Table of Contents
Introduction
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a prevalent hormonal disorder impacting millions of women globally. Managing weight is particularly challenging for those with PCOS, often leading to obesity and related health issues. Recently, PCOS weight loss medications have garnered significant interest as a promising solution. This guide will address the top 10 questions about PCOS weight loss medications, offering evidence-based answers to empower you in making informed health decisions.
What is PCOS?
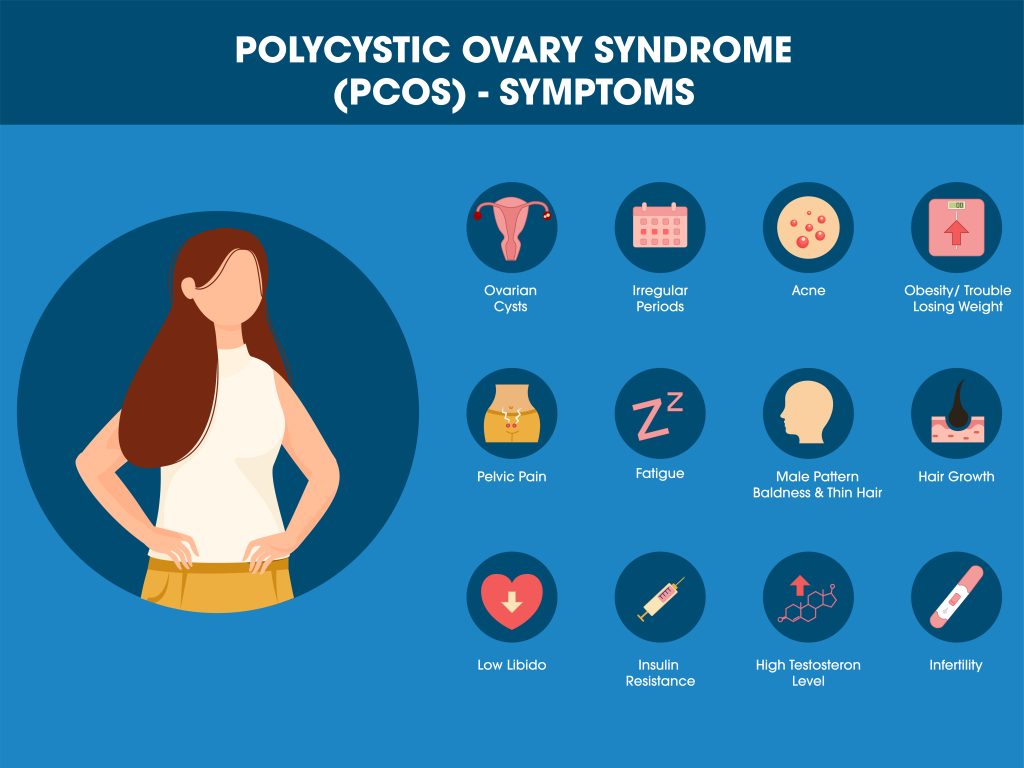
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal disorder impacting individuals with ovaries, especially during their reproductive years. Affecting up to 10% of those of childbearing age, it is one of the most common endocrine disorders among women. PCOS involves a combination of hormonal imbalances, metabolic disturbances, and a variety of symptoms that can significantly affect quality of life.
Hormonal Imbalances
PCOS primarily involves imbalances in sex hormones and insulin. Individuals with PCOS often have elevated levels of androgens, like testosterone, leading to symptoms such as:
- Hirsutism: Excessive facial and body hair
- Acne
- Male-pattern baldness
Additionally, PCOS often causes irregular or infrequent menstrual cycles, sometimes resulting in anovulation (failure to release eggs), which can cause infertility.
Metabolic Disturbances
Insulin resistance is another key feature of PCOS. Insulin, produced by the pancreas, regulates blood sugar levels and helps cells absorb glucose. In PCOS, cells become less responsive to insulin, resulting in higher insulin levels (hyperinsulinemia). This contributes to weight gain, increased fat storage, and a higher risk of type 2 diabetes.
