Table of Contents
Introduction
Semaglutide is a groundbreaking therapy that is transforming how doctors treat type 2 diabetes and help people manage their weight. It is part of a class of medications called GLP-1 receptor agonists. These medications work by mimicking a natural hormone in the body that regulates blood sugar levels, slows down digestion, and helps control appetite. Semaglutide is available in both injectable and oral forms, making it a versatile option for patients. Over the past few years, semaglutide has gained significant attention for its impressive results, particularly in helping people lose weight and improve their blood sugar levels.
The story of semaglutide begins with its primary use: the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). For people with diabetes, managing blood sugar is essential to prevent complications like heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage. Traditional treatments for diabetes include medications like insulin or metformin. However, semaglutide offers a newer and highly effective alternative. By acting like the natural GLP-1 hormone, it not only lowers blood sugar but also reduces the risk of other diabetes-related health problems.
In addition to diabetes treatment, semaglutide has also been approved for weight loss. Obesity is a major health concern worldwide, linked to conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. Losing weight can be very challenging, even with diet and exercise. For many people, semaglutide provides a powerful tool to help achieve meaningful and lasting weight loss. Clinical trials have shown that patients taking semaglutide lose significantly more weight compared to those using other treatments or lifestyle changes alone.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved different forms of semaglutide for these uses. For type 2 diabetes, it is sold under the brand names Ozempic (a weekly injection) and Rybelsus (a daily oral tablet). For weight management, semaglutide is marketed as Wegovy, a higher-dose weekly injection specifically designed to treat obesity or overweight individuals who have related health conditions like high cholesterol or type 2 diabetes. Each of these medications works in a similar way but is tailored to meet the needs of different patients.
The introduction of semaglutide has marked a turning point in medical treatment for diabetes and weight loss. Unlike many older medications, semaglutide offers multiple benefits in one therapy. It not only lowers blood sugar and promotes weight loss but also helps reduce appetite and cravings, which can make long-term lifestyle changes easier to maintain. Additionally, because it is taken weekly (in injection form), it is often more convenient for patients compared to daily medications. This convenience has improved treatment adherence, meaning patients are more likely to stick with the medication long enough to see positive results.
In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about semaglutide therapy. We will answer the most common questions about how it works, its effectiveness, side effects, safety, and who can use it. We will also explain how semaglutide is different from other treatments and what makes it a preferred option for many patients. This information will help you understand why semaglutide is considered a major breakthrough and how it is improving the lives of millions of people around the world.
By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of why semaglutide is such a powerful tool in modern medicine. Whether you are someone managing type 2 diabetes, struggling with weight loss, or simply curious about this innovative therapy, the following sections will provide all the information you need in a clear and easy-to-understand way. Semaglutide’s impact on diabetes and weight management is changing lives, and learning about it could help you or someone you know take control of their health.
What Is Semaglutide and How Does It Work?
Semaglutide is a medication that has gained a lot of attention in recent years. It is used to treat type 2 diabetes and help people lose weight. Semaglutide belongs to a group of drugs called GLP-1 receptor agonists. These drugs work by mimicking a natural hormone in the body called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1).
GLP-1 is a hormone made in the small intestine. It plays a big role in regulating blood sugar levels and appetite. After you eat a meal, GLP-1 is released into the bloodstream. This hormone helps lower blood sugar, slow down digestion, and tell your brain that you feel full. Semaglutide copies the actions of this hormone, which is why it is so effective. Let’s break down exactly how semaglutide works and why it is important for people with diabetes or weight concerns.
How Does Semaglutide Work in the Body?
- Regulates Blood Sugar Levels:
In people with type 2 diabetes, the body does not use insulin properly. Insulin is a hormone that helps move sugar (glucose) from the blood into the body’s cells for energy. When insulin doesn’t work well, blood sugar stays high, which can lead to serious health problems over time.
Semaglutide helps by increasing insulin release from the pancreas. However, it only triggers insulin when blood sugar levels are high. This means semaglutide lowers blood sugar but has a lower risk of causing hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) compared to some other diabetes drugs.
In addition, semaglutide reduces the amount of glucagon in the blood. Glucagon is another hormone that increases blood sugar by telling the liver to release stored glucose. By lowering glucagon levels, semaglutide helps keep blood sugar in a healthy range. - Slows Down Digestion:
Semaglutide also slows down how quickly food leaves your stomach. This is called delayed gastric emptying. Normally, after eating a meal, food moves into the small intestine where nutrients are absorbed. When this happens too quickly, blood sugar can spike.
By slowing digestion, semaglutide helps reduce these sharp spikes in blood sugar. This slower process also makes people feel full for a longer time, which can reduce overeating. - Reduces Appetite:
One of the main reasons semaglutide is so effective for weight loss is its effect on appetite. The medication acts on certain parts of the brain, particularly the areas that control hunger and fullness. Semaglutide sends signals to the brain that make you feel full, even after eating smaller portions of food.
This effect helps people naturally eat less, which leads to a decrease in calorie intake and, eventually, weight loss.
Forms of Semaglutide
Semaglutide is available in three main forms, each designed for a specific purpose:
- Ozempic: This is an injectable form of semaglutide used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is given once a week as a subcutaneous injection (under the skin). Ozempic not only lowers blood sugar but also helps people lose weight as a secondary benefit.
- Wegovy: This is also an injectable form, but it is approved specifically for chronic weight management. Wegovy is given as a once-weekly injection, similar to Ozempic. However, the doses for Wegovy are higher because it is designed for people trying to lose weight, not just manage blood sugar.
- Rybelsus: Unlike Ozempic and Wegovy, Rybelsus is a tablet taken by mouth. It is the first and only oral form of semaglutide. Rybelsus is used to treat type 2 diabetes but has not been approved for weight loss.
Each of these forms works in the same way, but their dosages and specific uses are slightly different. Doctors will decide which form is best for you based on your health needs and goals.
Why Is Semaglutide Important?
Semaglutide is important because it addresses two major health problems: type 2 diabetes and obesity. Both of these conditions are very common worldwide. They can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage.
The ability of semaglutide to control blood sugar, promote weight loss, and reduce appetite makes it a powerful tool in medicine. For people with type 2 diabetes, it helps manage their condition and lowers the risk of complications. For people who are overweight or obese, it provides a safe and effective way to lose weight, which can improve overall health.
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist that works by mimicking a natural hormone in the body. It lowers blood sugar, slows digestion, and reduces appetite. This triple-action process makes it very effective for both type 2 diabetes and weight loss.
The three forms of semaglutide—Ozempic, Wegovy, and Rybelsus—allow people to choose the option that best suits their health needs. Whether through injections or oral tablets, semaglutide has become a key breakthrough in helping people achieve better health outcomes.
What Conditions Is Semaglutide Approved For?
