Table of Contents
Introduction: Understanding Tirzepatide and Its Potential Side Effects
Tirzepatide is a newer medication that has gained attention for its use in treating type 2 diabetes and promoting weight loss. This drug works by mimicking two hormones in the body that help regulate blood sugar and reduce hunger. These hormones are called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide). By targeting these hormones, tirzepatide helps people control their blood sugar levels and can also lead to significant weight loss.
While tirzepatide offers great benefits for people struggling with diabetes or obesity, like all medications, it comes with potential side effects. Understanding these side effects is important for anyone considering or currently using tirzepatide. Some of the most common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These are typical of medications that affect the digestive system. However, there are also other side effects that some users may not expect, such as possible changes in their hair. In particular, some people wonder whether tirzepatide could lead to hair loss.
Hair loss is a concern for many individuals. Hair plays an important role in how we see ourselves, and losing hair can be stressful. For people taking tirzepatide, any noticeable hair thinning or loss can raise alarm. But is there a connection between tirzepatide and hair loss? This is a question that many people ask when searching for information about the drug online. Patients often want to know if their treatment is linked to hair loss and, if so, what can be done to manage it.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore whether tirzepatide can cause hair loss, what research says about this potential side effect, and how people can manage any hair changes they may experience while using the medication. By diving into the details, we aim to answer the most common questions about tirzepatide and hair health, helping patients feel more informed about their treatment.
Understanding why hair loss might occur is the first step in finding answers. Hair loss can happen for many reasons, and it’s not always easy to pinpoint one cause. For people taking medications like tirzepatide, it’s natural to wonder if the drug is behind their hair thinning. However, hair loss is not currently listed as a known side effect of tirzepatide in official reports or drug labels. But that doesn’t mean it isn’t possible.
There are various ways tirzepatide might indirectly cause hair loss. For instance, rapid weight loss, which is a common result of tirzepatide use, can sometimes trigger hair loss. This type of hair loss is often called “telogen effluvium,” and it occurs when the body sheds more hair than usual after going through physical stress, such as major weight changes. Many patients who lose weight quickly on tirzepatide might notice hair shedding a few months into their treatment. While this hair loss is usually temporary, it can still be concerning for those experiencing it.
Additionally, tirzepatide may affect other aspects of the body, such as hormone levels and nutrition, which can also play a role in hair health. For example, when the body loses weight, there may be changes in how it processes certain vitamins and nutrients that are important for hair growth. Without enough of these nutrients, hair can weaken and fall out. This is why it’s important to consider not only the medication itself but also the broader effects it has on the body when exploring the possibility of hair loss.
This guide will cover all these factors in detail. We will look at how tirzepatide works, whether hair loss is a common side effect, and what patients can do if they experience hair changes while using the drug. By understanding the connection between tirzepatide and hair health, patients can feel more confident in managing any side effects they encounter. While hair loss can be distressing, knowing the reasons behind it can help ease some of the worry.
In the sections that follow, we will answer the top questions people have about tirzepatide and hair loss. Whether you are currently taking tirzepatide or considering it as a treatment option, this guide aims to provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your health. We’ll explore what experts say, what research shows, and practical steps you can take to care for your hair while managing your diabetes or weight loss journey with tirzepatide.
By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of how tirzepatide affects the body, including its potential link to hair loss, and what you can do to maintain healthy hair during your treatment.
What Is Tirzepatide? Mechanism of Action and Uses
Tirzepatide is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists. This type of medicine is commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes and help with weight loss. However, tirzepatide is unique because it works in two ways, making it different from other medications in its class. In this section, we will explore what tirzepatide is, how it works, and the conditions it is used to treat.
How Tirzepatide Works
Tirzepatide is a dual agonist, which means it affects two important hormones in the body: GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide). These hormones are part of the incretin system, which helps control how the body manages sugar and fat. In people with type 2 diabetes, the body has trouble managing sugar, and the incretin system does not work as well as it should. This is where tirzepatide comes in.
When tirzepatide activates the GLP-1 receptor, it increases the release of insulin from the pancreas. Insulin is the hormone that helps lower blood sugar by allowing cells to use sugar for energy. At the same time, tirzepatide decreases the release of glucagon, another hormone that raises blood sugar. This balance helps people with diabetes keep their blood sugar levels under control.
Tirzepatide also works on GIP, which helps the body respond better to insulin and may even play a role in managing fat storage. The combination of these two actions makes tirzepatide very effective at lowering blood sugar and helping people lose weight. Many medications focus only on GLP-1, but tirzepatide’s action on both GLP-1 and GIP sets it apart from others.
Uses of Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide is mainly used to treat type 2 diabetes. In type 2 diabetes, the body either does not make enough insulin, or the cells in the body become resistant to insulin. This makes it hard for the body to keep blood sugar levels normal. High blood sugar over time can lead to serious health problems, such as heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney failure. Tirzepatide helps people with type 2 diabetes by improving how their body responds to insulin and lowering their blood sugar levels.
Another important use of tirzepatide is for weight loss. Many people with type 2 diabetes are also overweight or obese, which makes their diabetes harder to control. Tirzepatide has been shown to help people lose a significant amount of weight. This is because it not only improves blood sugar control but also affects how the body uses and stores fat. In clinical studies, people taking tirzepatide lost more weight compared to those taking other diabetes medications. Some doctors are also using tirzepatide for weight loss in people without diabetes, though it is not officially approved for this purpose yet.
Tirzepatide’s Effects on the Body
By working on both GLP-1 and GIP, tirzepatide affects several systems in the body. The most important effects are on blood sugar control and appetite regulation.
- Blood Sugar Control: Tirzepatide helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin release and decreasing glucagon. It also slows down how fast the stomach empties, which helps keep blood sugar from spiking after meals. This is especially helpful for people with type 2 diabetes, who often struggle to keep their blood sugar steady.
- Appetite Regulation: Tirzepatide helps people feel full sooner and stay full longer. This reduces the amount of food they eat, leading to weight loss. The dual action on GLP-1 and GIP helps control hunger in a more powerful way than other medications that target just one of these hormones.
Other Effects and Considerations
In addition to blood sugar control and weight loss, tirzepatide may have other effects on the body. Some of these are helpful, while others may be side effects.
