Table of Contents
Introduction
Semaglutide is a medication that has become quite popular in recent years, especially for treating type 2 diabetes and obesity. It works by helping to control blood sugar levels and by reducing appetite, leading to weight loss. This medication is usually given as an injection once a week, and it can be very effective for people who need help managing their diabetes or losing weight. However, like all medications, semaglutide can have side effects. One side effect that some people worry about is fever.
Understanding the side effects of a medication is important for both patients and healthcare providers. When people start a new medication, they often have questions and concerns about what might happen. Will it cause any unpleasant symptoms? Could it make them feel worse before they start to feel better? These are important questions that need clear and accurate answers.
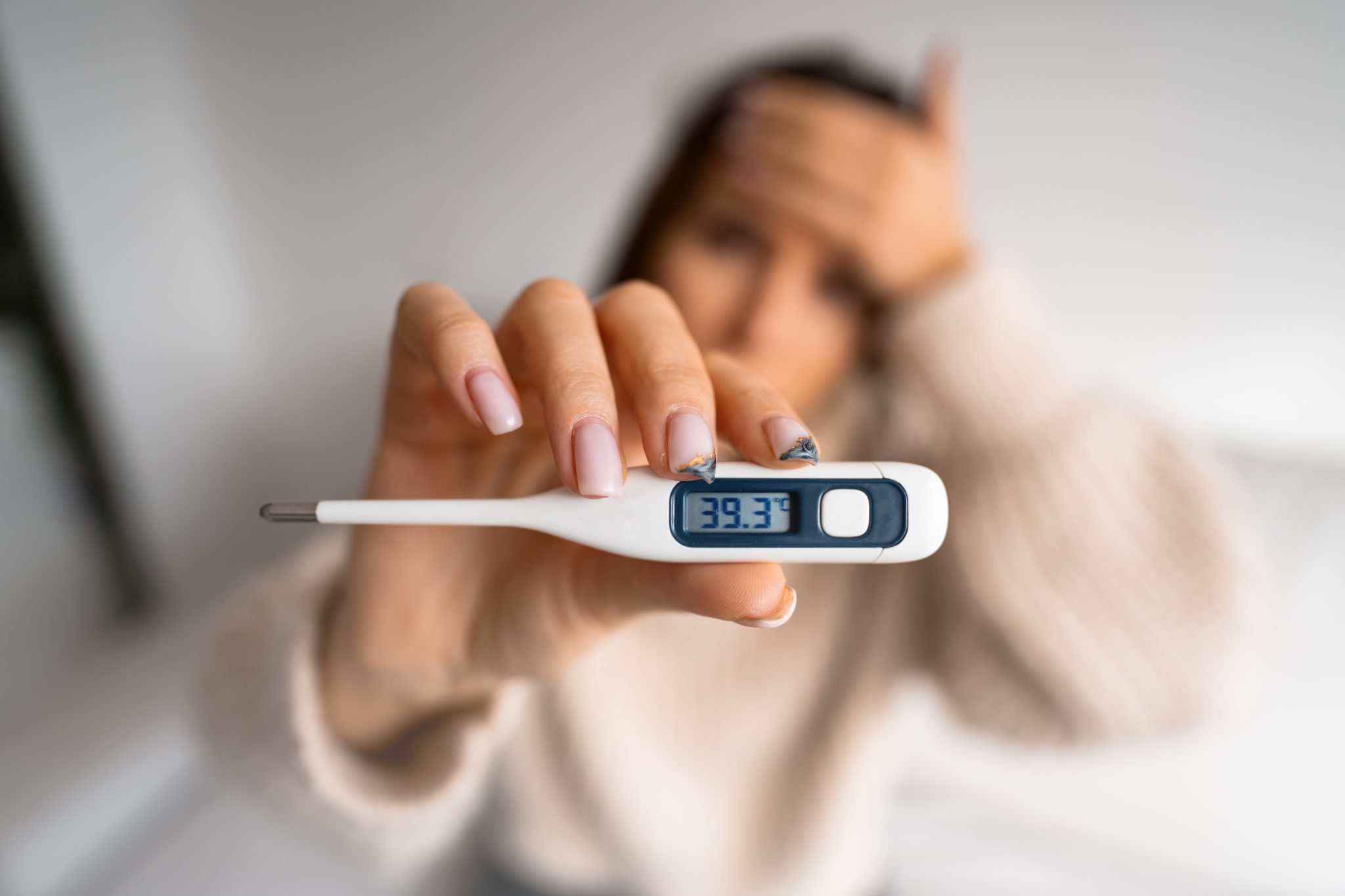
Fever is one symptom that can be concerning. A fever is when your body temperature goes higher than normal, usually above 100.4°F (38°C). It can be a sign that your body is fighting an infection, but it can also be caused by other things, including some medications. When people who are taking semaglutide experience a fever, they might wonder if the medication is the cause. This article will explore whether semaglutide can cause fever and what you need to know if you experience this symptom.
First, we will look at what semaglutide is and how it works. This will help us understand why it might cause certain side effects. Semaglutide is a type of drug called a GLP-1 receptor agonist. It works by mimicking a hormone in your body that helps to control blood sugar levels. This hormone, called GLP-1, increases the amount of insulin your body makes after you eat. Insulin is important because it helps to lower blood sugar levels. By increasing insulin, semaglutide helps to keep blood sugar levels under control.
Semaglutide also helps with weight loss by making you feel less hungry. It does this by acting on the brain, specifically the parts that control appetite. When you feel less hungry, you eat less, and over time this can lead to weight loss. This is why semaglutide is often prescribed not only for diabetes but also for obesity.
Next, we will discuss the common side effects of semaglutide. Like many medications, semaglutide can cause side effects. The most common ones are usually related to the digestive system. People might feel nauseous or experience vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation. These side effects are usually mild and tend to go away after a few days or weeks as the body gets used to the medication.