Semaglutide is a powerful medication approved for treating two main conditions: type 2 diabetes and chronic weight management. These approvals were granted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) after strong clinical evidence showed semaglutide’s ability to improve health outcomes for people struggling with these conditions. Below, we will discuss each condition in detail and explain the situations where semaglutide is used.
Semaglutide for Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a condition where the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot use insulin effectively. Insulin is the hormone that helps control blood sugar levels. When blood sugar levels remain too high for a long time, it can cause serious health problems like heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage.
Semaglutide is approved for treating adults with type 2 diabetes because it helps improve blood sugar control. It works by mimicking a natural hormone called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1). This hormone helps the body:
- Increase insulin production when blood sugar levels are high.
- Slow down digestion, which prevents blood sugar spikes after eating.
- Reduce the liver’s production of glucose (sugar), keeping blood sugar under control.
The brand name Ozempic is the most common form of semaglutide for diabetes treatment. It is injected under the skin once a week. A newer form, Rybelsus, is an oral tablet taken daily. Both options give people with type 2 diabetes flexibility in how they take the medication.
It is important to note that semaglutide is not approved for type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is a different condition where the body produces little or no insulin. Since semaglutide depends on the body’s insulin response, it is not effective for people with type 1 diabetes.
Semaglutide for Chronic Weight Management
In addition to diabetes, semaglutide is approved for chronic weight management in adults who are obese or overweight and have related health conditions. Being overweight can lead to problems like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and sleep apnea. Losing weight reduces the risk of these conditions and improves overall health.
The FDA approved semaglutide for weight loss after studies showed it could help people lose a significant amount of weight when combined with healthy diet and exercise. In clinical trials, many participants lost 10% to 15% of their body weight over several months. This is much more effective than most other weight loss medications currently available.
The brand name Wegovy is the version of semaglutide approved for weight loss. It is given as a once-weekly injection. Wegovy is designed for adults who meet the following criteria:
- Body Mass Index (BMI) of 30 or higher – This means they are considered obese.
- BMI of 27 or higher with at least one weight-related health condition – Conditions include high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, or high cholesterol.
Wegovy works for weight loss by reducing appetite and increasing feelings of fullness. By slowing digestion, semaglutide makes people feel satisfied with smaller meals, leading to fewer calories consumed. Over time, this helps people lose weight and keep it off.
Key Differences Between Diabetes and Weight Loss Use
While semaglutide is approved for both diabetes and weight loss, there are a few key differences:
- Doses: The dose of semaglutide for weight loss (Wegovy) is higher than the dose used for diabetes (Ozempic or Rybelsus). The higher dose allows for more significant appetite control and weight loss.
- Target Population: Wegovy is specifically for adults struggling with obesity or being overweight. Ozempic and Rybelsus are designed for adults with type 2 diabetes.
- Goals of Treatment:
- For diabetes: The main goal is to lower blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
- For weight loss: The goal is to help people lose weight and improve related health problems.
Not Approved for Everyone
While semaglutide is effective for many people, it is not approved for certain groups. For example:
- Children and teenagers: Semaglutide is currently not approved for people under the age of 18.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: It is not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding due to unknown effects on the baby.
- People with specific medical conditions: Those with a history of pancreatitis or a type of thyroid cancer called medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) should not take semaglutide.
Semaglutide is approved to treat two major health concerns: type 2 diabetes and obesity-related weight problems. Its ability to control blood sugar and promote weight loss makes it a valuable tool for improving health outcomes. However, it must be used correctly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safety and effectiveness.

How Effective Is Semaglutide for Weight Loss?
Semaglutide has been shown to be a highly effective treatment for weight loss in people with obesity or those who are overweight. It works by reducing hunger, increasing feelings of fullness, and helping people eat less. These effects are backed by strong clinical evidence from studies involving thousands of people. In this section, we will look at how much weight people can lose with semaglutide, how long it takes to see results, and the factors that can influence its success.
Clinical Trial Results and Evidence
Semaglutide has been tested in large clinical trials to understand how well it works for weight loss. One of the most important studies was called the STEP program. In these trials, researchers gave semaglutide to people with obesity or those who were overweight. Most participants also made healthy lifestyle changes, such as eating better and exercising regularly.
The results were very impressive:
- Average weight loss: People who took semaglutide lost around 10-15% of their body weight on average. Some participants lost even more. For example, someone weighing 200 pounds might lose 20 to 30 pounds with treatment.
- Comparison to placebo: In these studies, people who took a placebo (a treatment with no active drug) only lost about 2-3% of their body weight. This shows that semaglutide significantly improves weight loss compared to lifestyle changes alone.
The weight loss results were seen across different groups of people, including men and women, and those of different ages and ethnic backgrounds. The findings from these studies have been a major reason why semaglutide is now used as a treatment for weight loss.
How Long Does It Take to See Results?
People usually start noticing weight loss after a few weeks of using semaglutide. However, the best results happen over a longer period, usually around 6 to 12 months. The STEP trials showed that the most weight loss occurred during the first 6 months, with continued improvements up to a year.
The reason weight loss takes time is that semaglutide starts at a low dose and is gradually increased. This slow increase helps the body adjust to the medication and reduces side effects like nausea. Once people reach the full dose, they see greater benefits.
How Semaglutide Helps with Weight Loss
Semaglutide helps with weight loss in three key ways:
- Reduces appetite: Semaglutide targets the brain’s hunger centers to make people feel less hungry. This means they eat smaller portions and snack less.
- Increases fullness: It slows down the emptying of the stomach, so people feel full for a longer time after meals. This reduces the urge to eat frequently.
- Improves food control: Many people who struggle with obesity have difficulty controlling their eating habits. Semaglutide helps people stick to their calorie goals, making healthy eating easier.
These effects work together to create a calorie deficit, which is necessary for weight loss.
Factors That Influence Weight Loss with Semaglutide
While semaglutide is very effective, the amount of weight loss can vary from person to person. Several factors can influence how well the medication works:
- Diet and exercise: Semaglutide works best when combined with healthy eating and regular physical activity. People who follow a balanced, lower-calorie diet and exercise regularly tend to lose more weight.
- Consistency: Taking semaglutide as prescribed is important. Missing doses or stopping treatment early can reduce its effectiveness.
- Body response: Everyone’s body responds differently to medications. Some people lose weight quickly, while others may see slower progress.
- Medical conditions: Conditions like thyroid problems or hormone imbalances may affect weight loss outcomes.
It is important to set realistic goals and track progress over time. For example, losing 5-10% of body weight can already lead to significant health benefits, such as better blood pressure, improved blood sugar levels, and lower cholesterol.
Why These Results Matter
The effectiveness of semaglutide for weight loss is significant because obesity is a major health problem worldwide. Losing weight helps reduce the risk of serious diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and stroke. Even small amounts of weight loss can make a big difference in a person’s overall health and quality of life.
The strong clinical evidence behind semaglutide makes it a valuable tool for people who have struggled to lose weight through diet and exercise alone. It provides a science-backed option for people with obesity or weight-related health problems.