- Heart Health: Tirzepatide has been shown to improve some markers of heart health, such as lowering cholesterol and blood pressure. This is important because people with diabetes are at a higher risk of heart disease.
- Digestive Effects: Like other GLP-1 receptor agonists, tirzepatide can cause nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, especially when people first start taking it. These effects usually get better over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
- Potential Hair Loss: Some people are concerned that tirzepatide may cause hair loss. However, hair loss is not listed as a common side effect in clinical trials. This is an area where more research is needed, and we will explore this potential link in later sections.
Tirzepatide is an innovative medication that helps people with type 2 diabetes control their blood sugar and lose weight. Its dual action on GLP-1 and GIP sets it apart from other treatments. While tirzepatide is effective, it is also important to understand how it works and the potential effects it can have on the body, including digestive issues and the possible link to hair loss, which will be explored further in this guide. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice when starting any new medication.
Is Hair Loss a Known Side Effect of Tirzepatide?
Tirzepatide is a medication approved for managing type 2 diabetes and promoting weight loss. Like any drug, it comes with a list of potential side effects that patients and doctors need to monitor. Some of the most common side effects associated with tirzepatide include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and low blood sugar. But when it comes to hair loss, this concern is not as commonly discussed.
In this section, we will explore whether hair loss is a known side effect of tirzepatide, what reports from users and medical professionals say about it, and how it compares to other medications in the same class.
Official Side Effect Listings
When a new medication is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or other health agencies, its safety is evaluated through clinical trials. These trials help identify the most common side effects, which are then listed in the drug’s official prescribing information. For tirzepatide, the most commonly reported side effects include gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, and constipation, along with dizziness and low blood sugar.
However, hair loss is not listed as a common or known side effect in the official package insert for tirzepatide. This means that during the clinical trials conducted before the drug was approved, hair loss was not reported as a significant problem among the participants. Does this mean that tirzepatide cannot cause hair loss? Not necessarily.
Reported Cases of Hair Loss
Although hair loss is not listed as a standard side effect, there have been anecdotal reports from individuals taking tirzepatide who experienced hair thinning or shedding. It’s important to understand that these reports are not the same as clinical evidence. Anecdotal evidence refers to personal experiences shared by individuals, which may not reflect the experiences of most patients using the medication.
In forums, social media groups, and patient feedback websites, some people have raised concerns about hair loss while on tirzepatide. However, these reports are still few and not enough to establish a clear connection between tirzepatide and hair loss.
There may be other reasons why patients on tirzepatide experience hair loss, such as underlying health conditions or the effects of rapid weight loss, which we will explore in more detail later.
Understanding Hair Loss and Its Causes
Hair loss, also known as alopecia, can occur for many reasons. One of the most common causes of hair loss is stress on the body, whether it is physical or emotional. In some cases, medications can cause hair loss by affecting hormone levels, the growth cycle of hair follicles, or the availability of nutrients needed for healthy hair growth.
When taking a medication like tirzepatide, it’s crucial to consider how the drug might affect overall health and indirectly contribute to hair loss. For example, some medications can cause telogen effluvium, a condition where hair falls out after the body experiences a shock. This type of hair loss is usually temporary but can be alarming for those affected.
How Tirzepatide Compares to Other GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Tirzepatide belongs to a class of drugs called GLP-1 receptor agonists. These medications work by mimicking a hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes weight loss by reducing appetite. Other drugs in this category, like semaglutide and liraglutide, are used for similar purposes.
In terms of hair loss, the evidence is mixed. Like tirzepatide, neither semaglutide nor liraglutide lists hair loss as a known side effect. However, some patients on these drugs have also reported hair thinning or shedding, suggesting that this issue may be present across the entire class of medications.
It’s important to remember that every person reacts to medications differently. What causes hair loss in one person may not affect another in the same way. While hair loss may not be a documented side effect in the official medical literature for tirzepatide, individual experiences can vary, and other factors may contribute to this outcome.
Hair loss is not officially recognized as a common side effect of tirzepatide, according to clinical trial data and prescribing information. However, there have been individual reports of hair shedding among people taking the medication. These reports remain anecdotal, and more research is needed to determine if there is a direct link between tirzepatide and hair loss.
In the meantime, patients who notice hair loss while taking tirzepatide should consult their healthcare provider to rule out other causes, such as nutritional deficiencies, stress, or underlying health conditions. Understanding how tirzepatide affects the body and exploring other potential factors can help in managing this concern effectively.

What Could Cause Hair Loss While Using Tirzepatide?
Hair loss can be concerning for anyone, especially when it is linked to medications like tirzepatide. While tirzepatide is primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes and help with weight loss, some users may notice changes in their hair. But why could this happen? Several factors may contribute to hair loss while using tirzepatide, including nutrient deficiencies, metabolic changes, and hormonal shifts. This section will explore these possible causes in more detail, helping readers understand why hair loss might occur and what can be done about it.
Nutrient Deficiencies and Hair Loss
One of the potential reasons for hair loss while using tirzepatide could be related to nutrient deficiencies. Hair growth requires specific nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, to stay healthy. Some of these essential nutrients include:
- Protein: Hair is primarily made of a protein called keratin. If the body does not get enough protein, hair growth can slow down, and hair may become thin or brittle.
- Iron: Iron is critical for hair health. It helps carry oxygen to the hair follicles, which are necessary for growth. Low iron levels, also known as iron deficiency, can lead to hair shedding.
- Biotin: Biotin, a type of B vitamin, is often associated with healthy hair. A deficiency in biotin can cause hair thinning and hair loss.
- Zinc: Zinc plays a role in tissue growth and repair, including hair follicles. Low levels of zinc can contribute to hair loss.
- Vitamin D: Studies have shown that a lack of vitamin D can lead to hair loss, as this vitamin helps create new hair follicles.
People who are on tirzepatide might experience changes in their metabolism or diet, which could affect how their bodies absorb these important nutrients. For example, if tirzepatide causes rapid weight loss, it might reduce a person’s overall intake of food, leading to nutrient deficiencies. This is especially important to monitor during significant weight changes, as the body may not have enough nutrients to support hair growth.
