Table of Contents
Introduction
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can cause thick, red, scaly patches to appear on the skin, often leading to itching, pain, and discomfort. This condition, which can vary from mild to severe, impacts not only the skin but also the overall well-being of those who suffer from it. Psoriasis often affects the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back, but it can appear anywhere on the body. Many people with psoriasis also experience social and emotional challenges, as visible skin symptoms can lead to self-consciousness or even social isolation.
The causes of psoriasis are complex and involve both genetic and environmental factors. The immune system plays a major role in this condition, as psoriasis is considered an autoimmune disorder. In simple terms, this means that the body’s immune system, which normally defends against harmful invaders, mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This results in the rapid growth of skin cells, forming the thick, scaly patches seen in psoriasis.
Despite significant advancements in treatment, managing psoriasis can still be challenging. Traditional treatments include topical creams, light therapy, and oral or injected medications, all of which aim to reduce symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. However, each treatment has its limitations, and many people with psoriasis still search for ways to achieve better control over their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Recently, a new medication called semaglutide has gained attention for its potential benefits in managing psoriasis symptoms. Semaglutide is a medication that was originally developed to help control blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a group of drugs known as GLP-1 receptor agonists, which help regulate blood sugar, reduce appetite, and support weight loss. However, as more research is done, scientists are finding that semaglutide might also have other benefits, including the ability to reduce inflammation in the body.
The link between semaglutide and psoriasis is still being explored, but early findings show promise. Inflammation is a major factor in psoriasis, and semaglutide’s anti-inflammatory effects could potentially help reduce the severity of psoriasis symptoms. People with psoriasis who are struggling to find relief with traditional treatments may find this information exciting, as it represents a potential new option for managing their condition. However, it’s important to understand that research on semaglutide’s effects on psoriasis is still in the early stages, and more studies are needed to confirm its effectiveness and safety for this specific use.
This article aims to provide an in-depth guide to managing psoriasis with semaglutide. It is designed to answer common questions that people ask about semaglutide’s role in psoriasis treatment. You will find information about what psoriasis is, how semaglutide works in the body, and whether it can be effective for relieving psoriasis symptoms. The article will also cover important details about dosage, side effects, and how semaglutide might be used in combination with other psoriasis treatments.
Each section in this guide will take a closer look at different aspects of semaglutide and its potential in managing psoriasis. By the end of the article, you should have a clear understanding of what semaglutide is, how it works, and how it might fit into your overall psoriasis treatment plan. However, it’s essential to remember that while this guide provides valuable information, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you are considering semaglutide as a treatment option, consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial.
In summary, psoriasis is a complex condition that affects both the skin and the immune system. Its symptoms can make everyday life challenging, and finding effective treatments can be a struggle for many people. Semaglutide, a medication originally developed for diabetes and weight loss, may offer new hope for those with psoriasis. While more research is needed, early findings suggest that semaglutide’s anti-inflammatory effects could make it a useful addition to current psoriasis treatments.
With this guide, we hope to shed light on how semaglutide might help those with psoriasis achieve more effective relief from their symptoms. Whether you’re new to psoriasis treatments or looking for alternative options, this article will provide you with detailed, easy-to-understand information to help you make informed decisions about your psoriasis management journey.
What is Psoriasis? Understanding the Disease and Its Impact
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes red, scaly patches to form on the skin. These patches, also called plaques, can be itchy, painful, and often affect a person’s quality of life. While psoriasis mainly affects the skin, it is more than just a skin problem. It is an autoimmune disease, meaning it happens because the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, each with unique symptoms and areas it affects:
- Plaque Psoriasis: This is the most common type, affecting about 80-90% of people with psoriasis. It causes thick, red patches with silvery scales, often appearing on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. These plaques can crack and bleed, causing discomfort.
- Guttate Psoriasis: This type often starts in childhood or young adulthood. It appears as small, red spots on the skin, mostly on the trunk, arms, and legs. Guttate psoriasis is often triggered by infections, such as strep throat.
- Pustular Psoriasis: This type causes white, pus-filled blisters surrounded by red skin. It usually appears on the hands and feet, but in severe cases, it can cover larger areas of the body.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Inverse psoriasis occurs in body folds, like under the arms, behind the knees, or in the groin. It appears as bright red, shiny lesions and is often worsened by sweating and rubbing.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: This is a rare but severe form of psoriasis that can cover most of the body. It causes a widespread, red, peeling rash that can be very painful and itchy. Erythrodermic psoriasis can be life-threatening, and people with it should seek medical attention right away.
Each type of psoriasis has different triggers, but common ones include stress, infections, skin injuries, and certain medications.
Common Symptoms of Psoriasis
The main symptom of psoriasis is red, raised patches on the skin covered with silvery scales. However, symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity. Common symptoms include:
- Itching and Burning: Many people with psoriasis experience intense itching, which can lead to scratching. This can worsen the skin and lead to infections.
- Dry and Cracked Skin: The plaques in psoriasis often become very dry and may crack or bleed, causing discomfort and a risk of infection.
- Nail Changes: About half of people with psoriasis will see changes in their nails, such as pitting (small dents), discoloration, or thickening. In severe cases, the nails may crumble or separate from the nail bed.
- Joint Pain: Psoriatic arthritis is a condition where psoriasis affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. About 30% of people with psoriasis develop psoriatic arthritis, which can lead to permanent joint damage if not treated.
What Causes Psoriasis?
Psoriasis happens because of an overactive immune system. Normally, the immune system fights off harmful bacteria and viruses, but in people with psoriasis, it mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. This immune response causes skin cells to grow too quickly, resulting in the thick, scaly patches of psoriasis.
The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but researchers believe it is a combination of genetic and environmental factors. This means that while people may inherit genes that increase their risk, other factors like stress, infections, and lifestyle choices can trigger or worsen symptoms.
Some common triggers of psoriasis include:
- Stress: High levels of stress can lead to flare-ups or worsen existing symptoms.
- Infections: Certain infections, like strep throat, can trigger guttate psoriasis, especially in children and young adults.
- Injury to the Skin: Cuts, scrapes, or even sunburn can trigger psoriasis in a process known as the Koebner phenomenon.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as beta-blockers (for high blood pressure) and lithium (for mental health conditions), can worsen psoriasis symptoms.
How Psoriasis Affects Quality of Life
Psoriasis can have a major impact on a person’s daily life. The appearance of plaques on visible areas like the face, scalp, and hands can cause embarrassment, leading some people to avoid social situations. The constant itching, burning, and pain can make it difficult to concentrate on work or enjoy daily activities. Psoriatic arthritis can cause joint pain and stiffness, limiting mobility and making physical tasks challenging.
The psychological impact is also significant. Studies show that people with psoriasis are at a higher risk of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. Many people feel frustrated or helpless because there is no cure for psoriasis, only treatments to manage symptoms. This frustration can affect relationships, work life, and overall well-being.
Common Challenges in Managing Psoriasis
Managing psoriasis can be challenging, especially since symptoms may come and go, with periods of remission (when symptoms improve) and flare-ups (when symptoms worsen). Finding the right treatment often involves trial and error, as what works for one person may not work for another.
People with psoriasis must also manage lifestyle factors, like stress and diet, which can affect their symptoms. Staying consistent with treatment and managing triggers can be difficult, but it can lead to better symptom control.