Semaglutide is one of the most effective treatments for weight loss available today. With an average weight loss of 10-15%, it has helped many people achieve results that were previously hard to reach. When combined with lifestyle changes and proper medical guidance, semaglutide offers a promising solution for long-term weight management.
How Effective Is Semaglutide for Type 2 Diabetes?
Semaglutide has proven to be one of the most effective medications for managing type 2 diabetes. It works by helping the body control blood sugar levels and provides additional health benefits for people with diabetes. This section explains how semaglutide improves blood glucose control, compares it with other diabetes medications, and discusses its added benefits, such as protecting the heart.
Improving Blood Sugar Levels
Semaglutide belongs to a group of medications called GLP-1 receptor agonists. These drugs mimic a natural hormone in the body called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1). GLP-1 is released in response to food and has important effects that help regulate blood sugar:
- It stimulates the pancreas to release insulin when blood sugar levels are high. Insulin helps move sugar from the blood into the body’s cells, where it can be used for energy.
- It slows down digestion by delaying how quickly the stomach empties. This means sugar is absorbed into the bloodstream more slowly after eating.
- It reduces the release of glucagon, another hormone that raises blood sugar levels.
These combined effects help people with type 2 diabetes keep their blood sugar levels within a healthy range. In clinical trials, people taking semaglutide saw significant reductions in their HbA1c levels. HbA1c is a test that measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2 to 3 months. Lowering HbA1c is an important goal in diabetes management because high levels increase the risk of long-term complications.
On average, semaglutide lowers HbA1c by 1.5% to 2.0% when taken at the recommended doses. For many patients, this brings their HbA1c below the target level of 7%, which is the standard goal set by medical guidelines.
How Semaglutide Compares to Other Diabetes Medications
Semaglutide stands out because it provides strong blood sugar control while also offering other benefits. Compared to other diabetes drugs like metformin, sulfonylureas, or insulin, semaglutide has several advantages:
- Weight Loss: Unlike insulin and sulfonylureas, which can cause weight gain, semaglutide often leads to weight loss. This is a significant benefit for people with type 2 diabetes, as many struggle with obesity or being overweight. Weight loss can also improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier to manage blood sugar levels.
- Lower Risk of Hypoglycemia: Semaglutide does not cause low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) when used alone. However, when combined with insulin or sulfonylureas, the risk of hypoglycemia increases, so doses of other medications may need to be adjusted.
- Once-Weekly Dosing: Semaglutide is convenient to use because it is injected just once per week. This can make it easier for patients to stick to their treatment plan compared to medications that must be taken multiple times per day.
Studies show that semaglutide is more effective at reducing HbA1c and supporting weight loss compared to older GLP-1 receptor agonists like exenatide or liraglutide.
Additional Health Benefits
One of the most impressive aspects of semaglutide is its ability to protect against complications associated with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death for people with diabetes. Controlling blood sugar is important, but managing other risks, like heart disease, is just as critical.
Clinical trials have shown that semaglutide reduces the risk of major heart-related events. In the SUSTAIN-6 trial, semaglutide lowered the risk of heart attack, stroke, and death from cardiovascular causes in people with type 2 diabetes. This means that semaglutide does more than just lower blood sugar; it helps prevent life-threatening complications.
In addition to cardiovascular benefits, semaglutide may also help protect the kidneys. Kidney disease is a common complication of diabetes, and research suggests that semaglutide slows the progression of kidney damage in people with diabetes.
Long-Term Results
Studies have shown that semaglutide is effective in both the short and long term. People who use semaglutide for longer periods continue to see improvements in blood sugar levels and weight loss. However, the best results occur when semaglutide is combined with healthy lifestyle changes, such as eating a balanced diet and staying physically active.
Semaglutide is highly effective at managing type 2 diabetes by lowering blood sugar levels, supporting weight loss, and reducing the risk of heart disease. Compared to other diabetes treatments, semaglutide offers several advantages, such as fewer side effects, convenient weekly dosing, and long-term cardiovascular benefits. This makes it an important option for people with type 2 diabetes who need better blood sugar control and additional protection from complications.
What Are the Side Effects of Semaglutide?
Like all medications, semaglutide can cause side effects. While many people take semaglutide without major problems, it is important to know what side effects can happen. Most side effects are mild, but some can be serious. In this section, we will explain the common and rare side effects of semaglutide. We will also discuss what to do if side effects occur and who should avoid this medication.
Common Side Effects
The most common side effects of semaglutide are related to the digestive system. This is because semaglutide works by slowing down digestion, which can cause gastrointestinal issues. These side effects usually happen when someone first starts the medication or when the dose is increased. Most people find that these side effects improve over time as their body adjusts.
- Nausea
- Nausea is the most frequently reported side effect of semaglutide. This happens because the medication slows the movement of food from the stomach into the intestines. When food stays in the stomach longer, it can make you feel queasy.
- Tips to manage nausea:
- Eat smaller meals throughout the day instead of large meals.
- Avoid greasy, fried, or spicy foods.
- Drink water slowly and in small sips.
- Try eating bland foods like crackers, toast, or rice.
- Vomiting
- Some people may vomit, especially when they first start semaglutide. This is often linked to nausea and the slower digestion caused by the drug. Vomiting usually improves after a few weeks.
- If vomiting is severe, contact your doctor. Severe vomiting can lead to dehydration.
- Diarrhea and Constipation
- Semaglutide can cause changes in bowel habits. Some people may have diarrhea, while others may become constipated. These symptoms are usually mild and go away after a few weeks.
- Tips to manage diarrhea:
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Avoid foods high in fat, caffeine, or artificial sweeteners.
- Tips to manage constipation:
- Eat high-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Drink enough water throughout the day.
- Take short walks to help your digestion.
- Decreased Appetite
- Semaglutide reduces appetite, which is one of the reasons it helps with weight loss. While this can be a benefit for many people, it may also lead to eating too little, which can make you feel weak or tired.
- To avoid this:
- Make sure you eat balanced, nutritious meals even if you are not hungry.
- Focus on foods with protein and healthy fats to keep your energy up.
- Fatigue
- Some people report feeling more tired than usual when they start semaglutide. This may happen as the body adjusts to the medication and reduced calorie intake.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
While rare, semaglutide can cause more serious side effects. If you experience any of the following, stop taking the medication and contact your doctor immediately.
- Pancreatitis (Inflammation of the Pancreas)
- Pancreatitis is a rare but serious condition that can happen when taking semaglutide. Signs of pancreatitis include:
- Severe stomach pain that does not go away.
- Pain that may spread to your back.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Pancreatitis requires immediate medical care, as it can become life-threatening if left untreated.
- Pancreatitis is a rare but serious condition that can happen when taking semaglutide. Signs of pancreatitis include:
- Thyroid C-Cell Tumors
- Animal studies have shown that semaglutide can cause thyroid tumors in rodents. It is unknown if this happens in humans, but people with a family history of medullary thyroid cancer or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 should not take semaglutide.