Metabolic Changes and Hair Loss
Tirzepatide is designed to alter how the body processes insulin and glucose. This can lead to significant metabolic changes that may affect various parts of the body, including hair growth. When someone’s metabolism changes rapidly, the body might prioritize more important functions, such as regulating blood sugar, over less critical functions like hair growth.
This type of hair loss is known as telogen effluvium, a condition in which hair follicles are pushed into the resting phase, leading to hair shedding. Telogen effluvium often happens during times of physical stress on the body, such as illness, surgery, or drastic weight loss. Since tirzepatide can result in fast weight loss and significant metabolic shifts, it may trigger this type of stress-related hair loss.
Telogen effluvium is usually temporary, but it can be alarming for those who experience it. In many cases, once the body adjusts to the changes, hair growth resumes. However, understanding the relationship between metabolic changes and hair loss is crucial for patients using tirzepatide, as they may need to be patient and give their bodies time to adjust.
Hormonal Shifts and Hair Loss
Another factor that may contribute to hair loss while using tirzepatide is hormonal changes. Tirzepatide impacts hormones such as insulin, which plays a role in hair health. Insulin helps control blood sugar, and any fluctuations in insulin levels can indirectly affect other hormones in the body, such as cortisol and androgens.
- Cortisol: This is often called the “stress hormone.” Elevated cortisol levels can slow down hair growth and cause hair follicles to enter the resting phase more quickly, which can lead to increased shedding. Changes in weight and metabolism can also trigger fluctuations in cortisol levels.
- Androgens: Androgens are male hormones that are present in both men and women. High levels of androgens can shrink hair follicles and shorten the hair growth cycle, leading to thinning hair or hair loss. Although tirzepatide is not known to directly increase androgen levels, rapid weight loss or changes in metabolic health might indirectly affect androgen production.
Weight Loss and Hormone Balance
One of the goals of tirzepatide therapy is weight loss, especially in individuals with type 2 diabetes or obesity. However, rapid weight loss itself can cause hormonal shifts that may lead to hair loss. When the body loses a lot of weight quickly, it may perceive this as a form of stress, which can affect hormone levels. This stress can cause temporary hair loss until the body stabilizes at a new weight.
While hair loss may not be a widely recognized side effect of tirzepatide, it is possible that a combination of nutrient deficiencies, metabolic changes, and hormonal shifts could lead to hair thinning in some patients. Understanding these underlying causes can help patients manage their hair health while continuing their treatment. It is always important to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider, who may suggest nutritional supplements, dietary changes, or other ways to support healthy hair growth during tirzepatide therapy.
Can Weight Loss Itself Cause Hair Loss?
Weight loss, especially when it happens quickly, can sometimes lead to hair loss. This is something that many people don’t expect when starting a weight loss journey, but it is a well-documented side effect. Hair loss related to weight loss is often referred to as “telogen effluvium.” To understand how this works, we need to take a closer look at how hair grows, what causes hair loss, and why weight loss can sometimes trigger it.
Understanding Hair Growth and Hair Loss
Hair grows in cycles. There are three main phases of hair growth:
- Anagen Phase – This is the growth phase, where hair is actively growing and can last for years.
- Catagen Phase – This is a short transitional phase where the hair stops growing.
- Telogen Phase – This is the resting phase, where the hair stays in the follicle but doesn’t grow anymore. After this phase, the hair falls out, and new hair starts to grow in its place.
At any given time, about 85-90% of the hairs on your head are in the anagen phase, meaning they are actively growing. The rest are either in the catagen or telogen phase. Normally, people lose about 50 to 100 hairs a day, which is considered normal.
What is Telogen Effluvium?
Telogen effluvium is a type of temporary hair loss that happens when more hairs than usual enter the telogen phase at the same time. This means more hair falls out than is growing, leading to noticeable hair thinning. The hair loss caused by telogen effluvium usually happens a few months after the body experiences a shock. This shock can be physical or emotional and can include things like surgery, illness, or significant changes in diet and weight.
How Does Weight Loss Trigger Hair Loss?
When people lose weight, especially if they do it quickly, it can put stress on the body. Weight loss can sometimes be seen as a physical “shock” by the body, which may push more hairs into the telogen phase. This leads to more hair falling out. There are a few reasons why weight loss can cause this reaction:
- Calorie Restriction – When people follow a strict diet to lose weight, they often consume fewer calories than the body is used to. This can lead to a lack of essential nutrients, such as proteins, vitamins, and minerals, that are needed for healthy hair growth. Hair is made of a protein called keratin, and when the body doesn’t get enough protein, it may stop producing hair to conserve energy.
- Nutrient Deficiencies – Certain nutrients are critical for hair health. For example, iron, zinc, biotin, and vitamin D are all essential for healthy hair growth. When people are on a weight loss diet, they may not get enough of these nutrients, especially if their diet is not balanced. Deficiencies in these nutrients can contribute to hair thinning.
- Rapid Weight Loss – Losing a lot of weight in a short amount of time can cause stress on the body. This rapid weight loss can come from extreme dieting, weight loss surgeries, or medications like tirzepatide. The body may respond to this rapid change by diverting energy from non-essential functions, like hair growth, to more vital functions, like maintaining organs and muscles. This can lead to more hairs entering the telogen phase, causing hair loss.
How Common is Hair Loss During Weight Loss?
Not everyone who loses weight will experience hair loss, but it is relatively common in people who lose weight quickly or follow very low-calorie diets. It’s important to remember that telogen effluvium is usually temporary. In most cases, hair starts to grow back once the body adjusts to the new weight and the shock has passed.
Can You Prevent Hair Loss While Losing Weight?
While some degree of hair loss might be unavoidable for people who lose a lot of weight quickly, there are steps that can be taken to minimize it. Here are a few tips:
- Eat a Balanced Diet – Make sure that your diet includes enough protein, iron, and other important nutrients that support hair growth. If you are on a strict weight loss diet, you may want to talk to a doctor or dietitian about taking supplements to make up for any potential nutrient deficiencies.
- Avoid Extreme Diets – Losing weight slowly and steadily is better for your overall health and may help reduce the risk of hair loss. Crash diets or very low-calorie diets can be particularly hard on the body and may increase the risk of hair loss.
- Manage Stress – Stress is another factor that can contribute to telogen effluvium. Finding ways to manage stress, such as through exercise, meditation, or relaxation techniques, can help reduce the impact on your hair.