Psoriasis is a chronic and complex condition that goes beyond skin symptoms. It affects physical, emotional, and social aspects of life. Understanding psoriasis in depth helps individuals and healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment options, such as semaglutide, to potentially manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Semaglutide: Mechanism of Action and Primary Uses
Semaglutide is a medication that has gained significant attention for its ability to control blood sugar and support weight loss. This medication belongs to a group called GLP-1 receptor agonists. Understanding what semaglutide is and how it works can help explain why there’s interest in exploring its potential benefits for conditions like psoriasis, which is traditionally unrelated to its original purposes.
What is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is primarily prescribed to people with type 2 diabetes. It works by mimicking a natural hormone in the body called glucagon-like peptide-1, or GLP-1. This hormone is involved in blood sugar control, which is critical for people with diabetes. However, semaglutide has shown benefits beyond just blood sugar control. Research has also shown that it can help with weight loss, which led to its approval for weight management in people with obesity or who are overweight and have health problems related to weight.
How Does Semaglutide Work?
To understand how semaglutide works, it’s helpful to look at the role of GLP-1 in the body. GLP-1 is a hormone naturally produced in the intestines. Its main job is to regulate blood sugar levels, especially after eating. When GLP-1 is released, it helps the pancreas release insulin. Insulin is a hormone that lowers blood sugar levels by helping move sugar from the blood into the cells, where it’s used for energy.
Semaglutide, as a GLP-1 receptor agonist, acts similarly to natural GLP-1. When semaglutide is in the body, it attaches to GLP-1 receptors and activates them. This activation does several things:
- Increases Insulin Production: It signals the pancreas to produce more insulin after meals, which helps to lower blood sugar.
- Reduces Glucagon Release: Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar levels by signaling the liver to release stored sugar. By reducing glucagon, semaglutide helps prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Slows Down Stomach Emptying: Semaglutide slows the rate at which food moves from the stomach to the intestines. This can help people feel fuller for longer, which is one reason why it’s helpful for weight loss.
Primary Uses of Semaglutide
Ozempic has two main FDA-approved uses: managing type 2 diabetes and supporting weight loss.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Semaglutide is prescribed to help control blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. By lowering blood sugar levels and preventing spikes, it helps reduce the risk of complications related to diabetes, such as nerve damage, kidney problems, and vision issues.
- Weight Management: Semaglutide has also been approved as a weight management aid. People who are overweight or have obesity and who also have weight-related health problems may benefit from semaglutide. Its ability to make people feel full for longer can support weight loss goals. Clinical studies have shown that semaglutide can lead to significant weight loss when combined with diet and exercise.
How Might Semaglutide Benefit Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an inflammatory condition, and researchers believe that semaglutide’s effects may go beyond blood sugar control. Semaglutide may have anti-inflammatory properties that could potentially help reduce inflammation in the body. Since psoriasis is driven by inflammation, there’s interest in seeing if semaglutide could reduce psoriasis symptoms or flare-ups. Although this potential benefit is not fully proven, ongoing studies are exploring how semaglutide may impact inflammatory processes.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Inflammation
GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide may influence the immune system, which plays a key role in inflammation. Psoriasis is caused by an overactive immune response, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the skin, causing red, scaly patches. Some early research suggests that GLP-1 receptor agonists can modulate the immune system, potentially reducing inflammation markers in the body. This effect could make semaglutide helpful in conditions marked by inflammation, such as psoriasis.
Limitations and Current Research
While these possible benefits are promising, semaglutide has not been specifically approved for psoriasis treatment. This means that more research is needed to understand if and how semaglutide can help with psoriasis symptoms. Currently, scientists are studying how semaglutide affects inflammation and the immune system in different conditions, including psoriasis. Until more research is available, it’s important to use semaglutide only under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Semaglutide is a medication that was originally developed to help people with type 2 diabetes by controlling blood sugar. It has since been found to aid in weight loss as well, due to its ability to make people feel fuller for longer periods. The medication acts by activating GLP-1 receptors, which support insulin production, reduce glucagon, and slow down digestion. These effects contribute to semaglutide’s primary uses in diabetes and weight management. Due to its possible anti-inflammatory effects, researchers are now exploring if semaglutide could be beneficial in managing conditions involving inflammation, such as psoriasis.

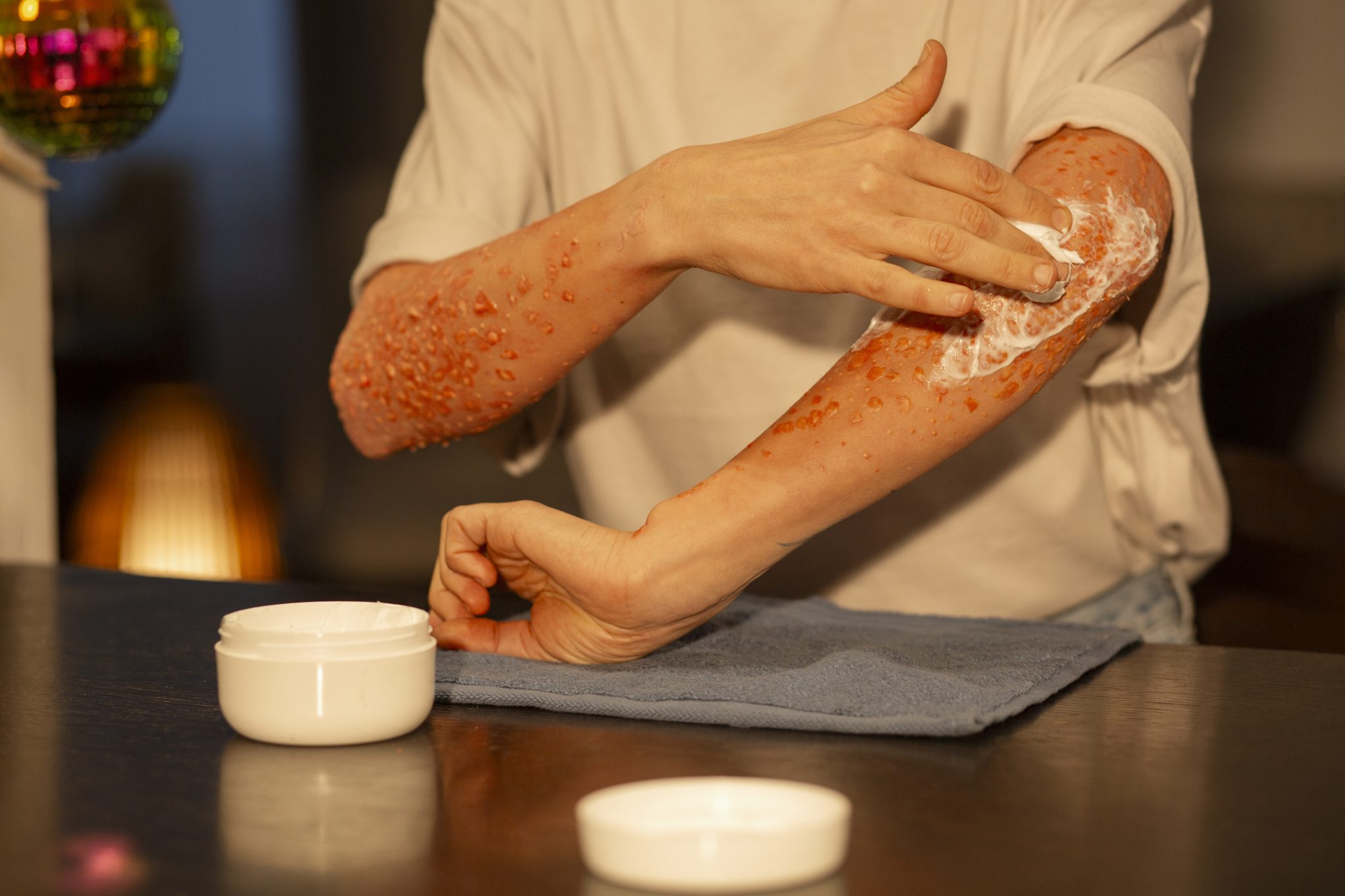
Can Semaglutide Help Alleviate Psoriasis Symptoms?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes red, scaly patches on the skin. It can be painful, itchy, and embarrassing, affecting a person’s quality of life. While there are many treatments available, finding one that effectively manages symptoms for everyone is still a challenge. Recently, researchers have been studying semaglutide—a medication primarily used for type 2 diabetes and weight loss—to see if it could help people with psoriasis.