However, some people worry about less common side effects, like fever. It is important to know whether fever is a side effect of semaglutide and how common it is. In the following sections, we will look at the evidence from clinical trials and patient reports to see if there is a link between semaglutide and fever.
We will also explore why semaglutide might cause fever. Fever can be a sign that your body is reacting to something new, like a medication. It might also happen if there is an infection or another underlying condition. Understanding the possible reasons behind a fever can help you know what to do if you experience this symptom.
If you are taking semaglutide and develop a fever, it is important to know how to manage it. We will provide some guidelines on what to do if you have a fever, including when to seek medical advice. It is always better to be safe and talk to your doctor if you are unsure about any symptoms you are experiencing.
Finally, we will discuss the importance of reporting side effects. If you experience any unusual symptoms while taking semaglutide, you should let your healthcare provider know. They can help determine if the medication is the cause and decide the best course of action. Reporting side effects also helps to improve our understanding of medications and their safety.
By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of whether semaglutide can cause fever and what to do if you experience this side effect. This information will help you feel more confident in managing your health while using semaglutide.
What is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes and, more recently, obesity. It belongs to a class of drugs called GLP-1 receptor agonists. These drugs help the body manage blood sugar levels more effectively. They also help with weight loss by reducing appetite and making you feel full sooner. Understanding how semaglutide works can help you see why it’s used and what to expect when taking it.
How Semaglutide Works
Semaglutide mimics a hormone in the body called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1). This hormone is naturally released in your intestines when you eat. It has several important effects:
- Increases Insulin Production: After you eat, GLP-1 helps your pancreas release insulin. Insulin is a hormone that lowers blood sugar by helping your cells take in glucose (sugar) from your blood.
- Decreases Glucagon Production: Glucagon is another hormone produced by the pancreas. It raises blood sugar by causing the liver to release stored glucose. GLP-1 reduces the amount of glucagon your body makes, which helps keep blood sugar levels lower.
- Slows Down Stomach Emptying: GLP-1 slows the rate at which food leaves your stomach. This makes you feel full longer and reduces how much you eat.
- Reduces Appetite: GLP-1 acts on the brain to decrease hunger. This helps people eat less and lose weight.
Uses of Semaglutide
Semaglutide is primarily prescribed for two main conditions:
- Type 2 Diabetes: In people with type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use insulin properly. This leads to high blood sugar levels, which can cause serious health problems over time. Semaglutide helps lower blood sugar levels, which reduces the risk of complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
- Obesity: Many people with obesity have difficulty losing weight through diet and exercise alone. Semaglutide can help by reducing appetite and increasing feelings of fullness. This makes it easier to eat less and lose weight.
Forms and Dosages
Semaglutide is available in different forms and dosages:
- Injectable Form: This is the most common form of semaglutide. It’s usually injected once a week using a pre-filled pen. The injection is simple and can be done at home.
- Oral Form: A newer form of semaglutide is available as a daily pill. This can be a more convenient option for some people, though it may not be as effective as the injectable form for everyone.
Benefits of Semaglutide
Semaglutide offers several benefits:
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: For people with type 2 diabetes, semaglutide can significantly lower blood sugar levels. This helps prevent complications and improves overall health.
- Weight Loss: Semaglutide can help people with obesity lose a significant amount of weight. This can lead to improved health and a lower risk of weight-related diseases.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: Studies have shown that semaglutide can reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems in people with type 2 diabetes.
Potential Side Effects
Like all medications, semaglutide can cause side effects. Common side effects include:
- Nausea: This is the most common side effect. It usually improves over time as your body gets used to the medication.
- Diarrhea: Some people may experience diarrhea, which can be managed with dietary changes or over-the-counter medications.
- Vomiting: This is less common but can occur, especially when first starting the medication.
- Decreased Appetite: While this can help with weight loss, it may be uncomfortable for some people.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
In rare cases, semaglutide can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Pancreatitis: This is an inflammation of the pancreas. Symptoms include severe stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. If you experience these symptoms, you should contact your doctor immediately.
- Thyroid Tumors: Studies in animals have shown an increased risk of thyroid tumors with semaglutide. However, it’s not clear if this risk applies to humans. Your doctor can discuss this with you in more detail.
Who Should Not Take Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is not suitable for everyone. You should not take it if you:
- Have a History of Pancreatitis: If you’ve had pancreatitis before, semaglutide may increase the risk of it happening again.
- Have Certain Thyroid Conditions: If you or a family member have had medullary thyroid carcinoma or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2, you should avoid semaglutide.
- Are Pregnant or Breastfeeding: The effects of semaglutide on an unborn baby or a nursing infant are not well known. If you’re pregnant or breastfeeding, talk to your doctor about other options.
Semaglutide is a powerful medication that can help manage type 2 diabetes and aid in weight loss. By mimicking the GLP-1 hormone, it helps control blood sugar levels, reduces appetite, and promotes weight loss. While it has many benefits, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider. Understanding how semaglutide works can help you use it safely and effectively to improve your health.
Common Side Effects of Semaglutide
Semaglutide is a medication used to help manage type 2 diabetes and obesity. It works by mimicking a hormone in the body that helps control blood sugar and appetite. Like any medication, semaglutide can cause side effects. Knowing these side effects helps patients and healthcare providers manage them better.
Gastrointestinal Issues
One of the most common side effects of semaglutide involves the digestive system. Many patients report nausea, which can range from mild to severe. This nausea usually happens when starting the medication and often gets better over time as the body adjusts. Some people may also experience vomiting, which can be more distressing. To help reduce these symptoms, doctors often recommend starting with a lower dose of semaglutide and gradually increasing it.
In addition to nausea and vomiting, semaglutide can cause diarrhea or constipation. Diarrhea is when you have loose or watery stools, and it can lead to dehydration if it is severe. Constipation is the opposite, where you have trouble having regular bowel movements. Both conditions can be uncomfortable but are usually manageable with dietary changes and staying hydrated.