- Signs to watch for:
- A lump or swelling in the neck.
- Trouble swallowing or breathing.
- Hoarseness or a persistent sore throat.
- Severe Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
- Semaglutide rarely causes low blood sugar on its own. However, when taken with insulin or certain diabetes medications (like sulfonylureas), it can lead to severe hypoglycemia.
- Signs of low blood sugar include:
- Shaking or sweating.
- Dizziness or confusion.
- Feeling very hungry.
- To treat low blood sugar, eat or drink something with fast-acting sugar, like juice or glucose tablets.
- Gallbladder Problems
- Semaglutide may increase the risk of gallstones or gallbladder inflammation. Signs of gallbladder problems include:
- Sudden, sharp pain in the upper right side of the abdomen.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Fever or yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice).
- Semaglutide may increase the risk of gallstones or gallbladder inflammation. Signs of gallbladder problems include:
Who Should Avoid Semaglutide?
Certain people should not take semaglutide due to the risk of serious side effects. These include:
- People with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid cancer.
- People with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2.
- Anyone who has had pancreatitis in the past.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women, as the effects on the baby are unknown.
When to Contact Your Doctor
If you are taking semaglutide and experience any unusual or severe symptoms, contact your healthcare provider. It is important to monitor how your body reacts to the medication. Your doctor may adjust your dose or recommend stopping the treatment if side effects are severe.
Most people who take semaglutide experience only mild side effects that go away with time. However, it is important to be aware of the possible risks and know when to seek medical help. By following your doctor’s instructions and reporting any problems, you can safely use semaglutide to manage diabetes or lose weight.
Who Can and Cannot Take Semaglutide?
Semaglutide has become a major treatment option for type 2 diabetes and weight loss. However, not everyone can use it safely. Doctors carefully consider a person’s health, age, and medical history before prescribing this medication. In this section, we will discuss who can take semaglutide and who should avoid it.
Who Can Take Semaglutide?
- Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
Semaglutide is approved for adults who have type 2 diabetes. It helps these individuals manage their blood sugar levels. Studies have shown that semaglutide lowers hemoglobin A1C, a key measure of blood sugar control. Better blood sugar levels help prevent complications like nerve damage, kidney problems, and vision loss.
Semaglutide is not insulin. It works differently by helping the pancreas release the right amount of insulin when blood sugar is high. It also slows down digestion, which helps people feel full for longer. - Adults Who Are Overweight or Obese
Semaglutide is also approved for adults who struggle with obesity or being overweight. For this use, people must have a Body Mass Index (BMI) of:- 30 or higher (considered obese), or
- 27 or higher (considered overweight) with weight-related health conditions, such as high blood pressure, heart disease, or sleep apnea.
- People in this category often benefit from semaglutide because it reduces appetite and helps them lose weight. Along with diet changes and exercise, semaglutide helps improve overall health.
- People with Weight-Related Health Problems
If someone has other health problems related to their weight, such as heart disease or high cholesterol, semaglutide can help. Losing weight reduces the risk of these conditions and improves overall well-being.
Who Should Not Take Semaglutide?
While semaglutide is safe for many people, some groups should avoid it. Taking the medication under these circumstances could lead to serious health risks.
- People with a Personal or Family History of Thyroid Cancer
Semaglutide is not recommended for people with a history of medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) or for those with a condition called Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). These are rare conditions involving abnormal thyroid growths.
In animal studies, semaglutide caused thyroid tumors. Although these results have not been proven in humans, people with thyroid cancer risks should avoid this medication.
If you or your family members have had thyroid cancer, you must tell your doctor before starting semaglutide. - People with a History of Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas, a gland that produces insulin and digestive enzymes. Semaglutide has been linked to a small risk of pancreatitis. If someone has had pancreatitis before, they may face a higher risk of it happening again while taking semaglutide.
Signs of pancreatitis include severe stomach pain that moves to the back, nausea, and vomiting. Anyone with a history of this condition should talk to their doctor to explore safer options. - Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women
Semaglutide is not recommended during pregnancy or while breastfeeding. The medication can harm an unborn baby, so pregnant women should not use it.
If a woman is planning to become pregnant, she should stop semaglutide at least two months before trying to conceive. This is because the drug stays in the body for a long time.
Breastfeeding mothers should also avoid semaglutide. It is not yet known if the drug passes into breast milk, and its effects on infants are unclear. - Children Under 18
Semaglutide is not approved for people under the age of 18. Researchers are still studying how the drug affects children and teenagers. Until more is known, doctors will not prescribe it to people in this age group. - People with Severe Gastrointestinal Problems
Semaglutide slows down the movement of food through the stomach. While this helps with appetite control, it can cause problems for people with serious stomach or digestive conditions.
For example, people with gastroparesis (delayed stomach emptying) may experience worse symptoms, such as bloating, nausea, and pain. Those with other gastrointestinal disorders should discuss their condition with their doctor before considering semaglutide.
Other Factors to Consider
In addition to the groups above, some people need extra care while taking semaglutide:
- People with Kidney Problems: Semaglutide can sometimes cause dehydration due to vomiting or diarrhea. Dehydration may worsen kidney function in people with existing kidney disease.
- People with Liver Problems: Doctors may need to monitor liver function during treatment.
- People Taking Other Medications: Semaglutide can interact with other drugs, including insulin or oral diabetes medications. Adjustments to dosages may be necessary.
Before starting semaglutide, doctors carefully review each patient’s medical history, current health, and other medications. Semaglutide is effective for many people with type 2 diabetes or obesity, but it is not for everyone. People with thyroid issues, pancreatitis, or severe digestive problems should avoid it. Pregnant or breastfeeding women and children under 18 should also steer clear of this treatment.
By identifying who can safely take semaglutide, healthcare providers ensure the best results while avoiding unnecessary risks. Patients should always discuss their full health history with their doctor to determine if semaglutide is right for them.
How Is Semaglutide Administered?
Semaglutide is available in two main forms: an injection and an oral tablet. How it is taken depends on the specific brand of semaglutide prescribed and the condition being treated. The injection form is more common and is typically used for both diabetes management and weight loss. The oral tablet is only approved for diabetes treatment.
Here is a detailed explanation of the two forms, how they are given, and what patients need to know to use them correctly.
Forms of Semaglutide
- Subcutaneous Injection (Wegovy and Ozempic):
- Subcutaneous means the medication is injected just under the skin.
- Wegovy is specifically approved for weight loss in adults with obesity or overweight who also have weight-related health conditions.
- Ozempic is used to treat type 2 diabetes and improve blood sugar control.
- Both Wegovy and Ozempic come in prefilled, single-use pens. These pens are designed for once-weekly injections.
- Oral Tablet (Rybelsus):
- Rybelsus is a tablet that you swallow.