In this section, we will explore how semaglutide might help with psoriasis, what researchers are discovering, and why this medication might reduce symptoms in some people with the condition. We’ll focus on how semaglutide’s properties may ease inflammation, improve immune response, and provide relief.
How Does Semaglutide Work?
Semaglutide belongs to a group of medications called GLP-1 receptor agonists. GLP-1 stands for glucagon-like peptide-1, which is a hormone the body naturally produces. This hormone helps regulate blood sugar levels by promoting insulin release, which lowers blood sugar. In addition to blood sugar control, GLP-1 also helps with weight management by reducing appetite, helping people eat less, and promoting weight loss.
For people with type 2 diabetes, semaglutide has been effective because it helps control both blood sugar and weight. It is usually given as an injection once a week, making it convenient for patients to manage their condition.
How Might Semaglutide Help With Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, meaning the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells. In psoriasis, this immune reaction causes skin cells to multiply too quickly, leading to thick, red patches on the skin. Because semaglutide has shown potential anti-inflammatory effects, researchers believe it could help with psoriasis.
The exact way semaglutide might benefit psoriasis patients isn’t fully understood yet. However, there are some important theories:
- Reducing Inflammation: Inflammation is a key feature of psoriasis. Semaglutide has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, which might help reduce the swelling, redness, and irritation seen in psoriasis patches. Lowering inflammation could also decrease the frequency of flare-ups, making the condition easier to manage daily.
- Immune System Regulation: Psoriasis is linked to an overactive immune system. Some researchers believe semaglutide might have a role in balancing immune responses. By influencing certain immune cells, semaglutide might help reduce the overreaction that causes psoriasis symptoms. This is still a theory, but it shows promise as scientists continue studying how GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide interact with the immune system.
- Supporting Weight Loss and Metabolism: For people with psoriasis, weight can sometimes make symptoms worse. Obesity has been linked to more severe psoriasis symptoms because excess weight can increase inflammation throughout the body. Semaglutide helps with weight loss, which may indirectly reduce psoriasis symptoms for some people. Losing weight might reduce inflammation levels and lessen the pressure on the immune system, potentially resulting in fewer or less severe psoriasis patches.
What Do Early Studies Show?
So far, research on semaglutide specifically for psoriasis is limited, but early studies are promising. Some people with psoriasis who used semaglutide for diabetes or weight loss reported an improvement in their psoriasis symptoms. Researchers are now working on more studies to understand if these improvements are directly related to semaglutide or are just coincidental.
One small study observed people with type 2 diabetes and psoriasis who were given semaglutide. These patients showed a reduction in both their blood sugar levels and their psoriasis symptoms. The exact numbers were not large enough to make strong claims, but the results were positive enough to encourage further research.
In another study, researchers found that GLP-1 receptor agonists (like semaglutide) could reduce inflammation markers in the body. Although this study did not focus solely on psoriasis, the decrease in inflammation may suggest that semaglutide could help manage inflammatory conditions like psoriasis.
Limitations of Current Research
Although these early findings are exciting, it’s important to note that more research is needed. Semaglutide has not been officially approved for treating psoriasis. Most studies have been small, and researchers are only beginning to understand the link between GLP-1 receptor agonists and psoriasis.
Another challenge is that psoriasis affects everyone differently. A treatment that works well for one person may not work as well for another. It’s also possible that semaglutide may only work for certain types of psoriasis or for people with specific underlying health conditions.
While it’s too early to say that semaglutide is a proven treatment for psoriasis, early findings suggest it could be helpful for some people. Its anti-inflammatory properties, ability to help regulate the immune system, and benefits for weight management all point to its potential in easing psoriasis symptoms. However, anyone interested in using semaglutide for psoriasis should consult with a healthcare provider to discuss its risks, benefits, and the current evidence supporting its use.
As more studies are completed, we may better understand exactly how semaglutide works for psoriasis and whether it could become a regular part of psoriasis management in the future. For now, it remains a promising option that researchers continue to explore.
What Does the Research Say About Semaglutide and Psoriasis?
In recent years, semaglutide has gained attention as a possible treatment for more than just diabetes and weight loss. Some researchers are now exploring how it might help manage chronic skin conditions like psoriasis. While semaglutide isn’t officially approved for treating psoriasis, early studies suggest it may have potential in this area. Understanding what the current research says about semaglutide and psoriasis can help people make informed choices when discussing options with their healthcare provider.
Current Studies and Findings on Semaglutide for Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, causing red, scaly patches. It results from an overactive immune system that speeds up the growth of skin cells, leading to visible and uncomfortable symptoms. Since semaglutide works by impacting the body’s immune and inflammatory responses, some researchers believe it may be able to reduce psoriasis symptoms.
Early studies have looked at how semaglutide affects inflammation in the body. Because inflammation plays a major role in psoriasis, drugs that reduce inflammation could potentially improve psoriasis symptoms. Semaglutide is known to decrease inflammation in people with type 2 diabetes, which is one reason why researchers are exploring its impact on other inflammatory conditions like psoriasis.
One area of interest is how semaglutide affects the release of certain immune cells and cytokines. Cytokines are proteins that act as messengers in the immune system, signaling other cells to trigger inflammation. In psoriasis, specific cytokines are overactive, leading to the skin’s rapid cell turnover. Research suggests that semaglutide might reduce the activity of these cytokines, helping to slow down the rapid skin cell production seen in psoriasis.
How Effective is Semaglutide for Psoriasis?
Currently, the effectiveness of semaglutide for psoriasis isn’t fully understood. Some people with psoriasis who take semaglutide for diabetes or weight loss have reported improvements in their skin. However, these are personal reports, not controlled scientific studies, so the evidence is limited.
In controlled studies on other inflammatory conditions, semaglutide has shown promising results in reducing inflammation markers. While these studies were not focused on psoriasis specifically, they do give researchers reason to believe that semaglutide might also help people with psoriasis. Some researchers hope to conduct more targeted studies on psoriasis in the future to determine if semaglutide could be an effective treatment option.
Safety and Tolerability of Semaglutide in Psoriasis
As with any medication, safety is a major consideration. Semaglutide is generally considered safe when used for its approved purposes, like managing blood sugar in type 2 diabetes and assisting with weight loss. Side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, especially when first starting the medication. For people with psoriasis, understanding these side effects is important because psoriasis can already cause skin discomfort, and adding gastrointestinal symptoms might complicate their experience.