Decreased Appetite
Semaglutide is designed to help people feel full faster and stay full longer. This effect helps with weight loss, but it can also lead to decreased appetite. While this is often a desired effect for those trying to lose weight, it can sometimes lead to unintentional undereating. Patients need to balance their food intake to ensure they get enough nutrients.
Injection Site Reactions
Semaglutide is usually given as an injection under the skin. Some patients may experience reactions at the injection site. These reactions can include redness, itching, or swelling where the injection was given. These symptoms are typically mild and go away on their own. Using different injection sites each time can help reduce these reactions.
Headache
Headaches are another reported side effect of semaglutide. These headaches can range from mild to moderate in intensity. Drinking plenty of water and resting can often help alleviate headache symptoms. If headaches persist or become severe, it is important to discuss them with a healthcare provider.
Fatigue
Some patients may feel unusually tired or fatigued while taking semaglutide. This feeling of tiredness can affect daily activities and overall quality of life. Fatigue can have many causes, so it is important to consider whether it might be related to semaglutide or other factors like diet, sleep, and stress.
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
When used with other diabetes medications, especially insulin or sulfonylureas, semaglutide can increase the risk of low blood sugar, also known as hypoglycemia. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include dizziness, sweating, confusion, and shakiness. It is important for patients to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and be aware of these symptoms. Having a quick source of sugar, like glucose tablets or juice, can help treat low blood sugar.
Pancreatitis
Although rare, semaglutide can cause inflammation of the pancreas, known as pancreatitis. Symptoms of pancreatitis include severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. If a patient experiences these symptoms, they should seek medical attention immediately. Pancreatitis is a serious condition and requires prompt treatment.
Kidney Problems
In some cases, semaglutide can affect kidney function. This is more likely to occur in patients who already have kidney issues. Symptoms of kidney problems can include swelling in the legs and feet, fatigue, and changes in urine output. Regular monitoring of kidney function through blood tests can help detect any issues early.
Allergic Reactions
Although rare, some people may experience an allergic reaction to semaglutide. Signs of an allergic reaction include rash, itching, swelling, severe dizziness, and trouble breathing. An allergic reaction can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Gallbladder Issues
Semaglutide can increase the risk of gallbladder problems, including gallstones. Gallstones can cause pain in the abdomen, nausea, and vomiting. If a patient experiences symptoms of gallstones, they should contact their healthcare provider.
Understanding the common side effects of semaglutide is crucial for patients and healthcare providers. While many of these side effects are manageable, some can be serious and require medical attention. Regular communication with a healthcare provider helps ensure that any side effects are promptly addressed and managed effectively. This proactive approach helps patients continue their treatment with semaglutide safely and effectively.

Can Semaglutide Cause Fever?
Fever is a common symptom that can occur due to various reasons, including infections, inflammation, and reactions to medications. For individuals using semaglutide, a medication primarily used for managing type 2 diabetes and aiding in weight loss, it is important to understand whether fever is a potential side effect.
Clinical Trial Data on Fever
Clinical trials are research studies conducted to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of new medications. These trials involve a large number of participants who take the medication under controlled conditions while being closely monitored for any adverse effects. Semaglutide has undergone extensive clinical trials to determine its safety profile.
In the clinical trials for semaglutide, researchers documented all side effects experienced by participants. Fever was reported by some individuals, but it was not among the most common side effects. The most frequently reported side effects included nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. While fever was noted in a small number of cases, it was not a prevalent or significant finding in the overall data.
Patient Reports and Real-World Data
In addition to clinical trials, real-world data from patients using semaglutide also provide valuable insights into its side effects. Patients who experience side effects while using the medication often report them to their healthcare providers or through post-marketing surveillance programs. This information helps build a more comprehensive understanding of the medication’s safety profile.
Real-world data have shown that some patients do report experiencing fever while using semaglutide. However, it is important to note that these reports are relatively rare. The occurrence of fever is not high enough to be considered a common or expected side effect of the medication.
Mechanisms Behind Fever Induction
Understanding the potential mechanisms by which semaglutide could cause fever requires a look at how the medication interacts with the body. Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. It works by mimicking the action of a natural hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels and appetite.
When a medication like semaglutide is introduced into the body, it can trigger various immune responses. The immune system may recognize the medication as a foreign substance, leading to the release of chemicals called cytokines. These cytokines can cause inflammation and, in some cases, result in fever as the body attempts to fight off what it perceives as an intruder.
Incidence Rate of Fever
While it is clear that fever can occur in some patients using semaglutide, the incidence rate remains low. In clinical trials and real-world data, the percentage of patients reporting fever is small compared to the overall population using the medication. This suggests that while fever is possible, it is not a common reaction to semaglutide.
Healthcare providers typically consider the overall benefit-risk profile of a medication when prescribing it to patients. For semaglutide, the benefits of improved blood sugar control and weight loss often outweigh the relatively low risk of developing a fever.
Monitoring and Reporting Fever
For patients using semaglutide, it is important to monitor for any unusual symptoms, including fever. If a patient experiences a fever while taking semaglutide, they should report it to their healthcare provider. The provider can assess the situation to determine if the fever is related to the medication or if there might be another underlying cause, such as an infection.
In most cases, fever related to medication use is mild and can be managed with supportive care, such as rest, hydration, and over-the-counter fever reducers like acetaminophen. However, if the fever is high, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, medical evaluation is necessary to rule out serious conditions.
While semaglutide can cause fever in some patients, it is not a common side effect. The incidence rate of fever is low, and when it does occur, it is typically mild and manageable. Patients should stay informed about potential side effects and communicate with their healthcare providers to ensure safe and effective use of semaglutide. By understanding the potential for fever and monitoring their health, patients can use semaglutide with confidence in its benefits for managing type 2 diabetes and supporting weight loss.
Mechanisms Behind Fever Induction
Fever is the body’s natural response to many things, including infections, inflammation, and sometimes medications. When you take medication, it can affect your body in different ways. One possible side effect is fever. But how exactly can a medication like semaglutide cause fever? Let’s explore this in detail.