The Ovarian Factor
The term “polycystic” refers to the presence of small, fluid-filled sacs called follicles in the ovaries. These follicles contain immature eggs and can accumulate, leading to enlarged ovaries with a characteristic appearance on ultrasound scans.
A Spectrum of Symptoms
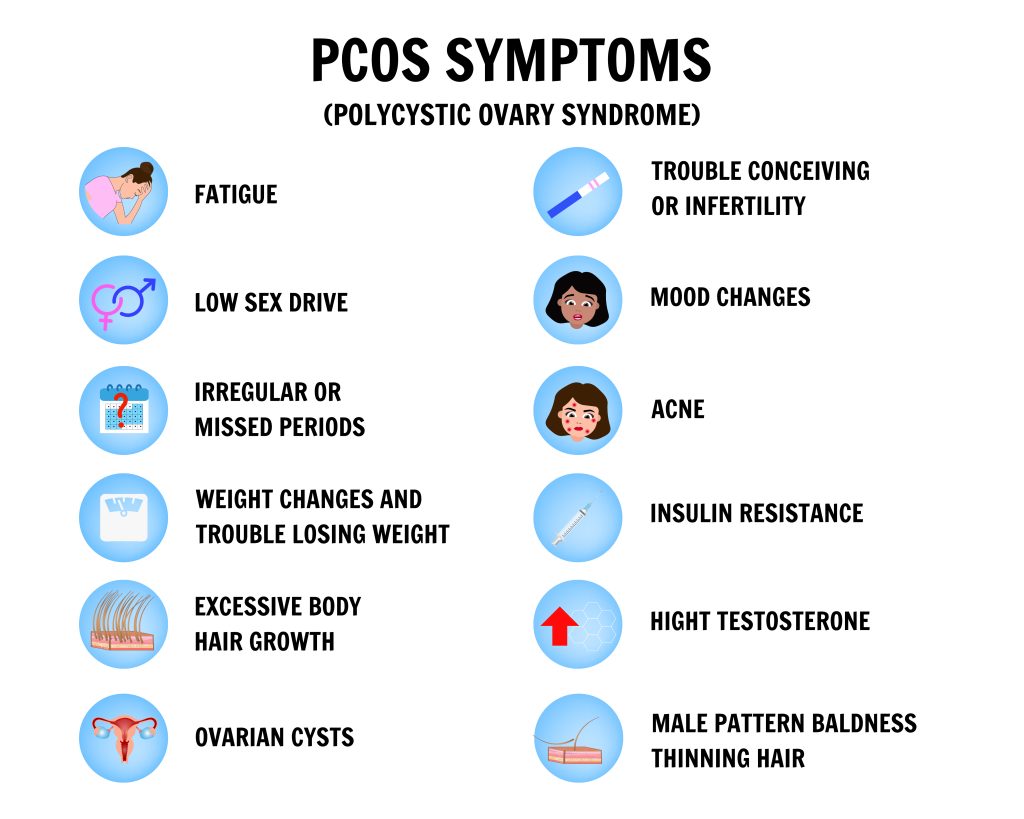
PCOS manifests differently in each person, with a range of symptoms that include:
- Irregular or absent menstrual periods
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Acne
- Unwanted hair growth (hirsutism)
- Thinning of scalp hair (male-pattern baldness)
- Weight gain and obesity
- Insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels
- High cholesterol and triglycerides
- Mood swings and depression
- Sleep apnea
- Fertility issues and difficulty conceiving
Diagnosis and Beyond
Diagnosing PCOS involves a thorough evaluation of medical history, symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests, including hormonal assessments and ultrasounds. PCOS is a diagnosis of exclusion, meaning other conditions with similar symptoms must be ruled out first.
Once diagnosed, managing PCOS is an ongoing process tailored to individual needs. Treatment strategies may include lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions. Addressing hormonal imbalances, metabolic issues, and related symptoms is crucial for improving overall health and well-being.
