important direction is the investigation of combination therapies. Researchers are exploring whether combining semaglutide with other medications can help reduce the risk of skin reactions. For example, combining semaglutide with medications that have anti-inflammatory properties might help prevent or lessen skin problems.
Importance of Patient Education and Support
Patient education is crucial in managing side effects and ensuring successful treatment with semaglutide. Researchers are developing educational materials and programs to help patients understand the potential side effects of semaglutide and how to manage them. These resources include detailed instructions on how to properly use the medication, tips for skincare, and advice on when to seek medical help.
Support from healthcare providers is also essential. Doctors, nurses, and pharmacists play a key role in monitoring patients for side effects and providing guidance on managing skin reactions. Researchers are studying the best ways to train healthcare providers to support patients using semaglutide.
Current research on semaglutide and skin sensitivity is focused on understanding the causes of skin reactions, developing new formulations and adjunct therapies, and utilizing personalized medicine to tailor treatments. Future research will continue to explore long-term effects, combination therapies, and patient education to improve the safety and effectiveness of semaglutide. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers, patients can successfully manage skin sensitivity and achieve the full benefits of semaglutide.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between semaglutide and skin sensitivity is crucial for patients using this medication. Throughout this article, we have explored various aspects of semaglutide, a medication primarily used to manage diabetes and support weight loss. We’ve delved into its mechanism of action, common uses, and the potential side effects it may cause, particularly focusing on skin sensitivity.
Semaglutide works by mimicking a hormone in your body that regulates blood sugar levels and helps control appetite. While it is highly effective for many patients, it can also lead to side effects, including skin reactions. Skin sensitivity can manifest as rashes, itching, redness, or even more severe reactions in some cases. These symptoms can vary in severity and duration, impacting patients’ quality of life.
We began by defining skin sensitivity and its common symptoms, such as redness, itching, and irritation. These symptoms can arise from various causes, including allergies, environmental factors, or reactions to medications. Skin sensitivity affects daily activities and can cause significant discomfort, making it important to understand its potential triggers.
One key question we addressed is whether semaglutide can cause skin sensitivity. Clinical trials and studies have shown that skin-related side effects, although not very common, can occur in some individuals using semaglutide. Dermatologists and endocrinologists have provided insights into these reactions, helping us understand that while they are not widespread, they are possible.
We also explored the types of skin reactions associated with semaglutide. These can include mild rashes, itching, and redness. In more severe cases, individuals might experience more intense reactions that require medical attention. Understanding the prevalence of these reactions helps set realistic expectations for patients starting semaglutide therapy.
To better grasp why these reactions happen, we examined the biological and chemical mechanisms that might cause skin sensitivity when using semaglutide. The medication can trigger an immune response or inflammation in the body, leading to visible skin reactions. Comparing semaglutide with other medications that cause similar side effects can provide a broader context for these reactions.
Identifying risk factors is another important aspect. Individuals with pre-existing skin conditions, allergies, or a history of sensitivity to medications might be more prone to experiencing skin reactions while on semaglutide. The dosage and duration of treatment can also influence the likelihood of these side effects, as can genetic and environmental factors.
Managing skin sensitivity while using semaglutide involves several practical steps. Patients can adopt skincare routines that include gentle, non-irritating products to soothe the skin. It’s also important to stay hydrated and avoid known triggers that can exacerbate skin sensitivity. Seeking medical advice when reactions occur ensures that patients receive appropriate care and adjustments to their treatment plan if necessary.
For those who experience severe or persistent skin reactions, considering alternative medications might be an option. Other GLP-1 receptor agonists might offer similar benefits with a lower risk of skin sensitivity. Weighing the pros and cons of switching medications should be done in consultation with a healthcare provider to ensure continued effective management of diabetes or weight loss.
Open communication with healthcare providers is vital. Patients should feel comfortable discussing any side effects they experience, including skin sensitivity. Asking the right questions and reporting symptoms accurately helps doctors make informed decisions about treatment adjustments. Regular monitoring and proactive management can prevent minor side effects from becoming major issues.
Current research on semaglutide and its side effects is ongoing. Scientists are continually exploring new formulations and adjunct therapies to minimize adverse reactions. Personalized medicine, which tailors treatment plans to individual patient needs, is an emerging trend that holds promise for better managing side effects, including skin sensitivity.