- It is only approved for type 2 diabetes, not for weight loss.
- Unlike the injection, Rybelsus must be taken every day.
How to Use the Injection Form of Semaglutide
The subcutaneous injection is straightforward and can be done at home. Most people find it easy to use because the pens are prefilled and do not require measuring the dose.
Steps for Administering the Injection:
- Choose the Injection Site:
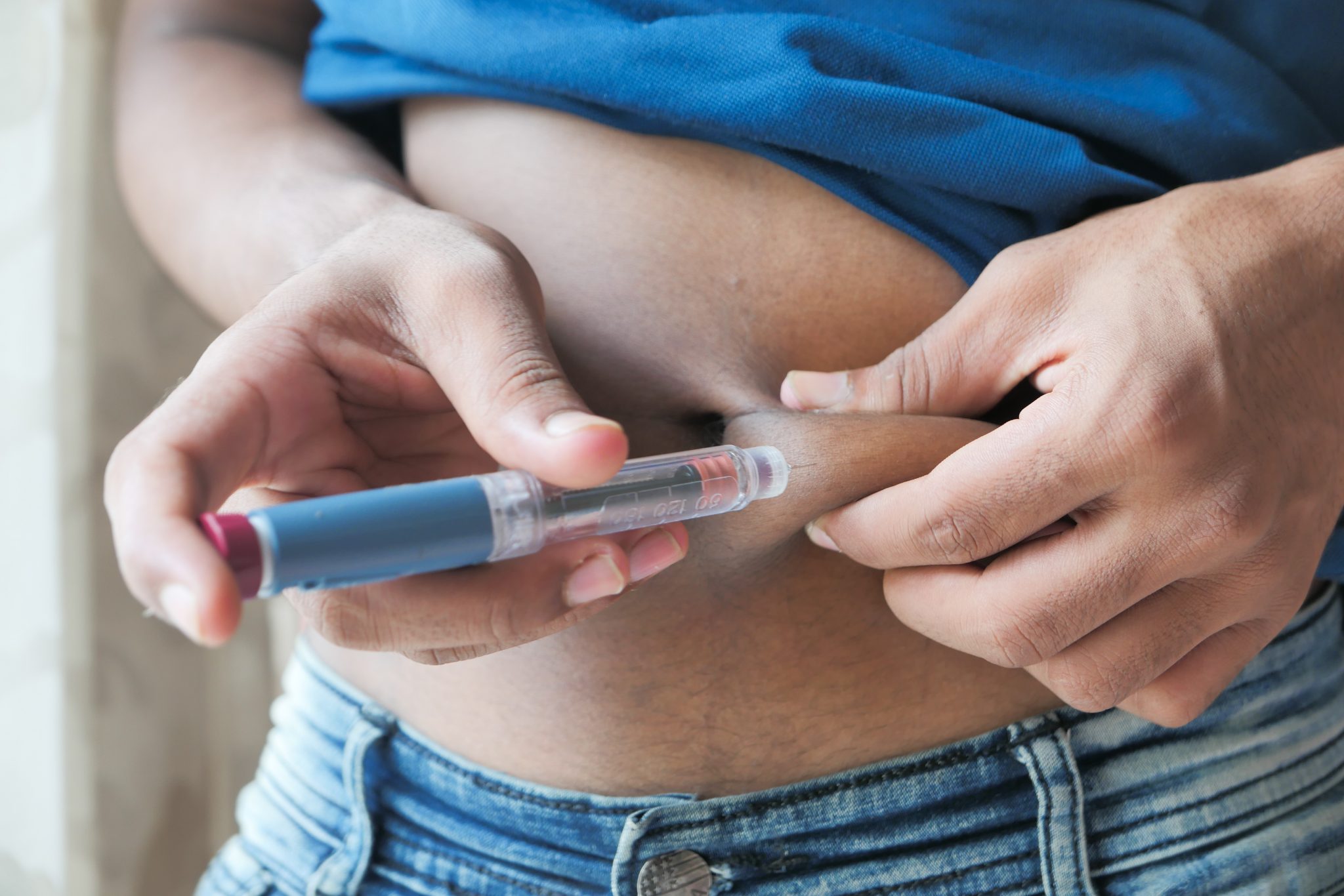
Semaglutide can be injected in three main areas:- The stomach (about 2 inches away from the belly button).
- The upper thigh (front of the leg).
- The upper arm (the fatty part).
- You should rotate the injection site each week to avoid irritation or hard lumps under the skin.
- Prepare the Pen:
- Check that the pen is not expired.
- Inspect the solution inside the pen. It should be clear and colorless. If it is cloudy or has particles, do not use it.
- Attach a new needle to the pen.
- Turn the dose selector on the pen to the correct dose prescribed by your doctor.
- Administer the Injection:
- Pinch a small area of skin at the chosen injection site.
- Push the needle straight into the skin at a 90-degree angle.
- Press the button on the pen to release the dose. Hold the pen in place for at least 6 seconds to ensure the full dose is delivered.
- Remove the pen and safely dispose of the needle.
- After the Injection:
- Store the pen properly, as instructed.
- Keep track of your weekly injection schedule. It is best to give the injection on the same day each week to help you remember.
How to Use the Oral Tablet Form of Semaglutide
Rybelsus is the only GLP-1 receptor agonist available in pill form. It must be taken very carefully to ensure the body absorbs it properly.
Steps for Taking Rybelsus:
- Take It on an Empty Stomach:
- You must take the pill first thing in the morning, on an empty stomach.
- Swallow the tablet with a small sip of plain water (about 4 ounces). Do not use other liquids like coffee, juice, or milk, as these can interfere with absorption.
- Wait 30 Minutes Before Eating or Drinking:
- After taking the pill, do not eat, drink, or take any other medication for at least 30 minutes.
- This waiting time is necessary to allow the medication to be properly absorbed into your bloodstream.
- Stick to a Daily Routine:
- Take the tablet at the same time every day to ensure it works effectively.
Dosage and Titration Schedules
Doctors usually start semaglutide at a low dose to reduce the risk of side effects like nausea. Over time, the dose is increased to reach the target amount. This process is called titration.
- For the injection:
- The starting dose is typically 0.25 mg once a week.
- After 4 weeks, the dose may increase to 0.5 mg once a week.
- The dose can be increased further, depending on how well your body tolerates the medication and how effective it is.
- For the oral tablet (Rybelsus):
- The starting dose is 3 mg once a day for 30 days.
- After that, the dose is increased to 7 mg once a day.
- If needed, the dose can be further increased to a maximum of 14 mg once a day.
It is very important to follow your doctor’s instructions about when and how to increase the dose.
Storage Instructions
Proper storage ensures that semaglutide remains safe and effective.
- Injection Pens (Wegovy and Ozempic):
- Store unused pens in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- After the first use, the pens can be stored at room temperature for up to 28 days.
- Never freeze the pens. If a pen has been frozen, it must not be used.