Understanding PCOS is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment. By addressing its multifaceted nature, individuals with PCOS can work towards achieving better health and quality of life.
Why is Weight Management Important for PCOS?
Weight management is crucial for the effective treatment of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Addressing excess weight is often the first step in managing PCOS symptoms and improving overall health.
Impact of Weight on PCOS Symptoms
Excess weight, affecting 50-80% of individuals with PCOS, exacerbates the condition’s symptoms. Here’s how:
- Insulin Resistance: Obesity worsens insulin resistance, a key feature of PCOS, leading to high blood glucose levels and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Excess fat disrupts hormonal balance, raising androgen and insulin levels, and worsening symptoms like hirsutism, acne, and menstrual irregularities.
- Fertility Challenges: Obesity impairs ovulation and menstrual regularity, complicating fertility. Achieving a healthy weight can enhance ovulation and improve conception chances.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity
Effective weight management boosts insulin sensitivity, enhancing blood sugar control and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Regulation of Menstrual Cycles
Weight management helps regulate menstrual cycles by reducing androgen production and improving the reproductive system’s response to hormonal signals, enhancing fertility and well-being.
Reducing Androgen Levels
Weight loss lowers androgen levels, alleviating symptoms like hirsutism, acne, and male-pattern baldness.
Decreasing the Risk of Comorbidities
Obesity increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, and sleep apnea. Managing weight reduces these risks, significantly improving cardiovascular health in individuals with PCOS.
Enhancing Emotional Well-Being
PCOS can lead to mood swings, anxiety, and depression. Weight management boosts self-esteem and mental health, helping individuals cope better with the emotional challenges of PCOS.
Individualized Approaches to Weight Management
Effective weight management for PCOS should be personalized. Consulting healthcare providers or registered dietitians helps create tailored plans combining dietary changes, exercise, and possibly medication.
Weight management is vital for managing PCOS, impacting symptom severity, hormonal balance, fertility, and overall health. By adopting lifestyle changes and, when necessary, medication, individuals with PCOS can improve their quality of life and reduce long-term health risks associated with this condition.
Empowering Lifestyle Changes for PCOS Weight Management
Lifestyle modifications are fundamental to effectively managing weight in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). This section delves into how targeted lifestyle adjustments not only support weight control but also enhance overall health for individuals with PCOS.
Dietary Strategies
To combat PCOS, informed dietary choices are key:
- Balanced Diet: Emphasize a diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Limit refined sugars and heavily processed foods to stabilize blood sugar levels and aid in weight management.
- Portion Awareness: Monitor portion sizes to avoid overeating and manage caloric intake efficiently.
- Low Glycemic Index Foods: Opt for foods that gradually release glucose into the bloodstream, preventing rapid blood sugar spikes.
- Consistent Eating Schedule: Regular, balanced meals and snacks prevent excessive hunger, reducing the temptation for poor dietary choices.
- Hydration: Focus on water and herbal teas to stay hydrated, avoiding sugary drinks.
Physical Activity
Integrating regular exercise into your routine is vital:
- Calorie Expenditure: Exercise burns calories, facilitating weight loss and maintenance.
- Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity: Regular physical activity improves the body’s insulin utilization, reducing resistance.
- Hormonal Balance: It can lower androgen levels and normalize menstrual cycles.
- Stress Reduction: Activities like walking, swimming, or yoga effectively manage stress, mitigating PCOS symptoms.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: Consistent exercise boosts heart health and lowers risks associated with PCOS.
Stress Management
Addressing stress is crucial:
- Implement mindfulness, meditation, and yoga to alleviate stress and enhance well-being.
Sleep Quality
Adequate sleep is essential:
- Target 7-9 hours per night to stabilize hormones and control hunger, reducing impulsive eating.
Behavioral Approaches
Effective behavioral strategies include:
- Goal Setting: Define realistic, measurable goals for weight and health.
- Progress Tracking: Use food diaries or apps to maintain accountability.