The good news is that studies have shown semaglutide to be well-tolerated in most cases. It is also worth noting that psoriasis itself doesn’t seem to worsen the side effects of semaglutide. However, more research specifically focused on psoriasis patients is needed to confirm these findings and to understand if there are any unique side effects for those with autoimmune skin conditions.
The Need for More Research on Semaglutide and Psoriasis
At this time, there isn’t enough research to recommend semaglutide as a primary treatment for psoriasis. The studies so far provide an encouraging foundation, but they are limited. Most studies on semaglutide have focused on diabetes, weight loss, and overall inflammation. Very few studies have directly examined its effect on psoriasis, so researchers don’t yet have a complete picture of its benefits or risks for people with this condition.
Future research might include clinical trials with people who have psoriasis to see if semaglutide truly helps reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. This research could look at the dosage, frequency, and long-term effects of semaglutide in people with psoriasis. As more studies emerge, doctors and patients may gain a clearer understanding of whether semaglutide can play a reliable role in managing psoriasis.
While semaglutide is showing promise in reducing inflammation and immune response, there is still a need for more studies directly linking it to psoriasis relief. Early findings are hopeful, suggesting that it might help some people with psoriasis due to its effects on inflammation. However, without specific clinical trials focused on psoriasis, it’s too soon to say for sure. Until more information is available, semaglutide should be considered an experimental option for psoriasis and used only under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
How Semaglutide May Influence the Immune System
Psoriasis is a complex condition linked to the immune system. In people with psoriasis, the immune system becomes overactive, mistakenly attacking healthy skin cells. This response causes the rapid buildup of cells on the skin’s surface, leading to the red, scaly patches characteristic of the condition. Understanding how the immune system contributes to psoriasis can help explain how certain treatments, like semaglutide, may offer relief.
The Immune System’s Role in Psoriasis
The immune system is the body’s defense system against infections, injuries, and other harmful substances. Normally, it helps to keep us healthy by fighting off bacteria, viruses, and other invaders. However, in autoimmune conditions like psoriasis, the immune system gets confused. Instead of only targeting harmful invaders, it mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues.
In psoriasis, the immune system sends signals that cause the skin cells to grow too quickly. In a healthy person, skin cells take about a month to rise to the skin’s surface, where they eventually shed. But in someone with psoriasis, this process speeds up, taking only a few days. As a result, the new skin cells pile up, forming thick, scaly patches on the skin’s surface.
How Semaglutide May Affect Immune Regulation
Semaglutide is a type of medication known as a GLP-1 receptor agonist. GLP-1 stands for glucagon-like peptide-1, which is a hormone that naturally occurs in the body. GLP-1 helps regulate blood sugar by signaling the pancreas to release insulin, which lowers blood sugar levels. Semaglutide works by activating GLP-1 receptors, making it especially useful for people with diabetes. Recently, researchers have started exploring how GLP-1 receptor agonists, like semaglutide, may also affect the immune system and inflammation.
One of the key findings is that GLP-1 may reduce inflammation in the body. Inflammation is the immune system’s natural response to injury or infection, but in conditions like psoriasis, it goes into overdrive. This overactivity causes chronic inflammation, which worsens psoriasis symptoms. By reducing inflammation, semaglutide may help slow down the immune system’s attack on healthy skin cells, potentially easing the symptoms of psoriasis.
How Semaglutide Reduces Inflammation
Research suggests that semaglutide may reduce inflammation through several mechanisms. Here are a few ways it could work:
- Decreasing Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines: Cytokines are proteins that act as messengers in the immune system. In psoriasis, certain cytokines tell the immune system to attack the skin. Some studies suggest that GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide may lower the levels of these pro-inflammatory cytokines, helping to reduce the immune response that causes psoriasis symptoms.
- Improving Oxidative Stress: Oxidative stress is a condition where there is an imbalance between free radicals (harmful molecules) and antioxidants in the body. This imbalance can trigger inflammation and worsen autoimmune responses. Semaglutide may help reduce oxidative stress, thereby decreasing inflammation in people with psoriasis.
- Supporting Regulatory Immune Cells: Some immune cells, known as regulatory T-cells, help keep the immune response balanced and prevent it from attacking healthy tissues. Research suggests that semaglutide might support the function of these regulatory cells, promoting a more balanced immune response.
Potential Benefits for Psoriasis Symptoms
If semaglutide can indeed reduce inflammation and balance the immune system, it may offer significant benefits for people with psoriasis. By calming the immune response, semaglutide may slow down the rapid production of skin cells, which could reduce the redness, scaling, and thickness of psoriasis patches. While research is still ongoing, early findings suggest that semaglutide might not only improve blood sugar and weight but also help with inflammation-related conditions like psoriasis.
Limitations and Need for Further Research
While the potential for semaglutide to influence the immune system is promising, it is essential to understand that this is still an emerging area of study. Most research on semaglutide focuses on its use in diabetes and weight management. Studies specifically looking at its effects on psoriasis and other autoimmune conditions are limited. Scientists need more evidence to confirm exactly how semaglutide works on the immune system and whether it is a safe and effective option for long-term psoriasis treatment.
Additionally, while semaglutide may help reduce inflammation, it is not designed to replace standard psoriasis treatments. Traditional treatments, like topical creams, phototherapy, and biologics, are still considered essential for managing psoriasis symptoms effectively. Semaglutide could potentially work as a complementary treatment, adding another layer of relief when used under medical guidance.
Working with Healthcare Providers
If someone with psoriasis is interested in trying semaglutide, it’s crucial to discuss this with a healthcare provider. Since semaglutide is not yet widely prescribed for psoriasis, a doctor’s guidance is necessary to understand the potential benefits, risks, and side effects. A healthcare provider can help determine if semaglutide could be a helpful addition to a patient’s treatment plan and monitor for any changes in psoriasis symptoms.
Semaglutide’s role in managing psoriasis is an exciting area of research. By potentially calming the immune system and reducing inflammation, semaglutide may offer new hope for those with psoriasis. However, more research is needed to fully understand its benefits and risks for this specific condition. For now, semaglutide remains a promising, yet supplementary, option for psoriasis management under the guidance of healthcare professionals.