The Body’s Immune Response
When your body detects something unusual, like an infection or a new medication, it can trigger an immune response. This is your body’s way of protecting itself. Part of this response can include raising your body temperature, which we recognize as fever. Fever helps your body fight off infections by making it harder for bacteria and viruses to survive.
Inflammation and Fever
Inflammation is another process that can lead to fever. When your body becomes inflamed, it releases chemicals called cytokines. These cytokines tell your brain to raise your body temperature. Inflammation can happen for many reasons, including as a reaction to medications. Even though semaglutide is designed to help manage blood sugar and promote weight loss, it can still cause some inflammation as your body adjusts to it.
Direct Effects of Semaglutide
Semaglutide works by mimicking a hormone in your body called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1). This hormone helps control your blood sugar levels by increasing insulin production and slowing down how fast your stomach empties. While this is great for managing diabetes and promoting weight loss, it also means semaglutide interacts with various systems in your body.
When semaglutide interacts with your body, it can sometimes cause unexpected side effects, including fever. This can happen because of the way your body responds to the medication. For example, your immune system might recognize semaglutide as something new and react by causing a slight fever.
Allergic Reactions
In rare cases, fever can be a sign of an allergic reaction to semaglutide. Allergic reactions happen when your immune system overreacts to a substance it sees as harmful, even if it’s not. If you’re allergic to semaglutide, your body might respond with symptoms like rash, itching, and fever. This type of fever usually happens soon after taking the medication and can be more severe than other types of drug-induced fever.
Drug-Induced Hyperthermia
Another way medications can cause fever is through a process called drug-induced hyperthermia. This is a rare but serious condition where a drug causes your body to overheat. While it’s uncommon with semaglutide, it’s important to be aware of this possibility. Symptoms of drug-induced hyperthermia include a very high fever, muscle rigidity, and confusion. If you experience these symptoms, you should seek medical help right away.
Your Body Adjusting to Semaglutide
Sometimes, fever can occur as your body gets used to a new medication. This is often called a “transient” fever, meaning it doesn’t last long. When you start taking semaglutide, your body might react with a slight fever as it adjusts to the new drug. This type of fever is usually mild and goes away on its own after a few days or weeks.
Monitoring and Managing Fever
If you develop a fever while taking semaglutide, it’s important to monitor your symptoms. Keep track of your temperature and any other symptoms you experience. Most fevers caused by medications are mild and don’t last long. However, if your fever is high, lasts more than a few days, or you have other concerning symptoms, you should contact your healthcare provider.
Fever can be a side effect of medications like semaglutide for several reasons. It can be part of your body’s immune response, a reaction to inflammation, or even an allergic reaction. Understanding these mechanisms can help you manage any side effects you experience and know when to seek medical advice. Always keep your healthcare provider informed about any side effects, including fever, to ensure you receive the best care possible.
Clinical Studies and Research Findings
Clinical studies and research are essential for understanding how medications like semaglutide affect patients. They provide valuable information about the benefits and risks, including potential side effects like fever. In this section, we will review the findings from various clinical studies and research to better understand the relationship between semaglutide and fever.
Clinical Trials and Fever Incidence
Semaglutide has undergone extensive clinical testing to evaluate its safety and effectiveness. During these trials, researchers monitored participants for any side effects, including fever. While fever is not one of the most common side effects of semaglutide, it has been reported in some cases.
One significant study involved patients with type 2 diabetes who were treated with semaglutide. The trial aimed to determine the medication’s efficacy in controlling blood sugar levels. Researchers found that fever was reported by a small percentage of participants. The incidence of fever was low, typically affecting less than 1% of those taking semaglutide. However, it is important to note that even though fever was rare, it still occurred and was documented as a potential side effect.
Understanding the Data
The data from clinical trials provide insight into the likelihood of experiencing fever while taking semaglutide. The low incidence rate suggests that fever is not a common side effect. However, the fact that it has been reported means that patients and healthcare providers should be aware of this possibility.
In addition to fever, clinical trials have also reported other side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These side effects are more common and are typically related to the gastrointestinal system. Understanding the full spectrum of side effects helps patients make informed decisions about their treatment.
Research Findings on Fever and Semaglutide
Beyond clinical trials, additional research has been conducted to explore the relationship between semaglutide and fever. Some studies have looked at how the body’s immune response to the medication might contribute to fever. These studies suggest that fever could result from the body’s reaction to semaglutide, particularly in the early stages of treatment.
Research also indicates that individual factors, such as a person’s overall health, other medications they are taking, and their unique biological responses, can influence the likelihood of experiencing side effects like fever. For example, patients with weakened immune systems or those taking multiple medications may be more susceptible to fever when starting semaglutide.
Comparative Studies
Comparative studies have also been conducted to evaluate the side effects of semaglutide against other medications used for similar purposes. These studies help to contextualize the risk of fever in relation to other treatments. For instance, when comparing semaglutide with other GLP-1 receptor agonists (a class of drugs to which semaglutide belongs), the incidence of fever is consistently low across the board.
One comparative study found that the rate of fever in patients taking semaglutide was similar to those taking other GLP-1 receptor agonists. This finding reinforces the idea that while fever is a possible side effect, it is not unique to semaglutide and occurs at a comparable rate in other treatments.
Real-World Evidence
Real-world evidence complements clinical trial data by providing insights from everyday use of semaglutide outside the controlled environment of a clinical trial. Post-marketing surveillance and patient registries collect data on side effects experienced by a larger and more diverse patient population.
Real-world data have shown that the incidence of fever remains low among semaglutide users. This information is valuable as it reflects the experiences of patients in real-life settings, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the medication’s safety profile.