- Community Support: Engage with professionals and support groups for motivation and guidance.
Commitment to Change
Acknowledge the journey:
- Understand that significant, lasting changes in weight and PCOS symptoms take time and persistence. Setbacks are part of the process, but consistency is key.
By embracing these lifestyle changes, individuals with PCOS can actively manage their weight, improve metabolic health, and significantly enhance life quality. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in tailoring these strategies to individual needs, ensuring both effectiveness and sustainability.
When is PCOS Weight Loss Medication Considered?
Deciding to use weight loss medication for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a significant step that should be made carefully and in consultation with a healthcare provider. Such medication is generally reserved for individuals who have not achieved desired weight loss through lifestyle changes or face serious health risks due to excess weight. Here, we outline key factors considered when determining the need for PCOS weight loss medication.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
Healthcare providers prioritize BMI when considering weight loss medication. BMI, calculated from height and weight, indicates if a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Medication is typically considered for those with a BMI in the overweight or obese range, especially if lifestyle changes have been ineffective or if there are significant health risks.
Lifestyle Modifications
Before medication is prescribed, significant efforts in lifestyle modifications are encouraged. This includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep. These changes are the first line of treatment and can often lead to substantial improvements in weight management and overall health.
Health Risks and Comorbidities
The presence of additional health risks and comorbidities heavily influences the decision to use medication. Individuals with PCOS who are overweight or obese are at increased risk for type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and cardiovascular disease. If these risks are significant and not adequately managed by lifestyle changes, medication may be considered to help mitigate these dangers.
Fertility Goals
For those struggling with infertility due to PCOS, achieving a healthy weight can enhance fertility. In such cases, weight loss medication may be prescribed to expedite weight loss and improve ovulatory function, though it is usually part of a broader fertility treatment plan.
Hormonal Imbalance
PCOS is marked by hormonal imbalances, such as elevated androgen levels and insulin resistance. Certain medications, like birth control pills, can help regulate menstrual cycles and reduce androgen levels, indirectly aiding weight loss. These medications might be considered for individuals with pronounced hormonal imbalances.
Individualized Assessment
The decision to prescribe weight loss medication is highly individualized, based on a thorough assessment of the person’s unique situation, goals, and health status. Factors such as age, overall health, medication tolerance, potential side effects, and patient preferences are all considered.
Ongoing Monitoring
Once medication is initiated, regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential. Continuous monitoring ensures the effectiveness of the medication, manages any side effects, and allows for necessary adjustments to the treatment plan, aligning with the individual’s health goals.
PCOS weight loss medication is considered when lifestyle changes alone are insufficient or when there are significant health risks due to excess weight. The decision is tailored to the individual’s BMI, lifestyle efforts, health risks, fertility goals, hormonal balance, and overall health. Healthcare providers guide patients through a comprehensive treatment plan, which may include weight loss medication to achieve optimal health outcomes.
Medications for PCOS Weight Loss
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) presents unique challenges in weight management. Various medications can help achieve weight loss goals, with a focus on emerging options like GLP-1 receptor agonists such as semaglutide.
Metformin
Metformin is commonly prescribed for PCOS, especially for those with insulin resistance. It improves insulin sensitivity and controls blood sugar levels, indirectly aiding in weight loss by enhancing glucose utilization. However, its effectiveness can vary among individuals.
Birth Control Pills
Certain birth control pills, containing hormones like ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone, can regulate menstrual cycles, lower androgen levels, and alleviate symptoms like hirsutism and acne. These hormonal adjustments may also contribute to weight management.
Anti-Obesity Medications
Anti-obesity medications are increasingly used for PCOS-related weight loss, often alongside lifestyle changes and medical supervision. Notable examples include:
- Orlistat: Reduces dietary fat absorption in the intestines, leading to lower calorie intake.
- Phentermine-Topiramate: Combines an appetite suppressant with an antiseizure drug to reduce appetite and increase fullness.