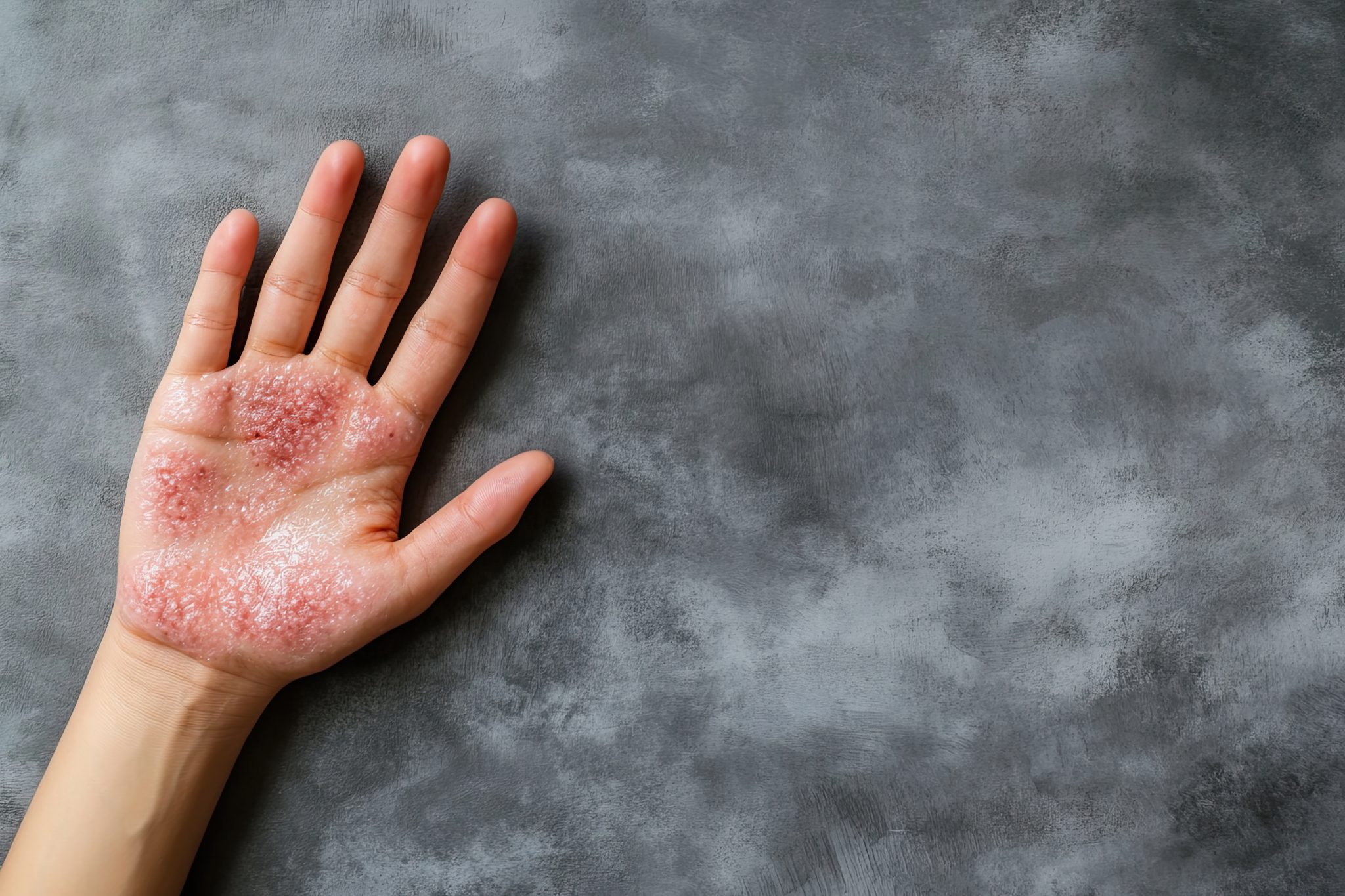
Dosage and Administration of Semaglutide for Psoriasis
When considering semaglutide as a possible treatment for psoriasis, understanding the correct dosage and how to administer the medication safely is essential. Although semaglutide is primarily used for diabetes and weight loss, emerging research suggests that it may help people with psoriasis, particularly due to its potential anti-inflammatory effects. However, since semaglutide is not officially approved for psoriasis, it’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and how to use it effectively.
Recommended Dosage Guidelines for Semaglutide
For people with diabetes, semaglutide is typically prescribed at doses that gradually increase over time. This approach is meant to help the body adjust to the medication, reducing the risk of side effects. The same method is often suggested when semaglutide is used for weight loss. For psoriasis, there are no specific dosage guidelines yet because the use of semaglutide in this context is still being researched. However, healthcare providers may follow a similar approach by starting with a low dose and slowly increasing it, depending on the patient’s response and tolerance.
The usual starting dose of semaglutide for other conditions is 0.25 mg once a week. This starting dose is generally maintained for about four weeks. After this initial period, the dose may be increased to 0.5 mg per week if the individual tolerates it well. For some people, healthcare providers may eventually recommend increasing the dose further, possibly up to 1 mg or even 2 mg per week, depending on the severity of the condition and how well the individual responds to the medication.
It is important to remember that these dosages are general guidelines based on the approved uses of semaglutide. When used for psoriasis, a healthcare provider may adjust these recommendations. Because each person’s response to treatment can vary, it’s essential to follow a personalized plan developed by a medical professional.
Important Considerations for Administration
Semaglutide is given as an injection under the skin, typically in the thigh, stomach, or upper arm. The injection is self-administered using a pre-filled pen. Learning how to use the pen correctly is essential for safe and effective treatment. Healthcare providers often give a demonstration to ensure that the patient knows how to inject the medication properly.
Administering the injection involves cleaning the injection site with an alcohol swab to prevent infection. Then, the pen is placed against the skin, and the medication is delivered by pressing a button on the pen. It’s important to hold the pen in place for a few seconds to ensure the full dose is given. The injection site should be rotated each week to avoid irritation in one area. For example, if the injection is given in the thigh one week, it could be administered in the stomach the next week.
Many people find it helpful to set a reminder to take the medication on the same day each week, as consistency is important for the effectiveness of semaglutide. Since semaglutide is a long-acting medication, missing doses or not taking it consistently can reduce its potential benefits.
Differences in Dosage for Psoriasis Compared to Other Conditions
Since semaglutide is not yet approved for treating psoriasis, there may be adjustments in the recommended dosage when it’s used off-label. In some cases, doctors may start with a lower dose than usual or adjust the increase schedule more slowly to monitor how it affects psoriasis symptoms. The goal is to determine the minimal effective dose, which can help reduce the risk of side effects. Some healthcare providers might recommend additional monitoring if the medication is being used off-label, such as more frequent check-ins or additional lab tests to ensure safety and effectiveness.
It’s important to discuss any changes in symptoms with a healthcare provider, as they may adjust the dosage based on how psoriasis responds to treatment. Additionally, if the patient experiences significant improvement at a lower dose, it may be possible to maintain that dose rather than increasing it further.
Potential Adjustments and Individualized Plans
Because each person responds differently to semaglutide, an individualized treatment plan is crucial. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider can help monitor the effectiveness and make necessary adjustments. The doctor may ask about improvements in psoriasis symptoms, any side effects experienced, and overall health. Based on this feedback, they may choose to increase, decrease, or maintain the current dosage.
For people with other health conditions, such as diabetes, adjustments in semaglutide dosing might also take these factors into account. Managing multiple health issues can sometimes require balancing the benefits and side effects of treatment. A personalized plan ensures that the dosage is appropriate not only for psoriasis but also for any other conditions.
The dosage and administration of semaglutide for psoriasis require careful consideration and close collaboration with a healthcare provider. By following a tailored plan and monitoring how the body responds, patients can increase their chances of finding relief from psoriasis symptoms while minimizing potential risks.
Possible Side Effects and Risks of Using Semaglutide for Psoriasis
When considering semaglutide for psoriasis management, it’s essential to understand the potential side effects and risks. Although semaglutide has shown promise in helping people with conditions like diabetes and obesity, and even more recently in managing psoriasis symptoms, it’s still important to be aware of possible side effects and to take precautions to ensure safe use.
Common Side Effects of Semaglutide
Like any medication, semaglutide can cause side effects, some of which are more common than others. Most of these side effects are mild and manageable. They include:
- Nausea: Nausea is one of the most frequently reported side effects of semaglutide, especially in the first few weeks of use. This happens because semaglutide slows down how fast the stomach empties. For most people, nausea decreases over time as their body adjusts to the medication.
- Vomiting: Some people experience vomiting, especially if nausea becomes severe. Staying hydrated and following dietary advice from a doctor can help reduce the risk of vomiting.
- Diarrhea: Semaglutide can also cause diarrhea. This side effect may be mild for some but bothersome for others. Drinking plenty of fluids can help prevent dehydration if diarrhea occurs.