Clinical studies and research findings indicate that fever is a rare but possible side effect of semaglutide. While the incidence rate is low, it is important for patients and healthcare providers to be aware of this potential risk. Ongoing research and real-world evidence continue to enhance our understanding of semaglutide’s safety and help ensure that patients receive the best possible care. By staying informed about potential side effects, patients can work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their treatment effectively and safely.

Identifying and Managing Fever While on Semaglutide
Fever is a common symptom that can be caused by many different factors, including infections, inflammatory conditions, and reactions to medications. If you are taking semaglutide and develop a fever, it is important to understand how to identify and manage it effectively. Here, we will discuss how to recognize fever, what steps to take when you have a fever, and when to seek medical advice.
Identifying Fever
Fever is characterized by an increase in body temperature above the normal range. The average normal body temperature is about 98.6°F (37°C), but it can vary slightly from person to person. Fever is generally considered to be a body temperature of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher.
Common signs and symptoms of fever include:
- Feeling hot to the touch
- Sweating
- Chills or shivering
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Weakness
- Dehydration
- Loss of appetite
It is important to measure your body temperature accurately to confirm whether you have a fever. You can use a digital thermometer to take your temperature orally, rectally, or under the armpit.
Managing Mild to Moderate Fever
If you have a mild to moderate fever while taking semaglutide, there are several steps you can take to manage it at home:
Rest
Getting plenty of rest is crucial when you have a fever. Your body needs extra energy to fight off whatever is causing the fever, so make sure to take it easy and avoid strenuous activities.
Stay Hydrated
Fever can lead to dehydration, so it is important to drink plenty of fluids. Water, clear broths, and electrolyte solutions are good options. Avoid drinks that can dehydrate you, such as alcohol and caffeinated beverages.
Use Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) can help reduce fever and relieve discomfort. Be sure to follow the dosage instructions on the label and avoid taking more than the recommended amount.
Keep Cool
To help lower your body temperature, wear lightweight clothing and use a light blanket if you feel cold. You can also use a cool, damp washcloth on your forehead or take a lukewarm bath to help reduce your fever.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While mild to moderate fever can often be managed at home, there are times when it is important to seek medical advice. Contact your healthcare provider if:
- Your fever lasts for more than three days.
- Your fever is 103°F (39.4°C) or higher.
- You have severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, confusion, persistent vomiting, or a severe headache.
- You have a pre-existing health condition that puts you at higher risk for complications from fever.
- You suspect your fever might be a reaction to semaglutide.
Communicating with Your Healthcare Provider
If you need to contact your healthcare provider about your fever, be prepared to provide detailed information. This can help your provider determine the cause of your fever and the best course of action. Information to provide includes:
- Your current body temperature and how you measured it.
- How long you have had the fever.
- Any other symptoms you are experiencing.
- Any other medications or supplements you are taking.
- Any recent changes in your health or exposure to illnesses.
Your healthcare provider may recommend additional tests or evaluations to determine the cause of your fever. In some cases, they may suggest adjusting your semaglutide dosage or switching to a different medication.
Monitoring Your Condition
If you have a fever while taking semaglutide, it is important to monitor your condition closely. Keep track of your body temperature and any other symptoms you experience. This information can be helpful for your healthcare provider if your fever does not improve or if you develop new symptoms.
By understanding how to identify and manage fever, you can take steps to ensure your health and safety while using semaglutide. Always communicate with your healthcare provider about any concerns or side effects you experience, and follow their recommendations for managing your condition.
Differentiating Fever Caused by Semaglutide from Other Causes
When someone experiences a fever while taking semaglutide, it’s essential to figure out if the medication is the cause or if there is another reason. This can help in making the right decisions for treatment and care. Here’s a detailed look at how to differentiate fever caused by semaglutide from other causes.
Understanding Fever and Its Causes
Fever is a rise in body temperature above the normal range, usually caused by an infection, inflammation, or other medical conditions. Common symptoms include feeling hot or cold, sweating, headache, and fatigue. While fever is often a sign that the body is fighting an infection, it can also be a side effect of some medications, including semaglutide.
How Semaglutide Might Cause Fever
Semaglutide, like other medications, can cause side effects. Fever, though not very common, has been reported by some patients. This could happen due to the body’s immune response to the medication. When the immune system reacts, it can release chemicals that cause the body temperature to rise. However, it’s important to remember that fever is not a typical side effect of semaglutide.
Checking for Other Causes of Fever
Before assuming that semaglutide is causing the fever, it’s crucial to rule out other common causes. These include:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections are the most common causes of fever. Common infections that might cause fever include the flu, cold, urinary tract infections, and pneumonia.
- Other Medications: Some medications, especially antibiotics, anti-seizure drugs, and some blood pressure medications, can also cause fever as a side effect.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as autoimmune diseases, cancer, and inflammatory disorders can cause fever.
- Recent Vaccinations: Some vaccines can cause a mild fever as the body builds immunity.
Steps to Determine the Cause of Fever
To figure out if semaglutide is the cause of the fever, follow these steps:
- Review Medical History: Check the patient’s medical history for any other medications they are taking or any known medical conditions that could cause fever.
- Assess Timing: Note when the fever started. If the fever began soon after starting semaglutide, it might be related. However, if the fever started much later, it might be due to another cause.
- Check for Infection: Look for signs of infection such as a cough, sore throat, pain during urination, or other symptoms that might suggest an infection.
- Evaluate Other Symptoms: Consider other symptoms that the patient might be experiencing. If there are symptoms like a rash, joint pain, or swelling, it could suggest another condition rather than a side effect of semaglutide.
Consulting Healthcare Providers
If you suspect that semaglutide might be causing the fever, consult a healthcare provider. They can perform tests to rule out infections or other medical conditions. Blood tests, urine tests, and imaging studies might be needed to pinpoint the cause of the fever.