Spironolactone
Spironolactone addresses acne, excessive hair growth, and hair loss due to high androgen levels. While not directly promoting weight loss, it can improve emotional well-being and indirectly support weight management.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, Including Semaglutide
GLP-1 receptor agonists, initially developed for type 2 diabetes, have shown significant weight loss effects. They mimic the hormone GLP-1, enhancing feelings of fullness, reducing food intake, and improving insulin sensitivity. Semaglutide, administered via weekly injection, has been particularly effective in clinical trials for PCOS weight management.
Individualized Medication Selection
Selecting the right medication for PCOS weight loss requires a personalized approach by a healthcare provider, considering factors like BMI, insulin resistance, hormonal profile, specific symptoms, and overall health goals. The choice should also account for potential side effects, medication tolerance, and patient preferences.
Medication alone is not a magic solution. Effective PCOS weight management combines medication with dietary changes, regular physical activity, and lifestyle modifications. Close monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider are crucial for tracking progress, assessing side effects, and adjusting the treatment plan as needed.
Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential to determine the most suitable treatment plan for each individual’s unique circumstances and health goals.
How Do PCOS Weight Loss Medications Work?
Understanding how PCOS weight loss medications function is vital for individuals considering these treatments and healthcare providers prescribing them. Each medication targets specific pathways to address insulin resistance, hormonal imbalances, and appetite regulation. Here’s an in-depth look at how these medications assist with PCOS-related weight loss.
Metformin
Metformin is a well-known medication for managing PCOS, primarily targeting insulin resistance. Its mechanisms of action include:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Metformin enhances how cells respond to insulin, helping regulate blood sugar levels and reducing weight gain associated with insulin resistance.
- Reduced Liver Glucose Production: Metformin decreases the liver’s glucose output, stabilizing blood sugar levels and aiding weight loss.
- Appetite Regulation: For some individuals, Metformin influences appetite, potentially reducing calorie intake.
Birth Control Pills
Certain birth control pills help address hormonal imbalances and regulate menstrual cycles in PCOS patients. Their mechanisms include:
- Hormonal Regulation: Birth control pills with hormones like ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone provide consistent hormonal signals to the ovaries, normalizing menstrual cycles and indirectly supporting weight management.
Anti-Obesity Medications
Anti-obesity medications, such as orlistat and phentermine-topiramate, are designed to aid weight loss. Their mechanisms include:
- Reduced Fat Absorption: Orlistat inhibits enzymes that break down dietary fat, reducing calorie absorption and promoting weight loss.
- Appetite Suppression: Phentermine, a component of phentermine-topiramate, suppresses appetite by affecting brain centers that regulate hunger, decreasing food intake.
Spironolactone
Spironolactone is prescribed for PCOS-related symptoms like acne, hirsutism, and hair loss. Its mechanisms include:
- Androgen Reduction: Spironolactone is an anti-androgen that lowers androgen levels, alleviating symptoms and potentially aiding weight management by addressing hormone-related factors.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, Including Semaglutide
GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as semaglutide, have shown significant weight loss benefits through unique mechanisms:
- Appetite Regulation: These medications mimic the hormone GLP-1, enhancing feelings of fullness, reducing food intake, and slowing gastric emptying.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: GLP-1 receptor agonists enhance insulin sensitivity, aiding in blood sugar control and indirectly supporting weight management.
- Brain Effects: Some GLP-1 receptor agonists influence brain appetite centers, promoting satiety.
- Fat Metabolism: They can impact fat metabolism, contributing to fat loss.
PCOS weight loss medications operate through various mechanisms, targeting insulin resistance, hormonal imbalances, and appetite regulation. Understanding these mechanisms helps inform treatment decisions and set realistic expectations. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial to determine the most suitable medication and treatment plan tailored to the individual’s unique circumstances and health goals.
Potential Benefits and Risks of PCOS Weight Loss Medications
Considering PCOS weight loss medications requires a thorough evaluation of their benefits and risks. These medications can significantly aid in weight management and alleviate PCOS symptoms, but they also come with potential side effects. In this section, we will explore the key benefits and risks associated with PCOS weight loss medications.