- Constipation: Ironically, semaglutide may also lead to constipation in some cases. Increasing fiber intake and drinking enough water can help with this side effect.
- Loss of Appetite: Many people report feeling less hungry while using semaglutide. While this can benefit those looking to lose weight, it’s important to ensure that nutritional needs are still being met.
These common side effects are usually temporary. They tend to occur when starting the medication or after a dose increase and often improve as the body gets used to semaglutide.
Less Common but Serious Side Effects
In addition to common side effects, semaglutide carries some less common but more serious risks. While these side effects are rare, they are important to be aware of:
- Pancreatitis: Semaglutide has been associated with pancreatitis, a condition in which the pancreas becomes inflamed. Symptoms of pancreatitis include severe stomach pain, vomiting, and nausea that doesn’t go away. Anyone experiencing these symptoms should stop using semaglutide and seek medical help immediately.
- Kidney Problems: In some cases, semaglutide may cause kidney problems, especially in people who experience severe vomiting or diarrhea and become dehydrated. Staying hydrated and monitoring fluid intake can help prevent kidney issues.
- Increased Heart Rate: Semaglutide may cause an increase in heart rate. This effect has been observed in some clinical studies, but it’s still unclear if it has long-term health effects. People with heart conditions should talk to their doctor before starting semaglutide.
- Eye Problems (Diabetic Retinopathy): In people with diabetes, semaglutide may worsen diabetic retinopathy (damage to the retina of the eye). This side effect is specific to individuals with diabetes, so it may not affect people using semaglutide for psoriasis, but it’s worth noting.
Risks for Individuals with Psoriasis
For people with psoriasis, it’s crucial to consider how semaglutide might interact with other psoriasis medications or affect symptoms. While semaglutide is not specifically designed for psoriasis, some people with the condition have experienced benefits in reducing inflammation. However, certain risks need attention:
- Interactions with Other Psoriasis Treatments: Psoriasis treatments such as corticosteroids, biologics, and methotrexate can have different effects on the immune system and inflammation. Combining these treatments with semaglutide could increase the chance of side effects, so it’s essential to inform healthcare providers about all medications being taken.
- Risk of Skin Reactions: Although uncommon, some individuals might experience skin reactions when using semaglutide. It’s important to watch for any unusual skin symptoms or worsening of psoriasis flare-ups and to report these to a healthcare provider.
Important Precautions When Using Semaglutide for Psoriasis
To reduce the risk of side effects, certain precautions can be taken:
- Start with a Low Dose: Starting at a lower dose of semaglutide and gradually increasing it as directed by a doctor can help the body adjust to the medication and reduce the severity of side effects like nausea and vomiting.
- Monitor Symptoms Closely: Keeping track of any new or unusual symptoms is key. This includes monitoring for signs of pancreatitis, kidney issues, or unusual skin reactions. Writing down symptoms and sharing them with a healthcare provider can help manage side effects effectively.
- Stay Hydrated: Given that some side effects like vomiting and diarrhea can lead to dehydration, it’s important to drink plenty of water and electrolytes. This precaution helps to maintain kidney health and reduce the risk of complications.
- Regular Check-ups: Scheduling regular check-ups with a healthcare provider is essential when taking semaglutide for any purpose, including psoriasis. During these visits, the provider can monitor any potential side effects, adjust dosages if necessary, and address concerns.
Symptoms to Monitor
It’s helpful to know what symptoms might signal a serious issue while taking semaglutide:
- Severe stomach pain (especially with vomiting) can be a sign of pancreatitis.
- Persistent vomiting or diarrhea may lead to dehydration and needs medical attention if it doesn’t improve.
- Changes in skin appearance or new skin reactions, especially for people with psoriasis, should be reported to a healthcare provider.
By staying aware of these possible side effects and risks, individuals can work with their healthcare providers to ensure that semaglutide is both safe and effective for managing their psoriasis symptoms.
Monitoring Progress: Tracking Psoriasis Improvement with Semaglutide
Using semaglutide to manage psoriasis is a promising approach, but it’s essential to track your progress to understand how well the treatment is working. Monitoring can help you see if semaglutide is relieving your symptoms and improving your quality of life. It also helps your doctor decide if adjustments to your treatment plan are necessary. In this section, we’ll cover the best ways to monitor psoriasis improvement, including what to look for, how often to check, and tips for working closely with your healthcare team.
Key Metrics for Tracking Psoriasis Improvement
When monitoring psoriasis, certain signs can show if your condition is improving. These metrics include changes in the appearance of your skin, reduction in discomfort, and overall changes in how you feel.
- Skin Appearance: One of the clearest indicators of improvement is a change in the appearance of your psoriasis patches. If semaglutide is working, you may notice that the red, scaly patches on your skin start to fade or shrink. The scales might become thinner, less flaky, or cover a smaller area. It’s a good idea to track any changes you notice in the size, color, and texture of these patches over time.
- Symptom Relief: Psoriasis can cause itching, burning, or pain, which can affect your daily life. Tracking these symptoms can help you measure progress. If semaglutide is effective, you may feel less discomfort in areas where you have psoriasis. A simple way to monitor this is by rating your pain or itchiness on a scale from 1 to 10 each day or week. Lower numbers over time may indicate that the medication is helping.
- Quality of Life: Psoriasis doesn’t just affect your skin—it can also impact your mental and emotional well-being. Keeping track of how psoriasis affects your mood, sleep, and social activities can provide insight into the treatment’s effectiveness. If you notice that you’re feeling less self-conscious or that your symptoms are interrupting your sleep or activities less often, it could be a sign that semaglutide is making a positive difference.
Frequency and Methods for Monitoring
Regular monitoring is crucial to get an accurate picture of your progress. Here are some effective ways to stay on top of changes in your psoriasis symptoms:
- Weekly or Biweekly Checks: For most people, checking and recording their symptoms once a week or every two weeks is enough to notice trends. Weekly checks allow you to catch gradual changes without feeling overwhelmed by frequent monitoring.
- Taking Photos: A simple yet powerful way to track progress is by taking photos of the affected areas. Photos can provide a clear visual record of how your skin changes over time. Try to take pictures in the same lighting and from the same angles each time, ideally once a week. This approach can make it easier to compare the photos and see if there are visible improvements in your skin’s appearance.
- Keeping a Symptom Log: Write down your symptoms in a journal or app each day or week. Note things like the level of itching, pain, or burning you feel, and any changes you notice in your skin patches. You can use a 1-10 scale to rate your symptoms, which makes it easy to see if things are getting better or worse over time.
- Using a Psoriasis Assessment Tool: Some people find it helpful to use a formal assessment tool, such as the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) or the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI). These tools are often used by doctors to measure psoriasis severity and quality of life. Your doctor can guide you on using these tools to track your progress in a structured way.
Working with Your Healthcare Provider
Monitoring your progress with semaglutide is most effective when you work closely with your healthcare provider. Here are some ways they can support you:
- Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular appointments to review your progress with your doctor. During these check-ups, you can share your symptom log, photos, and any concerns you have about your treatment. Your doctor may perform a physical exam and may use the PASI or DLQI scales to formally assess your condition.
- Adjusting Treatment as Needed: Based on your progress, your doctor may adjust your treatment plan. For example, if you’re not seeing enough improvement, they might suggest a higher dose, a combination of treatments, or even a different medication. By monitoring your symptoms and sharing them with your doctor, you help them make the best decisions for your care.