Adjusting Medication
If the healthcare provider suspects that semaglutide is the cause, they might suggest adjusting the dose or switching to a different medication. Do not stop taking semaglutide without consulting a healthcare provider, as this could affect blood sugar control.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
After any adjustments, it’s essential to monitor the patient closely. Keep track of their temperature and any other symptoms. Regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider are necessary to ensure that the fever resolves and that blood sugar levels remain stable.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
In some cases, a fever can be a sign of a severe reaction. Seek immediate medical attention if the patient experiences:
- A very high fever (above 103°F or 39.4°C)
- Difficulty breathing
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck
- Persistent vomiting or diarrhea
- Confusion or seizures
Differentiating the cause of fever in patients taking semaglutide requires careful evaluation of all potential factors. By systematically ruling out other causes and consulting healthcare providers, patients and caregivers can ensure that they receive appropriate care and treatment. Always stay vigilant and communicate openly with healthcare providers about any side effects or concerns.
Reporting Side Effects and Seeking Medical Advice
When taking any medication, including semaglutide, it is important to keep track of how your body responds. This includes noting any side effects, such as fever. Reporting side effects helps doctors understand how different patients react to the medication. It also helps improve the safety of the drug for everyone who uses it.
Steps to Report Side Effects
If you experience a fever or any other side effect while taking semaglutide, follow these steps to report it:
- Contact Your Doctor: The first and most important step is to call your doctor. Your doctor can help determine if the fever is related to semaglutide or another cause. They can also provide advice on how to manage the fever and whether you should continue taking the medication.
- Keep a Symptom Diary: Write down your symptoms, including when they started, how severe they are, and any other details that might be relevant. This information can be very helpful to your doctor in diagnosing the cause of the fever and deciding on the best course of action.
- Use Official Reporting Channels: In addition to talking to your doctor, you can report side effects to regulatory agencies. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has a program called MedWatch where you can report any adverse effects. You can fill out an online form on the FDA’s website or call their toll-free number to report your symptoms.
- Inform the Manufacturer: You can also report side effects directly to the company that makes semaglutide. The contact information is usually provided in the medication’s packaging or on the company’s website.
Why Reporting is Important
Reporting side effects is crucial for several reasons:
- Improving Drug Safety: When side effects are reported, regulatory agencies like the FDA collect the information and monitor for patterns or trends. If a particular side effect is reported frequently, it may lead to further investigation and action, such as updating the drug’s safety information or issuing warnings to healthcare providers and patients.
- Helping Other Patients: Your report can help other patients who are taking the same medication. By sharing your experience, you contribute to a larger pool of data that can help doctors and patients make more informed decisions about their treatment options.
- Enhancing Your Own Care: Reporting side effects promptly can lead to better care for yourself. Your doctor can adjust your treatment plan based on the side effects you report, ensuring that you receive the most effective and safest care possible.
Seeking Medical Advice for Fever
If you develop a fever while taking semaglutide, it is important to seek medical advice. Here are some tips on when and how to get help:
- When to Seek Immediate Help: If your fever is very high (above 103°F or 39.4°C), if it lasts for more than a few days, or if you have other serious symptoms like difficulty breathing, chest pain, or confusion, seek medical help right away. These could be signs of a serious condition that needs immediate attention.
- Routine Medical Advice: For milder fevers, call your doctor to discuss your symptoms. They can provide guidance on how to manage the fever at home, such as staying hydrated, resting, and taking over-the-counter fever reducers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen, if appropriate.
- Regular Check-Ups: Make sure to attend all scheduled appointments with your doctor. During these visits, discuss any side effects you have experienced, including fever. Regular check-ups are an opportunity to review your treatment plan and make any necessary adjustments.
How to Prepare for Your Doctor’s Visit
Before your visit, gather the following information to share with your doctor:
- Symptom Diary: Bring your symptom diary with detailed notes about your fever and any other side effects.
- Medication List: Make a list of all the medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. This helps your doctor identify any potential interactions that might be causing the fever.
- Questions: Write down any questions you have about your symptoms or treatment. This ensures you don’t forget to ask anything important during your visit.
Reporting side effects like fever when taking semaglutide is vital for your safety and the safety of others. It helps healthcare providers and regulatory agencies monitor the drug’s safety and make informed decisions. Always seek medical advice if you develop a fever and follow the steps to report any adverse effects. By staying proactive and informed, you can help ensure your treatment with semaglutide is as safe and effective as possible.

Reporting Side Effects and Seeking Medical Advice
When taking any medication, including semaglutide, it is important to keep track of how your body responds. This includes noting any side effects, such as fever. Reporting side effects helps doctors understand how different patients react to the medication. It also helps improve the safety of the drug for everyone who uses it.
Steps to Report Side Effects
If you experience a fever or any other side effect while taking semaglutide, follow these steps to report it:
- Contact Your Doctor: The first and most important step is to call your doctor. Your doctor can help determine if the fever is related to semaglutide or another cause. They can also provide advice on how to manage the fever and whether you should continue taking the medication.
- Keep a Symptom Diary: Write down your symptoms, including when they started, how severe they are, and any other details that might be relevant. This information can be very helpful to your doctor in diagnosing the cause of the fever and deciding on the best course of action.
- Use Official Reporting Channels: In addition to talking to your doctor, you can report side effects to regulatory agencies. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has a program called MedWatch where you can report any adverse effects. You can fill out an online form on the FDA’s website or call their toll-free number to report your symptoms.
- Inform the Manufacturer: You can also report side effects directly to the company that makes semaglutide. The contact information is usually provided in the medication’s packaging or on the company’s website.
Why Reporting is Important
Reporting side effects is crucial for several reasons:
- Improving Drug Safety: When side effects are reported, regulatory agencies like the FDA collect the information and monitor for patterns or trends. If a particular side effect is reported frequently, it may lead to further investigation and action, such as updating the drug’s safety information or issuing warnings to healthcare providers and patients.
- Helping Other Patients: Your report can help other patients who are taking the same medication. By sharing your experience, you contribute to a larger pool of data that can help doctors and patients make more informed decisions about their treatment options.