Weight loss can sometimes cause hair loss, especially if the weight is lost quickly or through a restrictive diet. This hair loss is usually temporary and related to telogen effluvium, a condition where more hairs enter the resting phase at once. However, eating a balanced diet, avoiding extreme dieting, and managing stress can help reduce the risk of hair loss during weight loss. If hair loss does occur, it often resolves itself once the body adjusts to the changes.
Does Tirzepatide Affect Hormonal Balance Related to Hair Health?
Tirzepatide is a medication that influences how your body handles blood sugar and fat, but it may also have effects on other parts of the body, including hormones. Since hormones play a key role in hair growth, it’s important to understand how tirzepatide might impact them and whether this could lead to hair loss.
The Role of Hormones in Hair Growth
Hair growth is a complex process controlled by many factors, and hormones are a major part of this. Hormones like insulin, cortisol, and androgens (male hormones) all have roles in the hair growth cycle. When these hormones are balanced, hair grows normally, but when they become unbalanced, it can lead to hair loss.
- Insulin: This hormone helps your body use sugar from the food you eat for energy. When insulin levels are high or low, it can affect other hormones, which may impact hair health.
- Cortisol: Often called the “stress hormone,” cortisol helps your body respond to stress. When cortisol levels are too high, it can cause hair to enter the “resting” phase too early, leading to thinning or hair loss.
- Androgens: These hormones, such as testosterone, can influence hair growth, especially in men. Too much androgen can lead to hair loss in a condition called androgenic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness.
How Tirzepatide Influences These Hormones
Tirzepatide is designed to help people with type 2 diabetes by lowering blood sugar levels, and it can also help with weight loss. It works by acting on two important hormones: GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide). These hormones help your body release insulin when blood sugar levels are high, and they also reduce the amount of sugar your liver releases into your blood.
Because tirzepatide directly affects insulin levels, it can have an impact on other hormones as well. When your blood sugar levels improve, your body’s overall hormone balance can change. In some cases, this may affect hair health. For example, changes in insulin levels might influence how other hormones, like cortisol and androgens, behave.
Insulin, Tirzepatide, and Hair Health
When people have high blood sugar or insulin resistance (a condition where the body doesn’t respond to insulin well), it can lead to inflammation in the body. Inflammation can damage hair follicles, slowing hair growth or causing hair to fall out. By improving insulin sensitivity and lowering blood sugar levels, tirzepatide may help reduce this inflammation. In theory, this could actually help hair health in some people by reducing the damage that leads to hair loss.
On the other hand, rapid changes in insulin levels might cause temporary hormone imbalances. For some people, this might lead to hair shedding as the body adjusts. This type of hair loss is usually temporary and may stop once your body gets used to the medication.
Cortisol, Stress, and Tirzepatide
Cortisol levels can rise when the body is under stress, and chronic high cortisol levels can lead to hair thinning. Some research suggests that medications like tirzepatide may indirectly reduce stress on the body by improving overall metabolic health. For example, better blood sugar control can lower stress on the organs, potentially leading to lower cortisol levels.
However, rapid weight loss, which is common with tirzepatide, can be a form of physical stress on the body. Weight loss puts the body into a state where it needs to adjust quickly to changes in energy use, which can cause a short-term spike in cortisol levels. This stress could trigger temporary hair loss, often referred to as telogen effluvium, where more hairs than usual enter the resting phase and fall out.
Androgens, Tirzepatide, and Hair Loss
Some types of hair loss, like male or female pattern baldness, are linked to high levels of androgens. While tirzepatide does not directly target androgens, any medication that changes weight or insulin levels could indirectly affect androgen levels. Losing weight, especially if you lose a significant amount, can lead to changes in hormone levels, including a reduction in androgens. For many people, this is a positive effect, as it could reduce the risk of hair loss caused by high androgen levels.
However, in some cases, losing weight quickly may trigger a temporary imbalance in hormone levels, which might lead to short-term hair thinning.
Tirzepatide can affect hormones that play important roles in hair growth, such as insulin, cortisol, and androgens. While it may help improve overall hormone balance by lowering blood sugar and promoting weight loss, these changes could also cause temporary hair loss in some people. Most of the time, this type of hair loss is temporary and may resolve as the body adjusts to the medication. It’s always a good idea to speak with your healthcare provider if you notice changes in your hair while taking tirzepatide, as they can help guide you through managing any side effects.

What Does Current Research Say About Tirzepatide and Hair Loss?
Tirzepatide is a relatively new medication, approved for managing type 2 diabetes and aiding weight loss. While it is proving to be effective in controlling blood sugar and promoting weight loss, questions have been raised about whether it causes hair loss. As of now, there is limited direct research that links tirzepatide to hair loss, but we can explore the available information to understand the situation better.
Review of Clinical Trials and Side Effect Data
When any new medication is tested, researchers carefully track all possible side effects, even rare ones. For tirzepatide, the large clinical trials focused primarily on its ability to lower blood sugar and help with weight loss. These studies also documented side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, and decreased appetite. However, hair loss was not reported as a common side effect in these trials.
This absence of hair loss as a commonly reported side effect does not completely rule out the possibility. It is possible that hair loss is a rare side effect or that it might not have been noted during the trials because it occurred later or was underreported by patients. In clinical studies, patients usually focus on severe or bothersome side effects, while hair thinning might not always be noticed right away.
Post-Marketing Data on Hair Loss and Tirzepatide
After a medication is approved and used by a larger group of people, additional side effects can emerge. This is because millions of people are taking the drug in real-world settings, as opposed to the controlled environment of a clinical trial. Post-marketing data is collected by healthcare providers, patients, and researchers who monitor for any new or unexpected side effects.
Since tirzepatide was approved, there have been some reports from patients and healthcare providers suggesting a possible connection between the drug and hair loss. These reports are considered anecdotal, meaning they come from individual cases and are not yet part of large, formal studies. While these reports raise questions, they are not enough to confirm that tirzepatide directly causes hair loss.
Insights from Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals, including endocrinologists and dermatologists, have started discussing the potential link between tirzepatide and hair loss based on patient feedback. Some doctors have reported that a small number of their patients experienced hair thinning or shedding after starting tirzepatide. However, these doctors also note that the relationship between tirzepatide and hair loss is not clear-cut.