Potential Benefits of PCOS Weight Loss Medications
- Weight Reduction: These medications can help individuals with PCOS achieve and maintain a healthier weight, improving insulin sensitivity, hormonal balance, and overall health.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Medications like metformin and GLP-1 receptor agonists enhance insulin sensitivity, helping cells utilize glucose more effectively. This reduces the risk of elevated blood sugar levels and insulin resistance, crucial for those with PCOS-related insulin issues.
- Hormonal Regulation: Birth control pills and spironolactone can regulate menstrual cycles and lower androgen levels, alleviating symptoms like irregular periods, excessive hair growth, and acne.
- Appetite Control: GLP-1 receptor agonists and phentermine-topiramate help regulate appetite, supporting weight loss and healthier food choices.
- Increased Self-Esteem: Achieving weight loss goals can boost self-esteem and emotional well-being, significantly benefiting those struggling with PCOS.
- Fertility Enhancement: Weight loss and hormonal regulation through medications may improve fertility for individuals with PCOS trying to conceive.
Potential Risks and Considerations
- Side Effects: Common side effects include gastrointestinal discomfort, headaches, dizziness, and changes in taste. Discuss these potential issues with a healthcare provider.
- Medication Tolerance: Not everyone tolerates these medications equally. Adverse reactions may necessitate discontinuation or alternatives, requiring close monitoring by a healthcare provider.
- Interactions with Other Medications: PCOS weight loss medications may interact with other medications. Provide a complete list of all medications, supplements, and herbal products to your healthcare provider to avoid potential interactions.
- Long-Term Safety: The long-term safety of newer medications like semaglutide is still being studied. Ongoing research aims to understand their effects over extended periods.
- Treatment Duration: The duration of medication use can vary. Some individuals may use them short-term to achieve weight loss, while others may need long-term use to maintain weight and manage symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Medications should complement, not replace, lifestyle changes. A balanced diet, regular physical activity, and stress management remain crucial for maximizing benefits and minimizing risks.
- Individual Response: Responses to medications vary. What works for one person may not be effective for another. Tailored treatment plans by healthcare providers are essential.
Consultation with a Healthcare Provider
Before considering PCOS weight loss medications, a thorough discussion with a healthcare provider specializing in PCOS or endocrinology is crucial. They will assess benefits and risks based on your unique situation, health goals, and medical history, monitoring effectiveness and side effects to adjust the treatment plan as needed.
PCOS weight loss medications can offer significant benefits in weight management, insulin sensitivity, hormonal regulation, and overall health. However, their potential risks must be carefully evaluated with a healthcare provider to make informed decisions about their suitability for your health goals.

PCOS Weight Loss Medication: Considerations and Alternatives
Deciding on PCOS weight loss medication involves careful consideration of several factors and exploring alternative strategies to ensure the best approach for your unique health needs. This section will guide you through these considerations and present alternative methods for managing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
Considerations Before Starting Medication
Lifestyle Modifications: Prioritize lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and sufficient sleep. These foundational efforts are crucial for effective weight management.
Health Goals: Clearly define your health goals with your healthcare provider. Whether your focus is on weight loss, hormonal balance, fertility, or symptom relief, your goals will guide the treatment approach.
Medication Tolerance: Evaluate your tolerance for potential side effects. Different medications have varying profiles, and individual responses differ. Openly discuss any side effects with your healthcare provider.
Patient Preferences: Consider your comfort with medication administration methods, whether oral or injectable. Communicate your preferences and concerns with your provider.
Comorbidities: Assess your risk for PCOS-associated conditions like type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and sleep apnea. Effective weight management can significantly impact these conditions.
Medication Duration: Understand the expected duration of medication use, whether short-term for weight loss or long-term for maintenance and symptom management.
Alternative Strategies for PCOS Weight Management
While medications can be effective, alternative strategies also play a vital role:
Dietary Modifications: Adopt a diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Limit processed and sugary foods. A registered dietitian can help create a personalized plan.