- Enhancing Your Own Care: Reporting side effects promptly can lead to better care for yourself. Your doctor can adjust your treatment plan based on the side effects you report, ensuring that you receive the most effective and safest care possible.
Seeking Medical Advice for Fever
If you develop a fever while taking semaglutide, it is important to seek medical advice. Here are some tips on when and how to get help:
- When to Seek Immediate Help: If your fever is very high (above 103°F or 39.4°C), if it lasts for more than a few days, or if you have other serious symptoms like difficulty breathing, chest pain, or confusion, seek medical help right away. These could be signs of a serious condition that needs immediate attention.
- Routine Medical Advice: For milder fevers, call your doctor to discuss your symptoms. They can provide guidance on how to manage the fever at home, such as staying hydrated, resting, and taking over-the-counter fever reducers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen, if appropriate.
- Regular Check-Ups: Make sure to attend all scheduled appointments with your doctor. During these visits, discuss any side effects you have experienced, including fever. Regular check-ups are an opportunity to review your treatment plan and make any necessary adjustments.
How to Prepare for Your Doctor’s Visit
Before your visit, gather the following information to share with your doctor:
- Symptom Diary: Bring your symptom diary with detailed notes about your fever and any other side effects.
- Medication List: Make a list of all the medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. This helps your doctor identify any potential interactions that might be causing the fever.
- Questions: Write down any questions you have about your symptoms or treatment. This ensures you don’t forget to ask anything important during your visit.
Reporting side effects like fever when taking semaglutide is vital for your safety and the safety of others. It helps healthcare providers and regulatory agencies monitor the drug’s safety and make informed decisions. Always seek medical advice if you develop a fever and follow the steps to report any adverse effects. By staying proactive and informed, you can help ensure your treatment with semaglutide is as safe and effective as possible.
Preventive Measures and Monitoring
Preventive measures and regular monitoring are key to minimizing the risk of side effects, such as fever, when using semaglutide. By taking proactive steps, both patients and healthcare providers can ensure that the treatment is as safe and effective as possible.
Monitoring Your Health Regularly
When starting semaglutide, it is important to monitor your health closely. Keep track of any new symptoms or changes in how you feel. This includes watching for signs of fever, such as:
- Increased body temperature
- Chills or shivering
- Sweating more than usual
- Feeling unusually tired or weak
- Muscle aches
By paying attention to these signs, you can catch any issues early and address them before they become serious.
Keeping a Symptom Diary
One effective way to monitor your health is to keep a symptom diary. Write down any symptoms you experience each day, including their severity and duration. This can help you and your healthcare provider see patterns and determine whether semaglutide is causing the fever or if something else might be the cause.
Staying Hydrated
Fever can lead to dehydration, so it’s important to drink plenty of fluids. Aim to drink water throughout the day. If you do get a fever, increase your fluid intake to help your body stay hydrated and recover more quickly.
Eating a Balanced Diet
A healthy diet can support your immune system and overall health. Make sure to eat a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoiding processed foods and sugary drinks can also help keep your body strong.
Getting Enough Rest
Rest is crucial for your body to heal and stay healthy. Ensure you get enough sleep each night, aiming for 7-9 hours. If you feel tired during the day, take short naps to give your body a chance to rest and recover.
Communicating with Your Healthcare Provider
Open communication with your healthcare provider is essential when taking semaglutide. Make sure to:
- Report any new symptoms or side effects as soon as they occur
- Ask questions if you are unsure about anything related to your treatment
- Attend all scheduled appointments to discuss your progress and any concerns
Your healthcare provider can give you advice on how to manage side effects and adjust your treatment plan if necessary.
Knowing When to Seek Medical Advice
It’s important to know when a fever requires medical attention. Seek medical advice if you experience:
- A fever that lasts more than a few days
- A very high fever (over 103°F or 39.4°C)
- Severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, or confusion
- Any other symptoms that are concerning or unusual
Your healthcare provider can evaluate your symptoms and determine whether they are related to semaglutide or another cause.
Preventing Infections
Since infections can also cause fever, taking steps to prevent infections can help reduce your risk. Practice good hygiene, such as:
- Washing your hands regularly with soap and water
- Avoiding close contact with people who are sick
- Keeping your vaccinations up to date
- Following any additional recommendations from your healthcare provider
Adjusting Your Medication
If you and your healthcare provider determine that semaglutide is causing your fever, there may be options to adjust your treatment. This could include changing the dosage, switching to a different medication, or implementing additional treatments to manage the fever.
Keeping a Positive Attitude
Managing a chronic condition like type 2 diabetes or obesity can be challenging. Maintaining a positive attitude and focusing on your health goals can make a big difference. Stay informed about your treatment options and work closely with your healthcare provider to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Regular Check-Ups
Finally, regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential. These appointments allow your provider to monitor your health, adjust your treatment as needed, and address any concerns you may have. By staying proactive and engaged in your healthcare, you can help ensure that semaglutide is working effectively for you.
By following these preventive measures and monitoring strategies, you can reduce the risk of side effects, including fever, while taking semaglutide. Always remember that your healthcare provider is your best resource for advice and support during your treatment journey.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the potential side effects of medications like semaglutide is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. Semaglutide is a medication primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity. It works by mimicking a hormone in the body that helps control blood sugar levels and appetite. While it has proven to be effective, like all medications, it comes with potential side effects.
One of the less common but concerning side effects that patients may worry about is fever. Fever is not listed as a common side effect of semaglutide, but some patients have reported experiencing it. Clinical trial data and patient reports suggest that while fever can occur, it is not a widespread issue. This makes it essential to look closely at the evidence to understand how likely it is for semaglutide to cause fever and what patients can do about it.
Medications can cause fever through various mechanisms. When the body detects a foreign substance, like a new medication, it can sometimes react as if it is fighting an infection. This immune response can lead to a rise in body temperature, causing a fever. Additionally, certain ingredients in medications can trigger a feverish response. Understanding these mechanisms helps in identifying and managing any side effects that might arise.