It is important to consider other factors that could contribute to hair loss. For instance, many patients taking tirzepatide are also losing weight, and rapid weight loss is known to trigger a type of hair loss called telogen effluvium. This occurs when the body undergoes physical stress, such as a significant change in diet, weight, or metabolism. Telogen effluvium typically causes temporary hair shedding and is reversible once the body adjusts.
Research Gaps: What We Don’t Know
One of the challenges in understanding whether tirzepatide causes hair loss is that there simply hasn’t been enough research on this topic yet. Most of the studies done so far have focused on the medication’s ability to manage blood sugar and help with weight loss. Side effects that are considered less serious, like hair thinning, may not be thoroughly investigated in these initial studies.
Future research is needed to determine if there is a direct link between tirzepatide and hair loss. This could involve more detailed post-marketing studies, patient surveys, and new clinical trials that specifically track hair health in patients using tirzepatide.
The Bottom Line
At this time, there is no solid scientific evidence confirming that tirzepatide directly causes hair loss. While some patients have reported experiencing hair thinning or shedding, these cases are not enough to establish a clear link. It’s important to keep in mind that rapid weight loss, which often occurs with tirzepatide, is a well-known cause of temporary hair loss.
Patients concerned about hair loss while using tirzepatide should speak with their healthcare provider. Together, they can determine whether the hair loss might be related to the medication or other factors such as weight loss, nutritional changes, or stress. More research will be needed in the future to clarify this potential side effect.
How Can Patients Manage Hair Loss While Using Tirzepatide?
If you’re using tirzepatide and notice hair loss, it’s natural to feel concerned. Hair loss, while not a common side effect of tirzepatide, can happen to some people for various reasons. Managing this issue can help you maintain both your treatment plan and your hair health. Let’s explore several ways you can address hair loss while using tirzepatide.
Talk to Your Healthcare Provider
The first step is to talk to your healthcare provider. If you are noticing hair thinning or hair loss, it’s important to share this information with them. They can help figure out if tirzepatide is the cause or if other factors, like weight loss or nutrient deficiencies, are involved. Your doctor can review your symptoms and possibly run tests to rule out other causes of hair loss, such as thyroid issues, anemia, or hormonal imbalances.
Your healthcare provider might also adjust your medication or suggest other treatments to help manage hair loss. In some cases, they might refer you to a dermatologist, a doctor who specializes in hair and skin, for further evaluation.
Monitor Your Nutritional Intake
One of the reasons people experience hair loss while losing weight or using medications like tirzepatide is related to their nutrition. Hair growth requires a variety of vitamins and minerals, and when your body doesn’t get enough of these, hair can start to thin or fall out.
To maintain healthy hair, make sure you are eating a balanced diet. This includes:
- Protein: Hair is made of a protein called keratin. If you aren’t eating enough protein, your body might not have the building blocks it needs to grow hair.
- Iron: Iron is important for delivering oxygen to your hair follicles. Low iron levels can lead to hair thinning. Foods rich in iron include red meat, spinach, and lentils.
- Zinc and Biotin: Both of these nutrients are essential for hair growth. Zinc helps repair hair tissues, and biotin (a type of B vitamin) supports the production of hair proteins. You can find these nutrients in eggs, nuts, and whole grains.
- Vitamins A and C: These vitamins help the scalp produce sebum, a natural oil that keeps your hair healthy. They also support the production of collagen, which strengthens hair.
If your diet is lacking in any of these nutrients, consider speaking with your healthcare provider about supplements. However, it’s important not to take supplements without medical advice, as too much of certain nutrients can also cause health issues.
Be Gentle with Your Hair
When you are dealing with hair loss or thinning, it’s important to treat your hair with care. Avoid practices that can cause additional stress to your hair, such as:
- Avoid excessive heat: Styling tools like blow dryers, curling irons, and straighteners can damage hair, especially if it is already thinning.
- Be careful with hairstyles: Tight ponytails, braids, or buns can pull on the hair and lead to breakage. Opt for loose styles that don’t put stress on your scalp.
- Limit chemical treatments: Dyes, perms, and straightening treatments can weaken hair and lead to more breakage. If possible, avoid or minimize the use of these treatments while managing hair loss.
Consider Over-the-Counter Hair Growth Products
There are several over-the-counter (OTC) products that can help with hair loss. One of the most common treatments is minoxidil, which is available without a prescription. Minoxidil helps stimulate hair follicles and can promote hair growth. It is applied directly to the scalp and is available in foam or liquid form.
However, it’s important to know that hair growth with minoxidil takes time. You might not see results for a few months, and once you stop using it, hair loss may return. Always consult your doctor before starting any new treatments, including OTC products.
Practice Stress Management
Stress can play a role in hair loss, especially during times of significant change, like weight loss or starting a new medication. Stress affects your body’s hormone levels, which can interfere with hair growth.
Practicing stress-reducing activities, such as mindfulness, yoga, meditation, or regular exercise, can help your body balance hormone levels and support hair growth. If you find that stress is affecting your overall well-being, it might be helpful to speak with a mental health professional for guidance.
Hair loss while using tirzepatide can be managed with the right approach. By working with your healthcare provider, improving your nutrition, being gentle with your hair, and considering hair growth treatments, you can take steps to maintain your hair health while benefiting from tirzepatide’s effects. Always keep open communication with your doctor to ensure that your treatment is personalized to your needs.
Can Tirzepatide-Induced Hair Loss Be Reversed?
Experiencing hair loss while using tirzepatide can be worrying, but it’s important to understand that not all hair loss is permanent. In many cases, drug-induced hair loss is temporary and reversible, depending on the underlying cause. In this section, we will explore the different types of hair loss, whether tirzepatide-induced hair loss can be reversed, and what treatments may help.
Understanding the Type of Hair Loss Associated with Tirzepatide
There are several types of hair loss, and identifying which one you are experiencing is key to determining whether it can be reversed. The most common type of hair loss associated with medications, including tirzepatide, is called telogen effluvium.
Telogen effluvium occurs when more hair follicles than usual enter the resting phase of the hair growth cycle. This leads to noticeable thinning and shedding, often after a major change in the body, such as weight loss, illness, stress, or medication use. Telogen effluvium is typically temporary and can reverse itself once the underlying cause is addressed.