Regular Physical Activity: Engage in enjoyable physical activities like walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing for at least 150 minutes per week. Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity and aids in weight loss.
Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing, or yoga. Stress reduction helps regulate hormones and emotional well-being.
Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Proper sleep is essential for hormonal balance and overall health.
Support Groups: Join support groups or seek counseling to manage the emotional challenges of PCOS. Emotional support is key to maintaining motivation and mental well-being.
Mindful Eating: Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues, avoiding emotional eating and mindless snacking.
Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating. Use measuring tools and track your food intake if necessary.
Behavioral Strategies: Work with a healthcare provider or therapist to develop strategies addressing emotional eating, cravings, and other weight management challenges.
Medical Supervision: Regular consultations with a healthcare provider or dietitian can help monitor progress, adjust treatment plans, and provide lifestyle guidance.
Combining Medication and Lifestyle Changes
For some, combining medication with lifestyle changes may be the most effective approach. These strategies can complement each other, addressing the complex factors contributing to weight gain and PCOS symptoms. This combined approach should be tailored to your specific needs by a healthcare provider.
Considering PCOS weight loss medication requires evaluating lifestyle modifications, health goals, medication tolerance, preferences, comorbidities, and duration. Exploring and integrating alternative strategies like dietary changes, physical activity, stress management, and behavioral approaches ensures a comprehensive approach to managing PCOS. Partner with a healthcare provider to achieve your health and weight management goals.
Conclusion
Navigating weight management in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex journey that demands informed decisions and strong collaboration between patients and healthcare providers. As highlighted in this comprehensive discussion, PCOS weight loss medication offers a strategic tool to tackle weight gain and hormonal imbalances.
PCOS weight loss medication isn’t a universal remedy; it’s a personalized approach tailored to individual circumstances, health goals, and medical histories. Open, transparent discussions with healthcare providers are essential to determine the best course of action. These medications can significantly aid weight reduction, improve insulin sensitivity, regulate hormones, control appetite, and alleviate PCOS symptoms, especially when lifestyle changes alone fall short.
However, the choice to use PCOS weight loss medication must be made with a full understanding of potential risks and considerations. Side effects, medication tolerance, and individual responses require careful evaluation. Medication should be seen as one component of a comprehensive treatment plan, which includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and behavioral strategies. These lifestyle modifications not only enhance the effectiveness of medication but also contribute to long-term well-being.
Moreover, alternative strategies such as dietary changes, exercise, and stress reduction should not be overlooked. Often, a combination of medication and lifestyle adjustments provides the most effective approach to managing PCOS-related weight gain.
In conclusion, managing weight in PCOS is a dynamic and personalized process. By partnering with healthcare providers, staying informed about treatment options, and adopting a holistic approach that includes medication, lifestyle changes, and emotional support, individuals with PCOS can achieve improved health, enhanced well-being, and empowered self-management. The ultimate goal extends beyond weight loss to achieving a healthier, happier, and more fulfilling life for those living with PCOS.