- Managing Side Effects: Like any medication, semaglutide can have side effects. Regular monitoring can help you notice any new symptoms that might be related to the medication, like nausea or fatigue. If you notice side effects, report them to your doctor right away so they can help you manage them.
Tips for Effective Monitoring
- Be Consistent: Try to monitor your symptoms on the same day each week and in the same way each time. Consistency makes it easier to spot changes over time.
- Stay Positive: Managing psoriasis can be a long journey, and improvements might not happen overnight. Celebrate small victories and remind yourself that even minor improvements can mean that you’re on the right track.
- Involve Your Support System: If you feel comfortable, involve family members or friends in your monitoring routine. They can help you take photos, remind you to log symptoms, or just provide emotional support along the way.
Keeping track of your psoriasis symptoms is a key part of seeing if semaglutide is working for you. By focusing on specific changes in your skin, discomfort, and quality of life, you can better understand the effects of the treatment. Regular monitoring and working closely with your doctor can help ensure you get the best results from semaglutide and stay on top of any adjustments you might need for effective psoriasis relief.
How Can Semaglutide Be Combined with Other Psoriasis Treatments?
For people with psoriasis, treatment can often involve a mix of therapies to manage symptoms effectively. Adding semaglutide to the treatment plan may offer additional benefits, but it’s important to understand how it can work alongside other psoriasis therapies. This section explains the common psoriasis treatments and explores how semaglutide might be combined with them. It also highlights key considerations for safe and effective use under healthcare supervision.
Common Psoriasis Treatments
Psoriasis is usually treated with medications that target the immune system, as well as therapies that work directly on the skin. Here’s a look at some common treatments:
- Topical Treatments: These are creams, ointments, and gels that are applied directly to the skin. They help reduce inflammation, itching, and redness. Examples include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, and retinoids.
- Phototherapy: Also known as light therapy, phototherapy uses controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light to slow down skin cell growth and reduce inflammation. It can be effective but requires careful monitoring to avoid skin damage.
- Systemic Medications: These are drugs taken by mouth or injection that work throughout the body. They’re often prescribed for moderate to severe psoriasis. Common systemic medications include methotrexate, cyclosporine, and newer biologic drugs.
- Biologic Drugs: Biologics are a type of systemic medication that targets specific parts of the immune system, helping to reduce inflammation. They are often used for severe psoriasis or cases that haven’t responded well to other treatments. Examples include adalimumab, etanercept, and ustekinumab.
Each of these treatments can play an important role in managing psoriasis symptoms. However, since semaglutide is a newer option for psoriasis, it’s useful to look at how it might fit into a multi-therapy approach.
How Semaglutide Might Complement Existing Therapies
Semaglutide, primarily used for diabetes and weight loss, has anti-inflammatory effects that could make it useful in managing psoriasis. Here’s how it might work alongside other therapies:
- Reducing Inflammation: Psoriasis is driven by chronic inflammation, and semaglutide’s action as a GLP-1 receptor agonist might help reduce this inflammation. By targeting immune pathways, semaglutide could work with biologics and systemic medications to further lower inflammation levels. This could lead to better symptom control, especially for people with severe psoriasis.
- Supporting Weight Loss: Many people with psoriasis also struggle with weight management. Since semaglutide can help with weight loss, it could indirectly benefit psoriasis symptoms. Research shows that reducing excess weight can lessen the severity of psoriasis. In this way, semaglutide might enhance the effects of existing treatments by helping patients reach and maintain a healthier weight.
- Improving Skin and Joint Health: For those with psoriatic arthritis, a common condition linked to psoriasis, semaglutide’s potential anti-inflammatory effects may also help reduce joint pain and swelling. This could complement treatments specifically aimed at psoriatic arthritis, giving patients broader symptom relief.
Important Considerations for Combining Semaglutide with Other Treatments
When using multiple therapies, there are several key points to consider. Here’s a breakdown of factors to discuss with a healthcare provider:
- Potential Interactions: Combining semaglutide with other medications could lead to interactions. For example, taking semaglutide alongside systemic drugs that affect the immune system might alter how each medication works. Healthcare providers need to monitor for any changes in effectiveness or side effects. It’s essential to share a full list of medications with the doctor to avoid possible risks.
- Dosing Adjustments: When semaglutide is added to the treatment plan, it’s important to monitor if the dosages of other medications need adjustment. This is especially relevant for people taking biologics or systemic drugs, as their dosages may need to be changed based on how semaglutide affects the body’s inflammation levels and immune response.
- Monitoring Side Effects: Each medication comes with potential side effects, and combining them might increase the likelihood of certain symptoms. Semaglutide’s common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and fatigue, while other treatments for psoriasis have their own side effect profiles. Regular check-ups can help manage any issues that arise and ensure all medications are working as intended.
- Healthcare Supervision: Since psoriasis is a chronic condition, it requires ongoing care. Adding semaglutide to a psoriasis treatment plan should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider familiar with both semaglutide and psoriasis treatments. They can help create a plan that balances effectiveness with safety.
Working with Your Healthcare Provider
Combining semaglutide with other psoriasis treatments offers potential benefits, but it’s essential to take a coordinated approach. People with psoriasis should work closely with their healthcare providers to:
- Discuss All Options: Healthcare providers can explain how semaglutide might fit into a broader treatment strategy and help weigh the pros and cons of using multiple therapies.
- Monitor Progress: Regular check-ins help track how the combined therapies are working and allow for adjustments as needed. Monitoring symptoms, weight changes, and overall health can provide valuable feedback on the effectiveness of the combined approach.
- Adjust the Treatment Plan: Psoriasis symptoms can change over time, and treatment plans may need adjustments to stay effective. By collaborating with a healthcare provider, patients can make informed decisions about how and when to modify their treatments.
Using semaglutide in combination with other psoriasis treatments can create a more effective approach to managing symptoms. By understanding how semaglutide might complement therapies like biologics, topicals, and phototherapy, people with psoriasis can work with their healthcare providers to find a treatment plan that best fits their needs. With careful monitoring, open communication, and a focus on long-term care, combining semaglutide with other treatments may offer meaningful relief and improve quality of life for those with psoriasis.
Conclusion
Using semaglutide for managing psoriasis is an exciting and emerging area of treatment that offers new hope to those struggling with the condition. Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the skin, but its impact goes beyond visible symptoms. It can lead to itching, pain, and significant emotional stress. Traditional treatments, such as topical creams and light therapy, often help, but many people continue to face flare-ups and other challenges. Because of its anti-inflammatory effects and ability to regulate certain immune responses, semaglutide is being researched for its potential in helping reduce psoriasis symptoms.
Semaglutide is a type of medication known as a GLP-1 receptor agonist. Initially, it was developed and approved to help manage type 2 diabetes by regulating blood sugar levels. It also became popular for promoting weight loss, as it reduces appetite and helps individuals feel fuller. However, studies are now exploring its benefits for inflammation-related conditions, like psoriasis. Semaglutide works by interacting with specific receptors in the body, which helps control blood sugar, reduce inflammation, and possibly influence the immune system in a way that could ease psoriasis symptoms.
Current research on semaglutide and psoriasis is promising but still in its early stages. While some studies suggest that semaglutide may help reduce inflammation and improve skin health for those with psoriasis, there is no solid evidence yet. These studies indicate that semaglutide may help to calm the immune response, which is what causes the skin to react in individuals with psoriasis. Because semaglutide can lower inflammation, researchers believe it could offer an added benefit to those who have psoriasis along with diabetes or other health issues.