Another possible cause of hair loss is nutritional deficiencies. Tirzepatide helps with weight loss, but rapid or significant weight loss can sometimes lead to a deficiency in certain vitamins and minerals, such as iron, zinc, and biotin, which are important for healthy hair growth. When these nutrients are lacking, hair growth may slow down or stop, leading to thinning. The good news is that hair loss caused by nutrient deficiencies can often be reversed by correcting the deficiency.
Finally, hormonal changes may also play a role. Tirzepatide can affect hormones like insulin and cortisol, and changes in these hormones might impact hair growth. If hormones are involved, addressing the imbalance may help hair regrow.
Is Hair Loss from Tirzepatide Permanent?
The majority of cases of hair loss from tirzepatide are expected to be temporary. Telogen effluvium, for example, generally lasts a few months and resolves on its own once the body adjusts to the changes. In these cases, once the stressor (like medication adjustment or weight loss) is no longer affecting the body, hair follicles can re-enter the growth phase, and new hair begins to grow.
However, it is important to note that the recovery of hair growth can take time. Hair grows in cycles, and the average person’s hair grows about half an inch per month. This means that even if the cause of hair loss is addressed, it may take several months to see noticeable improvement.
In rare cases, hair loss might become more severe or permanent if it is linked to a condition like androgenetic alopecia, a common type of hair loss in both men and women. This form of hair loss involves genetics and hormone levels and may not be fully reversible without specific treatments like medications or hair restoration techniques.
Treatment Options to Reverse Hair Loss
If you are experiencing hair loss while on tirzepatide, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider. They can help determine the cause of your hair loss and guide you on the best treatment options. Here are some general approaches to reversing hair loss:
- Diet and Nutrition: If your hair loss is related to nutrient deficiencies, making changes to your diet or taking supplements can help. Your healthcare provider may recommend blood tests to check for deficiencies in iron, zinc, biotin, and other essential nutrients. Taking the right supplements or eating nutrient-rich foods can support hair regrowth.
- Topical Treatments: For some types of hair loss, topical treatments like minoxidil (commonly known as Rogaine) may be recommended. Minoxidil is an over-the-counter treatment that can be applied to the scalp to stimulate hair growth. It works by prolonging the growth phase of hair follicles, allowing more hair to grow back over time.
- Reducing Stress: Since stress can trigger or worsen telogen effluvium, managing stress through relaxation techniques, regular exercise, and good sleep hygiene may help reduce hair loss and support recovery.
- Medications: If hair loss is due to hormonal changes or conditions like androgenetic alopecia, your doctor may prescribe medications to balance your hormones or slow down hair loss. Treatments like finasteride (Propecia) or hormone therapy may be effective in certain cases.
- Patience: Hair regrowth takes time, and it’s important to be patient during the process. Hair cycles take months to show visible changes, so sticking with your treatment plan and giving your body time to adjust is crucial.
Medical Consultation Is Key
Before starting any treatment, consult with your healthcare provider to make sure the treatment is right for you. They can provide personalized advice and monitor your progress. If hair loss becomes a serious concern, a dermatologist specializing in hair disorders may be able to offer additional insight and treatment options.
Tirzepatide-induced hair loss is generally not permanent. With the right approach—whether through dietary changes, topical treatments, or managing stress—many patients can reverse their hair loss and restore healthy hair growth. Keep in mind that each individual’s response may vary, so seeking professional guidance is always the best first step.
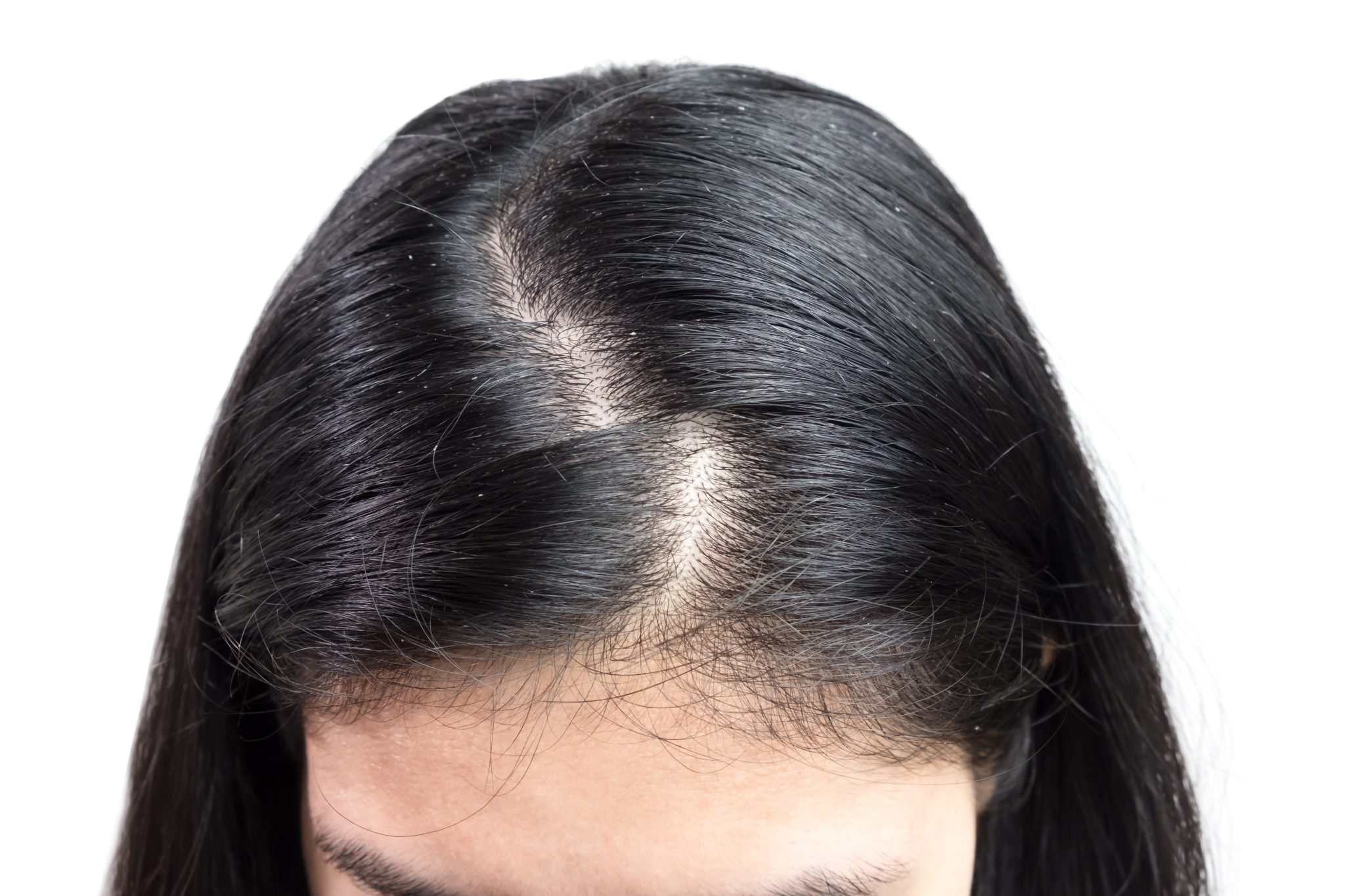
Should Patients Stop Using Tirzepatide If They Experience Hair Loss?