- Oral Tablets (Rybelsus):
- Store the tablets at room temperature in a dry place.
- Keep the tablets in their original container to protect them from moisture.
Semaglutide is easy to use, but it is important to follow the specific instructions for each form. The injection is taken once a week, while the oral tablet must be taken daily on an empty stomach. Always follow your doctor’s advice about dosage, injection sites, and titration schedules. Proper use of semaglutide ensures it works effectively and reduces the risk of side effects.
What Makes Semaglutide Different From Other Weight Loss and Diabetes Treatments?
Semaglutide stands out as a unique treatment for both weight loss and type 2 diabetes. It is different from older medications in several important ways. These differences include its mechanism of action, longer-lasting effects, dual benefits for weight and blood sugar, and improved convenience. Let’s explore these factors in detail.
- Unique Mechanism of Action
Semaglutide works differently than many older treatments for diabetes and weight loss. It is a GLP-1 receptor agonist. GLP-1 stands for “glucagon-like peptide-1,” which is a natural hormone in your body. When you eat, your body releases GLP-1. This hormone helps control blood sugar and hunger.
Semaglutide mimics the action of GLP-1, but it lasts much longer than the body’s natural hormone. Here’s how it works:
- Blood Sugar Control: Semaglutide helps the pancreas release insulin when blood sugar is high. It also lowers the production of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar.
- Appetite Reduction: Semaglutide interacts with the brain to reduce hunger. It makes people feel full sooner and for a longer time after eating.
- Slows Digestion: Semaglutide delays gastric emptying, which means food moves more slowly from the stomach to the intestines. This helps control blood sugar spikes and reduces appetite.
Older weight loss drugs, like orlistat, work by blocking fat absorption in the intestines. Orlistat does not affect appetite or hunger. Other diabetes medications, such as metformin, mainly lower blood sugar but do not impact weight loss significantly. This is why semaglutide is a major advancement—it targets both blood sugar and weight at the same time.
- Longer Duration of Action
Another big difference is that semaglutide lasts much longer in the body than many other treatments. For example:
- Older GLP-1 Drugs: Earlier GLP-1 receptor agonists like exenatide require daily injections.
- Semaglutide: A key advantage of semaglutide is its weekly dosing. Once injected, it works steadily in the body for 7 days.
The weekly schedule makes it much more convenient for patients compared to daily medications or injections. For those using semaglutide in its oral form (Rybelsus), it is taken once daily, which is still a simple routine.
This long duration helps patients stick to their treatment plan. Fewer doses mean fewer chances to forget or skip a treatment. This improves long-term results for managing both blood sugar and weight.
- Dual Benefits for Weight Loss and Blood Sugar Control
Semaglutide is unique because it provides two major benefits at the same time:
- Weight Loss: Semaglutide has been proven to help people lose significant weight. Clinical trials, such as the STEP trials, showed that people using Wegovy lost, on average, 15% of their body weight. This is a much higher success rate than older weight loss medications.
- Blood Sugar Control: For people with type 2 diabetes, semaglutide lowers HbA1c levels. HbA1c measures average blood sugar levels over several months. Lowering HbA1c reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications like heart disease and kidney problems.
Other diabetes treatments, such as insulin and sulfonylureas, are effective at controlling blood sugar but often cause weight gain. This weight gain can make diabetes harder to manage. In contrast, semaglutide lowers blood sugar and promotes weight loss, making it more effective for many patients.
- Better Weight Loss Results Compared to Older Medications
Older weight loss medications, such as orlistat or phentermine, do not provide the same level of weight loss as semaglutide. For example:
- Orlistat: Helps patients lose around 5-7% of their body weight, but it often causes unpleasant side effects like oily stools and gas.
- Phentermine: A stimulant that suppresses appetite but is only approved for short-term use due to safety concerns.
Semaglutide outperforms these medications in clinical trials. Patients using Wegovy (semaglutide) consistently achieve 10-15% weight loss, and some lose even more. This level of success is closer to the results seen with weight loss surgeries like gastric bypass.
- Cardiovascular and Health Benefits
Semaglutide offers additional health benefits that many older treatments do not. For patients with type 2 diabetes, semaglutide has been shown to lower the risk of cardiovascular events like heart attacks and strokes. This is especially important because people with diabetes have a higher risk of heart disease.
These benefits set semaglutide apart from other medications, which may focus only on blood sugar or weight without improving overall health outcomes.
Why These Differences Matter
Semaglutide is different because it works in ways that older treatments cannot. It:
- Targets both blood sugar and weight loss.
- Has a longer duration of action, reducing the number of doses.
- Provides better weight loss results.
- Improves cardiovascular health for people with diabetes.
These differences make semaglutide a significant advancement in medical treatment. It gives doctors a powerful option to help patients manage type 2 diabetes and achieve meaningful weight loss. For many people, this therapy offers life-changing results.
Is Semaglutide Safe for Long-Term Use?
Semaglutide has been shown to be safe and effective for long-term use in both weight management and type 2 diabetes treatment. While short-term benefits are clear, many people wonder what happens if they use this medication for months or years. This section explains what the current research says about the long-term safety, sustained results, and ongoing monitoring of semaglutide therapy.
What the Long-Term Studies Show
Clinical trials have evaluated semaglutide for extended periods, and the results are promising. In studies lasting over a year, participants continued to see significant benefits:
- For Weight Loss: Research, such as the STEP trials, showed that people taking semaglutide for over a year maintained or even increased their weight loss. On average, participants lost about 10-15% of their body weight. Importantly, this weight loss was sustained as long as they continued the medication.
- For Diabetes Control: In studies focused on people with type 2 diabetes, semaglutide lowered blood sugar levels (measured as HbA1c) and kept them within healthy ranges for up to 2 years. Patients also experienced improvements in other health markers, such as blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
These results suggest that semaglutide works well in the long run, but the key is consistent use. If a person stops taking semaglutide, the benefits for weight loss and blood sugar control may gradually decrease.
Side Effects Over the Long Term
Like all medications, semaglutide can cause side effects. However, studies show that most people tolerate it well, even with long-term use.
Common Side Effects:
The most common side effects are gastrointestinal (stomach-related) and tend to happen early in treatment. These include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
In most cases, these symptoms improve or disappear as the body adjusts to the medication. Doctors usually start patients on a low dose and gradually increase it. This helps reduce the severity of side effects.
Serious Side Effects:
Although rare, some serious side effects need to be monitored:
- Pancreatitis: This is inflammation of the pancreas. People using semaglutide should be aware of symptoms like severe stomach pain, nausea, or vomiting. If these occur, they should contact their doctor right away.
- Thyroid Tumors: Animal studies have linked semaglutide to thyroid C-cell tumors. However, this has not been proven in humans. To be cautious, semaglutide is not recommended for people with a family or personal history of medullary thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2.