Research Citations
Here are some research citations related to PCOS and weight loss medications:
- Domecq JP, Prutsky G, Mullan RJ, et al. Lifestyle modification programs in polycystic ovary syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(12):4655-4663. doi:10.1210/jc.2013-1287
- Morley LC, Tang T, Yasmin E, Norman RJ, Balen AH. Insulin-sensitising drugs (metformin, rosiglitazone, pioglitazone, D-chiro-inositol) for women with polycystic ovary syndrome, oligo amenorrhoea and subfertility. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;11(11):CD003053. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003053.pub6
- Naderpoor N, Shorakae S, de Courten B, Misso ML, Moran LJ, Teede HJ. Metformin and lifestyle modification in polycystic ovary syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2015;21(5):560-574. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmv025
- Teede HJ, Misso ML, Costello MF, et al. Recommendations from the international evidence-based guideline for the assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod. 2018;33(9):1602-1618. doi:10.1093/humrep/dey256
- Arentz S, Abbott JA, Smith CA, Bensoussan A. Herbal medicine for the management of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and associated oligo/amenorrhoea and hyperandrogenism; a review of the laboratory evidence for effects with corroborative clinical findings. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14:511. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-14-511
- Legro RS, Dodson WC, Kris-Etherton PM, et al. Randomized controlled trial of preconception interventions in infertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(11):4048-4058. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-2776
- Aroda VR, Bain SC, Cariou B, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide versus once-daily insulin glargine as add-on to metformin (with or without sulfonylureas) in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 4): a randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, multinational, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(5):355-366. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30092-4
- Cussons AJ, Watts GF, Mori TA, et al. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation decreases liver fat content in polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized controlled trial employing proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94(10):3842-3848. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-0375
- Moran LJ, Pasquali R, Teede HJ, Hoeger KM, Norman RJ. Treatment of obesity in polycystic ovary syndrome: a position statement of the Androgen Excess and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Society. Fertil Steril. 2009;92(6):1966-1982. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.09.018
- Ehrmann DA, Liljenquist DR, Kasza K, Azziz R, Legro RS, Ghazzi MN. Prevalence and predictors of the metabolic syndrome in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(1):48-53. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-1329
These studies provide insights into various treatment modalities for PCOS, including lifestyle modification, insulin-sensitizing medications like metformin, and other interventions commonly used for weight management in PCOS patients. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before initiating any treatment regimen for PCOS.
Questions and Answers about PCOS weight loss medications
PCOS weight loss medication refers to medications prescribed to individuals with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) to assist in managing their weight. These medications work through various mechanisms, such as improving insulin sensitivity, regulating hormones, controlling appetite, and reducing calorie absorption.
Candidates for PCOS weight loss medication are typically individuals with PCOS who have struggled to achieve their weight management goals through lifestyle modifications alone, especially when there are significant health risks associated with excess weight.
Common PCOS weight loss medications include metformin, birth control pills, anti-obesity medications like orlistat and phentermine-topiramate, spironolactone, and GLP-1 receptor agonists such as semaglutide.
Yes, PCOS weight loss medications can have potential side effects, which may vary depending on the medication. Common side effects include gastrointestinal discomfort, headaches, dizziness, changes in taste perception, and more. It’s important to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider.
The duration of PCOS weight loss medication use can vary. Some medications may be prescribed for a specific period to achieve weight loss goals, while others may be used long-term to maintain weight loss and manage PCOS symptoms. The duration is determined by the individual’s health goals and healthcare provider’s recommendations.
PCOS weight loss medications can contribute to weight loss, but individual responses vary. Success often depends on factors such as adherence to medication, concurrent lifestyle changes, and the specific medication used. Weight loss is not guaranteed, and outcomes may differ among individuals.
Some PCOS weight loss medications can indirectly enhance fertility by regulating menstrual cycles and improving hormonal balance. However, they should be considered as part of a comprehensive fertility treatment plan in consultation with a healthcare provider.
Yes, there are alternative strategies for managing PCOS-related weight gain. These include lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and behavioral strategies. Alternative approaches can be effective and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Yes, in many cases, a combination of PCOS weight loss medication and lifestyle changes can be the most effective approach. These strategies can complement each other, addressing multiple factors contributing to weight gain and PCOS symptoms.
The decision to use PCOS weight loss medication should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider. Factors to consider include your health goals, medication tolerance, potential side effects, and individual circumstances. A healthcare provider can provide guidance and develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.

Dr. Jay Flottman
Dr. Jay Flottmann is a physician in Panama City, FL. He received his medical degree from University of Texas Medical Branch and has been in practice 21 years. He is experienced in military medicine, an FAA medical examiner, human performance expert, and fighter pilot.
Professionally, I am a medical doctor (M.D. from the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston), a fighter pilot (United States Air Force trained – F-15C/F-22/AT-38C), and entrepreneur.