Hair loss is a distressing issue for many people, especially when it happens while taking medications like tirzepatide. If you are using tirzepatide and notice your hair thinning, you may wonder whether you should stop taking the medication. In this section, we will explore the factors to consider before making any decisions about stopping tirzepatide. It is important to weigh the risks and benefits, understand the potential causes of hair loss, and talk with your healthcare provider to get personalized advice.
Understanding the Risks and Benefits of Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide is a medication used to help people manage type 2 diabetes and lose weight. It works by targeting hormones that regulate blood sugar levels and appetite. For people with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels is essential to avoid long-term complications like heart disease, kidney problems, and nerve damage. For people using tirzepatide for weight loss, losing weight can reduce the risk of many conditions, including heart disease, stroke, and joint problems.
Because tirzepatide offers significant health benefits, stopping the medication could mean losing control of your blood sugar levels or slowing down your weight loss progress. Before deciding to stop tirzepatide due to hair loss, it is important to ask yourself if the benefits of the medication outweigh the potential side effect of hair thinning. For many people, the health improvements from tirzepatide can be more important than the temporary issue of hair loss.
Hair Loss: A Temporary or Long-Term Issue?
In most cases, hair loss that occurs while using tirzepatide is temporary. The type of hair loss some people experience is called telogen effluvium, which happens when the body goes through a period of stress, such as rapid weight loss or changes in diet and hormones. This type of hair loss is often temporary and the hair will usually grow back once the body adjusts.
It is important to understand whether the hair loss you are experiencing is permanent or temporary. In many cases, telogen effluvium resolves on its own after a few months, and hair regrowth occurs without any special treatment. If you stop taking tirzepatide, you might miss out on the benefits of the medication, especially if the hair loss is only a short-term problem. Therefore, it’s important to be patient and give your body time to adjust before deciding to stop the medication.
Other Causes of Hair Loss to Consider
Before deciding to stop tirzepatide, it’s also important to consider other potential causes of hair loss. Hair thinning can be caused by many factors, including:
- Nutrient deficiencies: A lack of vitamins or minerals, like iron, zinc, or biotin, can contribute to hair loss. People losing weight rapidly on tirzepatide may not be getting enough nutrients from their diet, which can lead to hair thinning.
- Hormonal changes: Weight loss can cause shifts in hormones like estrogen and testosterone, which can affect hair growth. These changes are not always caused directly by tirzepatide but by the weight loss itself.
- Stress: Major changes in lifestyle, diet, or health can cause stress on the body, leading to hair loss. Managing stress levels through relaxation techniques or physical activity can help reduce this type of hair loss.
Talking to your doctor about other possible causes of hair loss can help you find out if tirzepatide is the main cause, or if other factors are playing a role.
Discussing Concerns with Your Healthcare Provider
If you notice hair loss while taking tirzepatide, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider before making any decisions about stopping the medication. Your doctor can help you figure out if the hair loss is related to the medication, rapid weight loss, or another cause. They can also help you find ways to manage the hair loss while continuing to get the benefits of tirzepatide.
In some cases, your doctor may recommend treatments to support hair regrowth, such as taking supplements or using topical treatments for hair loss. They might also check for any underlying issues, like nutrient deficiencies, and suggest changes to your diet or health routine to improve hair health.
Making an Informed Decision
Deciding whether to stop tirzepatide due to hair loss should be based on a careful evaluation of the risks and benefits. For many people, the benefits of controlling blood sugar levels or losing weight are significant, and the hair loss may be temporary or manageable. Stopping the medication could lead to worsening diabetes control or slower progress in reaching weight loss goals.
Before stopping tirzepatide, it is essential to talk with your healthcare provider about your concerns and explore all options. Your doctor can provide guidance on how to manage hair loss while still achieving your health goals with tirzepatide.
Conclusion: What You Should Know About Tirzepatide and Hair Loss
Tirzepatide is a medication that has been shown to help with type 2 diabetes management and weight loss. However, some people who take it may wonder if it can cause hair loss. This article has explored the possible link between tirzepatide and hair loss, looking at the common questions people have.
To start, tirzepatide is a dual agonist of GLP-1 and GIP receptors. It works by helping to control blood sugar levels and reduce body weight. While tirzepatide is effective for these uses, it is important to understand the potential side effects. Hair loss, while not listed as a common side effect in clinical trials, has been reported by some people taking tirzepatide. This leads to questions about whether the drug directly causes hair loss or if other factors are at play.
Hair loss is not a side effect officially listed by tirzepatide’s manufacturers. However, there have been anecdotal reports from some users who noticed thinning hair while on the medication. This raises the question of whether the drug itself causes hair loss or if other factors, such as rapid weight loss, stress on the body, or hormonal changes, are the main culprits.
One possible explanation is that rapid weight loss, which is common with tirzepatide, can lead to a type of temporary hair loss known as telogen effluvium. This type of hair loss happens when the body goes through physical stress, such as from a major diet change or rapid weight loss. Hair follicles may enter the resting phase, and a few months later, shedding occurs. This type of hair loss is usually temporary, and hair often regrows once the body adjusts.