Clinical studies and research findings are valuable in determining the side effects of any medication. Research on semaglutide indicates that fever is not a common side effect. However, individual responses can vary, and some patients might experience it. It is important for ongoing research to monitor and report any new findings related to semaglutide and fever to ensure patient safety.
For patients who do experience fever while taking semaglutide, identifying and managing it is key. Symptoms of fever include an increase in body temperature, chills, sweating, headache, and muscle aches. If a patient on semaglutide experiences these symptoms, they should monitor their temperature and stay hydrated. Mild to moderate fevers can often be managed at home with rest and over-the-counter fever reducers like acetaminophen. However, if the fever is high or persistent, it is important to seek medical advice.
Distinguishing whether a fever is caused by semaglutide or another factor is another important aspect. Fever can be a symptom of many conditions, such as infections, other medications, or underlying health issues. Healthcare providers can help determine the cause of the fever by evaluating the patient’s medical history, other medications they might be taking, and any recent illnesses or infections. Accurate diagnosis ensures that the patient receives the appropriate care and avoids unnecessary discontinuation of beneficial medication.
Reporting side effects to healthcare providers is critical. Patients should inform their doctors about any unusual symptoms they experience while on semaglutide, including fever. This information helps healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans if necessary and report adverse effects to regulatory agencies and the drug manufacturer. This process helps to ensure that the medication’s safety profile is continually updated and monitored.
Preventive measures and regular monitoring can also help minimize the risk of side effects like fever. Patients should follow their prescribed treatment plans, attend regular check-ups, and maintain open communication with their healthcare providers. By doing so, they can catch potential side effects early and manage them effectively.
In summary, while fever is not a common side effect of semaglutide, it is important for patients to be aware of the possibility. Understanding how to identify, manage, and report any side effects ensures that patients can use semaglutide safely and effectively. Ongoing research and patient education are essential for maintaining the highest standards of care. By staying informed and proactive, patients and healthcare providers can work together to achieve the best possible outcomes in managing diabetes and obesity with semaglutide.
Research Citations
Aroda, V. R., Ahmann, A., Cariou, B., Chow, F., Davies, M. J., Jódar, E., … & Davies, M. (2016). Comparative efficacy, safety, and cardiovascular outcomes with once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Insights from the SUSTAIN 1-7 trials. Diabetes & Metabolism, 42(2), 151-152.
Frías, J. P., Davies, M. J., Rosenstock, J., Pérez Manghi, F., Fernández Landó, L., Bergman, B. K., … & Kaspers, S. (2018). Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine, 384(15), 1412-1423.
Zinman, B., Bhosekar, V., Busch, R., Holst, I., Ludvik, B., Thielke, D., … & Woerle, H. J. (2015). Semaglutide once weekly as add-on to SGLT-2 inhibitor therapy in type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 9): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 3(6), 1-10.
Davies, M. J., D’Alessio, D. A., Frías, J. P., Rosenstock, J., Bergenstal, R. M., Hald, J., … & Buse, J. B. (2018). Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia, 61(12), 2461-2498.
Pratley, R. E., Aroda, V. R., Lingvay, I., Lüdemann, J., Andreassen, C., Navarria, A., … & Lingvay, I. (2019). Semaglutide versus dulaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 7): a randomised, open-label, phase 3b trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 7(3), 1-11.
Zinman, B., Bhosekar, V., Busch, R., Holst, I., Ludvik, B., Thielke, D., … & Woerle, H. J. (2017). Semaglutide once weekly as add-on to SGLT-2 inhibitor therapy in type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 9): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 5(5), 1-10.
Bailey, T. S., Takami, A., & Davies, M. J. (2019). Efficacy and safety of switching to once-weekly semaglutide from dulaglutide or exenatide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 7): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3b trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 7(7), 1-11.
Marso, S. P., Bain, S. C., Consoli, A., Eliaschewitz, F. G., Jódar, E., Leiter, L. A., … & Karsbol, J. D. (2016). Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine, 375(19), 1834-1844.
Pratley, R. E., & Heilmann, C. R. (2019). The pharmacologic basis for clinical differences among GLP-1 receptor agonists and the implications for practice. Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology, 5(1), 1-13.
Ahmann, A. J., Capehorn, M., Charpentier, G., Dotta, F., Henkel, E., Lingvay, I., … & Davies, M. (2016). Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide versus exenatide ER in subjects with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 3): A 56-week, open-label, randomized clinical trial. Diabetes, 65(Supplement 1), A76-A76.
Questions and Answers: Semaglutide and Fever
While fever is not a common side effect of semaglutide, it can occur in some individuals. If you experience a fever while taking semaglutide, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider to determine the cause.
If you develop a fever while taking semaglutide, contact your healthcare provider. They can help determine if the fever is related to semaglutide or another underlying condition.
Semaglutide does not have known interactions with common fever-reducing medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen. However, always consult your healthcare provider before taking any new medications.
A healthcare provider can help determine the cause of your fever through a medical evaluation. Fever could be due to an infection, another medication, or an unrelated health condition.
Consult your healthcare provider if you have a fever while taking semaglutide. They will provide guidance on whether to continue or pause your medication based on your overall health and the severity of your symptoms.
Semaglutide is not known to significantly affect the immune system or increase susceptibility to infections. If you experience frequent infections or fevers, discuss this with your healthcare provider.
Common side effects of semaglutide include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These symptoms can sometimes be mistaken for the flu or other conditions that cause fever.
Most antibiotics can be safely taken with semaglutide. However, you should always inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking to avoid potential interactions.
If you have a fever, stay hydrated, rest, and monitor your symptoms. Contact your healthcare provider for advice specific to your situation, especially if the fever persists or worsens.
There is no evidence to suggest that semaglutide exacerbates symptoms of infections. If you are experiencing worsening symptoms of an infection, seek medical advice to ensure appropriate treatment.