- Gallbladder Problems: Some studies have noted a higher risk of gallstones or gallbladder inflammation in people using semaglutide. This risk increases with rapid weight loss.
Doctors closely monitor these risks during treatment. Patients are advised to report any unusual symptoms, like severe stomach pain, difficulty swallowing, or persistent vomiting.
Benefits Outweigh the Risks for Most People
For most people, the benefits of semaglutide outweigh the risks. Long-term use has been linked to several important health improvements, including:
- Reduced Cardiovascular Risk: Semaglutide helps lower blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and body weight. These benefits reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes in people with type 2 diabetes.
- Better Quality of Life: Sustained weight loss and blood sugar control lead to improved energy levels, better sleep, and reduced joint pain. Many patients also experience a boost in overall well-being.
Doctors recommend semaglutide for long-term use when the benefits are clear and the risks are manageable.
Ongoing Research and Monitoring
Because semaglutide is a newer medication, researchers are still studying its long-term effects. So far, the results from extended trials and real-world use are encouraging. Medical experts continue to track:
- Safety Data: New findings help doctors better understand any rare risks over time.
- Efficacy Over Years: Researchers are studying whether people can maintain weight loss and diabetes control for 5 years or more.
Patients taking semaglutide for a long time should have regular check-ups with their healthcare provider. These visits ensure that the medication is working well and that any side effects are managed quickly.
Semaglutide is safe and effective for long-term use in most people. Clinical trials show that its benefits for weight loss and diabetes control can last for years. While some side effects may occur, they are usually mild and manageable. Serious risks are rare but should be monitored closely. With ongoing research and regular doctor visits, semaglutide continues to offer a safe way to improve health in the long run.
How Much Does Semaglutide Cost, and Is It Covered by Insurance?
Semaglutide, sold under brand names like Wegovy, Ozempic, and Rybelsus, is an effective treatment for weight loss and type 2 diabetes. However, its cost can be high, and many people wonder how much it will cost them out of pocket. This section explains the pricing, insurance coverage, and ways to save money on this medication.
The Cost of Semaglutide
The price of semaglutide depends on the brand and whether you have insurance coverage. Here is an approximate breakdown of the costs:
- Wegovy (for weight loss):
- Wegovy is specifically approved for chronic weight management.
- Without insurance, Wegovy can cost around $1,300 to $1,400 per month in the United States.
- The price can vary depending on the pharmacy, location, and whether any discounts apply.
- Ozempic (for type 2 diabetes):
- Ozempic is approved to treat type 2 diabetes.
- The cost of Ozempic without insurance is roughly $900 to $1,000 per month for a single pen (four weekly doses).
- Rybelsus (oral version for type 2 diabetes):
- Rybelsus comes in tablet form and is taken once a day.
- Without insurance, the price for a 30-day supply is about $800 to $900.
These prices can change depending on the dosage, location, and pharmacy. Higher doses cost more since they require more medication.
Does Insurance Cover Semaglutide?
Whether or not semaglutide is covered by insurance depends on your health plan, the reason for taking the medication, and your insurance company’s policies.
- Coverage for Diabetes Treatment (Ozempic and Rybelsus):
- Most insurance plans, including Medicare Part D, cover Ozempic and Rybelsus for people with type 2 diabetes.
- Insurance providers recognize that these medications help control blood sugar levels and reduce complications of diabetes.
- Coverage for Weight Loss (Wegovy):
- Wegovy, which is approved for weight loss, may not always be covered by insurance.
- Many insurance plans view weight loss treatments as “lifestyle medications” and may not include them in their drug coverage.
- However, some employers or private insurance plans have started covering Wegovy due to its proven medical benefits for people with obesity.
- Prior Authorization:
- Some insurance companies require prior authorization before they approve coverage for semaglutide.
- This means your doctor must explain to the insurance company why you need the medication.
- Approval can take time, and you may need to meet certain conditions, such as trying other treatments first.
- Medicare and Medicaid:
- Medicare Part D usually covers Ozempic for type 2 diabetes, but it does not cover Wegovy for weight loss.
- Medicaid coverage for semaglutide depends on the state program. Some states may cover it for diabetes but not for weight loss.
Ways to Save on Semaglutide
The high cost of semaglutide can be a challenge for many patients, especially those without insurance. Here are some ways to reduce the cost:
- Manufacturer Savings Programs:
- Novo Nordisk, the company that makes Wegovy, Ozempic, and Rybelsus, offers savings programs for eligible patients.
- For example:
- Patients with commercial insurance may qualify for a discount card, reducing the out-of-pocket cost significantly.
- Some savings cards bring the price of Wegovy or Ozempic down to as little as $25 per month for eligible patients.
- Patient Assistance Programs:
- For patients without insurance or with low income, Novo Nordisk also offers patient assistance programs.
- These programs can provide free or reduced-cost medication to qualifying individuals.
- Applications typically require proof of income and medical need.
- Pharmacy Discounts and Coupons:
- Websites like GoodRx and SingleCare offer discount coupons for semaglutide.
- These coupons can lower the price at participating pharmacies, sometimes saving hundreds of dollars.
- Generic and Biosimilar Options:
- Semaglutide is still a relatively new medication, so there are no generic versions yet.
- However, biosimilar versions may be developed in the future, which could reduce costs.
- Check Different Pharmacies:
- Prices for semaglutide can vary between pharmacies. Shopping around or using tools like GoodRx can help you find the lowest price in your area.
- Talk to Your Doctor:
- If the cost of semaglutide is too high, talk to your doctor. They may be able to:
- Apply for insurance approval.
- Help you enroll in savings programs.
- Explore dose adjustments to reduce costs.
- If the cost of semaglutide is too high, talk to your doctor. They may be able to:
Outlook on Cost and Coverage
As semaglutide becomes more widely used for both diabetes and weight loss, insurance coverage may improve. More health insurers and employers are beginning to understand the long-term benefits of these medications for reducing healthcare costs associated with diabetes, obesity, and related complications.
However, for now, the high price can be a significant hurdle for many patients. Being aware of savings programs, coupons, and insurance options is key to making this medication more affordable.
The cost of semaglutide varies widely depending on the brand, dosage, and insurance coverage. Wegovy (for weight loss) can cost over $1,300 per month, while Ozempic and Rybelsus (for diabetes) cost around $900 to $1,000 monthly. Insurance often covers diabetes treatments but may not cover weight loss medications. Programs like manufacturer savings cards and pharmacy coupons can help reduce costs. If you’re considering semaglutide, working with your doctor and exploring savings options can help make this effective treatment more accessible.
Conclusion
Semaglutide has transformed the way doctors treat type 2 diabetes and manage weight loss. This medication, known under the brand names Ozempic, Wegovy, and Rybelsus, has gained worldwide attention for its effectiveness and benefits. Its impact on both weight management and blood sugar control has made it a groundbreaking therapy in modern medicine. In this article, we explored what semaglutide is, how it works, its results, safety, and how it compares to other treatments. Now, let’s summarize its role and why it is changing lives.