In conclusion, understanding and managing skin sensitivity in patients using semaglutide is essential for improving their overall treatment experience. By being aware of potential side effects, identifying risk factors, and adopting effective management strategies, patients can continue to benefit from semaglutide’s therapeutic effects while minimizing discomfort. Ongoing research and patient education will further enhance our ability to address and mitigate these side effects, ensuring a better quality of life for those on this medication.
Research Citations
Aroda VR, Rosenstock J, Terauchi Y, et al. Effect and safety of semaglutide compared with dulaglutide and exenatide ER in subjects with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 10). Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21(5):1008-1018. [PubMed]
Capehorn MS, Catarig AM, Furberg JK, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide 1.0 mg vs once-daily liraglutide 1.2 mg as add-on to 1-3 oral antidiabetic drugs in subjects with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 10). Diabetes Metab. 2019;45(10):872-880. [PubMed]
Davies MJ, Bain SC, Atkin SL, et al. Efficacy and safety of semaglutide versus dulaglutide as add-on to metformin and/or sulfonylurea in subjects with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 7): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, phase 3b trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6(4):275-286. [PubMed]
Davies MJ, D’Alessio DA, Fradkin J, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. 2018;61(12):2461-2498. [PubMed]
Dungan KM, Povedano ST, Forst T, et al. Once-weekly dulaglutide versus once-daily liraglutide in metformin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes (AWARD-6): a randomised, open-label, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2014;384(9951):1349-1357. [PubMed]
Gardner CD, Trepanowski JF, Del Gobbo LC, et al. Effect of low-fat vs low-carbohydrate diet on 12-month weight loss in overweight adults and the association with genotype pattern or insulin secretion: the DIETFITS randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018;319(7):667-679. [PubMed]
Hathaway CK, Agarwal N, Planas LG, et al. Impact of GLP-1 receptor agonists on blood pressure, heart rate and hypertension among patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21(11):2467-2475. [PubMed]
Kalra S, Jena BN, Yeravdekar R. Emotional and psychological needs of people with diabetes. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2018;22(5):696-704. [PubMed]
Kaplan W, Laing R. Priority medicines for Europe and the world. “A public health approach to innovation”. WHO Publ. 2004;104-129.
Lau J, Bloch P, Schaffer L, et al. Discovery of the once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogue semaglutide. J Med Chem. 2015;58(18):7370-7380. [PubMed]
Questions and Answers: Semaglutide and Skin Sentivity
Yes, semaglutide can cause skin sensitivity in some individuals. This may present as redness, itching, or irritation at the injection site.
Common skin reactions include redness, itching, swelling, and bruising at the injection site. These are typically mild and resolve on their own.
To reduce skin sensitivity, ensure you rotate the injection sites, use a clean needle for each injection, and avoid injecting into areas with scars or moles. Applying a cold pack to the area before and after the injection can also help.
While a mild rash can occur at the injection site, a widespread or severe rash is uncommon and should be reported to a healthcare provider, as it may indicate an allergic reaction.
There is no strong evidence that semaglutide directly causes eczema or worsens it. However, if you have a history of eczema and notice a flare-up, it’s important to consult your doctor.
If you experience severe skin reactions such as blistering, severe redness, or swelling, you should contact your healthcare provider immediately. These could be signs of an allergic reaction.
Long-term skin issues are rare with semaglutide use. Most skin reactions are mild and temporary. However, if persistent skin problems occur, it’s advisable to discuss them with your healthcare provider.
Yes, using topical creams such as hydrocortisone or antihistamines can help manage mild skin irritation. However, it’s best to consult your healthcare provider before using any medication.
Skin sensitivity can vary depending on the injection site. Common areas include the abdomen, thigh, and upper arm. Rotating injection sites can help minimize irritation
Mild skin sensitivity is common and usually not a reason to stop using semaglutide. However, if you experience severe or persistent skin reactions, consult your healthcare provider for guidance.

Dr. Kevin Kargman
Dr. Kevin J. Kargman is a pediatrician in Sewell, New Jersey and is affiliated with multiple hospitals in the area, including Cooper University Health Care-Camden and Jefferson Health-Stratford, Cherry Hill and Washington Township. (Learn More)