The immune system plays a significant role in psoriasis. Psoriasis is known as an autoimmune condition, meaning the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells. In psoriasis, this reaction causes the rapid growth of skin cells, resulting in scaly patches and red, inflamed skin. By potentially moderating this immune response, semaglutide could help reduce these symptoms and slow down the process that leads to skin irritation. Although more studies are needed to fully understand this effect, the ability of semaglutide to target inflammation makes it a promising option for those with psoriasis.
When considering semaglutide as a treatment for psoriasis, it’s essential to understand the importance of dosage and administration. Semaglutide is typically given as an injection once a week, and the dose is gradually increased. This approach is intended to help the body adjust to the medication and minimize side effects. However, using semaglutide specifically for psoriasis may require different guidance, so it is important to follow a healthcare provider’s instructions closely. Dosage adjustments should always be made under medical supervision, as side effects are possible.
As with any medication, semaglutide may have side effects, including nausea, stomach pain, or fatigue. It is important for patients to be aware of these and discuss any concerns with their doctor. For people with psoriasis, monitoring symptoms and side effects is key. Keeping a symptom diary can help track changes over time, making it easier to see if semaglutide is effective. Tracking improvements and flare-ups can also give healthcare providers important insights into whether the treatment is working or if adjustments are needed.
Using semaglutide together with other treatments can be another option for those with psoriasis. Many people find relief through a combination of therapies, such as topical creams, light therapy, and medications that specifically target psoriasis. Semaglutide could potentially be combined with these treatments to provide a more comprehensive approach. However, any combination therapy should be supervised by a healthcare provider to ensure there are no interactions between medications.
In summary, semaglutide shows potential as a helpful tool in managing psoriasis, but more research is needed to fully confirm its effectiveness for this condition. Semaglutide’s anti-inflammatory properties may be beneficial, especially for individuals who have struggled with standard psoriasis treatments. While it is not yet widely prescribed specifically for psoriasis, the ongoing research into semaglutide’s effects on the immune system is promising. For those interested in trying semaglutide, consulting a healthcare provider is essential. This treatment may provide relief for some, but it must be monitored to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Research Citations
Costanzo, G., Curatolo, S., Busà, B., Belfiore, A., & Gullo, D. (2021). Two birds one stone: Semaglutide is highly effective against severe psoriasis in a type 2 diabetic patient. Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism Case Reports, 2021(1), Article EDM21-0007. https://doi.org/10.1530/EDM-21-0007
Bioscientifica
Malavazos, A. E., Meregalli, C., Sorrentino, F., Vignati, A., Dubini, C., Scravaglieri, V., Basilico, S., Boniardi, F., Spagnolo, P., Malagoli, P., Romanelli, P., Secchi, F., & Iacobellis, G. (2023). Semaglutide therapy decreases epicardial fat inflammation and improves psoriasis severity in patients affected by abdominal obesity and type-2 diabetes. Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism Case Reports, 2023(3), Article 23-0017. https://doi.org/10.1530/EDM-23-0017
Medical Research
Tran, K. A., & Kaffenberger, B. H. (2024). Weighing in on glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in dermatology. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 90(1), 1-2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2024.05.001
JAAD
VanSickle, M. (2024, September 17). The link between psoriasis and semaglutide: A detailed overview for better management. BMI Doctors. https://bmidoctors.com/the-link-between-psoriasis-and-semaglutide-a-detailed-overview-for-better-management/
BMI Doctors
Girnita, D. (2024, September 29). GLP-1 drugs Ozempic, Zepbound, and Mounjaro for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatologist OnCall. https://rheumatologistoncall.com/2024/09/29/glp-1-drugs-ozempic-zepbound-and-mounjaro-for-psoriasis-and-psoriatic-arthritis/
Rheumatologist On Call
Stalvey, K. (2024, October 8). GLP-1 drugs for psoriasis: Can they help or harm? MyPsoriasisTeam. https://www.mypsoriasisteam.com/resources/glp-1-drugs-for-psoriasis-can-they-help-or-harm
My Psoriasis Team
Noted Dermatology. (2024, June 30). Ozempic for psoriasis: Can it help? What you should know! Noted Dermatology. https://www.noteddermatology.com/blog/can-you-treat-psoriasis-with-ozempic
Noted Dermatology
Ferrier, C. (2024, June 11). Exploring semaglutide-induced rash: Causes, prevention, and treatment. BMI Doctors. https://bmidoctors.com/exploring-semaglutide-induced-rash-causes-prevention-and-treatment/
BMI Doctors
Benz, M. (2023, August 28). Psoriasis: Case study finds weight loss drug semaglutide reduced fat around heart. MedicalResearch.com. https://medicalresearch.com/psoriasis-case-study-finds-weight-loss-drug-semaglutide-reduced-fat-around-heart/
Medical Research
JAMA. (2024). As semaglutide’s popularity soars, rare but serious adverse effects are reported. JAMA, 332(15), 1515-1516. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2024.1515
JAMA Network
Questions and Answers: Semaglutide and Psoriasis
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist, commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes and for weight management. It mimics a hormone in the body called GLP-1, which helps regulate blood sugar levels, slows digestion, and reduces appetite. This action helps lower blood sugar and can support weight loss.
Research on semaglutide’s direct effects on psoriasis is limited. However, since semaglutide reduces inflammation and promotes weight loss, it might indirectly benefit psoriasis, as excess weight and inflammation can worsen psoriasis symptoms.
Yes, semaglutide has anti-inflammatory effects due to its impact on blood sugar regulation and weight loss. Psoriasis is an inflammatory condition, so reducing inflammation may help improve symptoms in some individuals.
No, semaglutide is not approved to treat psoriasis. It is approved for managing type 2 diabetes and weight loss. Any effects on psoriasis would be considered secondary and would need further research to confirm.
Weight loss can positively impact psoriasis because excess weight is linked to more severe psoriasis symptoms. Losing weight may reduce the severity and frequency of psoriasis flare-ups in some patients.
Currently, there is limited research specifically linking semaglutide to psoriasis improvement. Some evidence suggests that weight loss and lower inflammation levels, which semaglutide can support, may help reduce psoriasis symptoms, but more studies are needed.
While semaglutide does not directly trigger psoriasis, it may cause side effects such as gastrointestinal issues, which can indirectly stress the body. In some people, stress can be a psoriasis trigger, so monitoring for any effects is important.
Generally, semaglutide is safe for people with psoriasis, especially under the supervision of a healthcare provider. However, as psoriasis patients often have other health concerns, it’s best to discuss all medications with a doctor to avoid any adverse interactions.
Semaglutide doesn’t directly interact with most psoriasis treatments, but combining multiple medications can have complex effects. It’s essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications to ensure safe and effective treatment planning.
People with psoriasis who are also dealing with obesity or type 2 diabetes may benefit from semaglutide. Since weight management is a key factor in controlling psoriasis, semaglutide could be helpful. However, it should be considered in consultation with a healthcare provider to tailor the approach to individual needs.

Dr. Jay Flottman
Dr. Jay Flottmann is a physician in Panama City, FL. He received his medical degree from University of Texas Medical Branch and has been in practice 21 years. He is experienced in military medicine, an FAA medical examiner, human performance expert, and fighter pilot.
Professionally, I am a medical doctor (M.D. from the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston), a fighter pilot (United States Air Force trained – F-15C/F-22/AT-38C), and entrepreneur.