Semaglutide belongs to a group of drugs called GLP-1 receptor agonists. These drugs mimic a natural hormone in the body called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1). This hormone helps the pancreas release insulin, slows down digestion, and reduces appetite. By mimicking this hormone, semaglutide helps people with type 2 diabetes improve their blood sugar levels and also helps people lose weight. Unlike many older medications, semaglutide offers a “dual benefit” for both conditions, which is why it is considered a major breakthrough.
In clinical trials, semaglutide has shown impressive results. For weight loss, studies like the STEP trials proved that people could lose 15% or more of their body weight over time. This level of weight loss is far greater than what older medications have achieved. People using semaglutide for weight loss experienced major improvements in health, especially those who were overweight or obese. For individuals with type 2 diabetes, semaglutide helps lower blood sugar by reducing HbA1c levels. Studies also show that it reduces the risk of complications like heart disease. This makes semaglutide a very effective option for long-term diabetes management.
The success of semaglutide also comes from its convenience. Unlike other medications that must be taken daily or multiple times a day, semaglutide is often administered just once a week as an injection. This weekly schedule helps people stick to their treatment plans more easily. For those who prefer not to use injections, Rybelsus offers semaglutide in a tablet form that is taken once a day. The simple dosing options have improved patient compliance, leading to better outcomes.
Safety is a key part of any treatment, and semaglutide has been shown to be safe for most people. Like all medications, it does have side effects. The most common ones are nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. For many people, these side effects get better over time as their bodies adjust to the medication. However, semaglutide does have some serious risks, such as pancreatitis and a potential link to thyroid cancer. Because of this, it is not recommended for people with a history of certain thyroid conditions. Doctors carefully monitor patients to ensure safety, and ongoing research continues to provide more information on long-term effects.
Despite its benefits, semaglutide is not for everyone. It is approved only for people with type 2 diabetes or for adults who are obese or overweight with related health issues, such as high blood pressure. It is not meant for those with type 1 diabetes, and it should not be used by pregnant or breastfeeding individuals. Patients need to work closely with their healthcare providers to see if semaglutide is the right option for them.
One challenge for many patients is the cost of semaglutide. The medication can be expensive, especially for those using it for weight loss. While insurance often covers it for diabetes treatment, it is less likely to be covered for weight management. However, some patient assistance programs and discount options are available to help with affordability.
In summary, semaglutide has set a new standard for treating type 2 diabetes and obesity. Its ability to control blood sugar and promote significant weight loss has helped thousands of patients improve their health. With its proven results, long-term benefits, and flexible dosing options, semaglutide is changing the way doctors approach these common health challenges. While it may not be the perfect option for everyone, it has opened doors to better outcomes for many people struggling with weight or diabetes. As research continues, semaglutide could lead to even more advancements in treatment, offering hope for a healthier future.
Research Citations
Marso, S. P., Bain, S. C., Consoli, A., Eliaschewitz, F. G., Jódar, E., Leiter, L. A., … & Lingvay, I. (2016). Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine, 375(19), 1834-1844. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1607141
Wilding, J. P., Batterham, R. L., Calanna, S., Davies, M., Van Gaal, L. F., Lingvay, I., … & Kushner, R. F. (2021). Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. New England Journal of Medicine, 384(11), 989-1002. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
Wadden, T. A., Bailey, T. S., Billings, L. K., Davies, M., Frias, J. P., Garvey, W. T., … & Ruderman, N. B. (2021). Semaglutide 2.4 mg for the treatment of obesity in adults. New England Journal of Medicine, 384(11), 989-1002. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
Pratley, R. E., Aroda, V. R., Lingvay, I., Nauck, M. A., Barrett, H., Berngen, T., … & Rosenstock, J. (2021). Semaglutide versus placebo as add-on to insulin in type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 5): a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 9(9), 561-572. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00125-4
Davies, M., Pieber, T. R., Hartoft-Nielsen, M. L., Larsen, S. K., Hansen, T. K., Søndergaard, K., … & Rossing, P. (2017). Efficacy of liraglutide and semaglutide compared to placebo and active comparators in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 19(11), 1666-1674. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13067
Rubino, D., Abraham, W. T., & Zaccardi, F. (2021). Semaglutide and obesity: A review of current evidence. Obesity Reviews, 22(S2), e13138. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.13138
Blundell, J. E., Finlayson, G., Axelsen, M., Bojsen-Møller, K. N., Rössner, S., Stridsberg, M., … & Rasmussen, M. (2017). Effects of continued weekly subcutaneous semaglutide versus placebo in subjects with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 1): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3a trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 5(12), 941-952. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30302-9
Davies, M., Pieber, T. R., Hartoft-Nielsen, M. L., Larsen, S. K., Hansen, T. K., Søndergaard, K., … & Rossing, P. (2018). Efficacy of liraglutide and semaglutide compared to placebo and active comparators in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 20(4), 820-832. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13151
Davies, M., Bergenstal, R., Bode, B., Kushner, R. F., Lewin, A., Skjøth, T. V., … & SUSTAIN 7 Study Group. (2018). Efficacy of once-weekly semaglutide versus once-daily exenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 7): a randomised, open-label, phase 3b trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 6(7), 580-591. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30177-0
Kristensen, M., Røsjø, H. T., Knop, F. K., Holst, J. J., Vilsbøll, T., & Madsbad, S. (2016). Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: cardiovascular effects and future perspectives. Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease, 7(4), 194-212. https://doi.org/10.1177/2040622316652412
Questions and Answers: Semaglutide Therapy
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 receptor agonist used to manage type 2 diabetes and obesity. It mimics the hormone GLP-1, which helps regulate blood sugar, slow gastric emptying, and reduce appetite.
Semaglutide is approved for managing type 2 diabetes (under the brand name Ozempic® or Rybelsus®) and for weight management in obesity (Wegovy®).
Semaglutide is available as a once-weekly subcutaneous injection (Ozempic® or Wegovy®) or a once-daily oral tablet (Rybelsus®).
Semaglutide lowers blood glucose levels, reduces HbA1c, aids weight loss, and decreases cardiovascular risks associated with diabetes.
Yes, semaglutide (Wegovy®) has been shown to help individuals with obesity or overweight lose significant weight by reducing appetite and caloric intake.
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain, which are usually mild and improve over time.
Individuals with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid cancer, multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN2), or a history of severe hypersensitivity to semaglutide should avoid its use.
Most patients see improvements in blood sugar within 1–2 weeks and significant weight loss over several months of consistent use.
Yes, semaglutide may delay gastric emptying, which can affect the absorption of oral medications. Discuss any medications with a healthcare provider before starting semaglutide.
Yes, semaglutide can be combined with other medications like metformin or SGLT2 inhibitors, but caution is needed with insulin or sulfonylureas to avoid hypoglycemia.