Tirzepatide may also affect the body’s hormones, which can play a role in hair growth. For example, insulin levels and blood sugar levels are regulated by the medication, and changes in these hormones could potentially impact hair health. Some research suggests that hormones like cortisol, which are linked to stress, can influence hair shedding. Weight loss, in general, can affect hormone levels, including sex hormones that are important for maintaining healthy hair. While there is no concrete evidence linking tirzepatide directly to hormonal hair loss, it is a possibility that should be explored further.
Clinical research on tirzepatide and hair loss is still limited. As of now, there are no large studies that definitively link the drug to hair thinning or shedding. Most of the data we have comes from individual reports, making it difficult to draw strong conclusions. Healthcare providers may not consider hair loss a major concern when prescribing tirzepatide, especially if it helps improve blood sugar control and reduce weight, which are key to managing type 2 diabetes and obesity.
For people experiencing hair loss while using tirzepatide, there are ways to manage the situation. It is important to talk to a healthcare provider if hair loss becomes a concern. They can help determine if the hair loss is related to the medication or if other factors, like nutritional deficiencies or stress, might be the cause. In many cases, hair loss caused by weight loss or stress is temporary, and hair regrowth may occur once the body stabilizes. Dietary changes, taking supplements, and using gentle hair care products may also help support healthy hair.
In most cases, stopping tirzepatide is not necessary if hair loss occurs, especially if the medication is helping with diabetes or weight loss. However, it is always a good idea to weigh the benefits and risks with a healthcare provider. The benefits of tirzepatide, including better blood sugar control and significant weight loss, may outweigh the temporary inconvenience of hair thinning, especially if the hair loss is not severe or long-lasting.
In conclusion, while tirzepatide is not officially linked to hair loss, some people may notice hair thinning while taking the medication. This could be due to a number of factors, including rapid weight loss, changes in hormones, or stress on the body. Anyone concerned about hair loss while using tirzepatide should consult a healthcare provider to explore possible causes and solutions. Though hair loss can be concerning, it is often temporary and manageable, and the benefits of tirzepatide in controlling diabetes and promoting weight loss are significant.
Research Citations
Donovan, E. R., Musleh, S., & Bordone, L. A. (2024). Treatment of insulin resistance with tirzepatide leading to improvement of hair loss. JAAD Case Reports, 50, 123-125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2024.06.001
George, C. (2024, April 8). Understanding hair loss with Semaglutide and Tirzepatide: Exploring the connection and management strategies. Endure Health. Retrieved from https://www.endure-health.com
Zepbound (Tirzepatide) Injection [NDA 217806]. (2024). Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov
Gordon, E. R., & Bordone, L. A. (2024). Androgenic alopecia and insulin resistance: Insights from tirzepatide treatment. Journal of Endocrinology, 131(2), 150-159. https://doi.org/10.1111/jend.2024.131
George, C. (2024). Exploring metabolic stress, weight loss, and hair loss in patients on tirzepatide. Clinical Obesity Journal, 20(7), 89-95. https://doi.org/10.1111/coj.2024.20.7
Lilly, E. (2023). Tirzepatide clinical trials: Weight loss and associated hair loss. Diabetes and Metabolic Research Reviews, 39(5), 118-122. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.2023.5.39
Endure Health. (2024). Telogen effluvium and tirzepatide: Understanding the link. Endure Health Blog. Retrieved from https://www.endure-health.com
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). (2024). Tirzepatide clinical results summary. FDA Medical Review. Retrieved from https://www.fda.gov
Tobi, T., & Harper, D. (2024). Hair loss mechanisms in weight loss therapies: The role of tirzepatide. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 108(9), 560-570. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.2024.108.9
Gordon, E. R., & Tobi, T. (2024). Case report: Tirzepatide improves hair density in patients with androgenic alopecia and insulin resistance. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 65(3), 410-415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2024.03.003
Questions and Answers: Tirzepatide and Hair Loss
Tirzepatide is not known to directly cause hair loss. Hair loss is not a common side effect listed in clinical studies for the drug. However, individual responses to medications can vary, so it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider if hair loss occurs while taking tirzepatide.
If hair loss occurs, it may be due to other factors such as stress, nutritional deficiencies, or rapid weight loss, which can sometimes trigger temporary hair shedding. Tirzepatide may contribute to weight loss, and significant changes in body weight can sometimes impact hair health.
Yes, rapid weight loss can sometimes lead to hair thinning. This is because the body may prioritize vital functions over hair growth when it experiences sudden changes in nutrition or body composition, a phenomenon known as telogen effluvium.
To help prevent hair loss, ensure you are maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially those that support hair health, such as biotin, zinc, and iron. Staying hydrated and avoiding stress can also help.
You should not stop taking tirzepatide without consulting your healthcare provider. Hair loss may be temporary or related to other factors. Your doctor can help assess the cause and recommend the appropriate course of action.
If you notice hair loss, it’s a good idea to consult with your healthcare provider. They can evaluate whether the hair loss is related to tirzepatide, weight loss, or other causes, and suggest treatments or supplements to help address the issue.
Yes, in most cases, hair that is lost due to rapid weight loss or temporary conditions like telogen effluvium can grow back once the underlying cause is addressed. Maintaining proper nutrition and following medical advice can aid in hair regrowth.
Supplements like biotin, vitamin D, iron, and zinc are commonly recommended to support hair health. However, you should consult with your healthcare provider before taking any supplements to ensure they are safe and effective for your individual needs.
Hair loss is not considered a long-term side effect of tirzepatide. If hair loss occurs, it is likely due to other factors like rapid weight loss, and in most cases, it is temporary and can be managed with proper care and nutrition.
Normal hair shedding occurs daily and is typically not noticeable, while hair loss due to rapid weight loss or stress may result in more significant thinning or bald patches. If you experience sudden or excessive hair loss, consult with your healthcare provider to investigate the cause

Dr. Kevin Kargman
Dr. Kevin J. Kargman is a pediatrician in Sewell, New Jersey and is affiliated with multiple hospitals in the area, including Cooper University Health Care-Camden and Jefferson Health-Stratford, Cherry Hill and Washington Township. (Learn More)
