Table of Contents
Introduction
Vitamin B12 shots have become more popular in recent years, especially among people trying to lose weight. These injections are often advertised as a way to boost energy, speed up metabolism, and help the body burn fat more quickly. Some weight loss clinics and health spas offer B12 shots as part of their wellness or fat-burning programs. But many people are left wondering: do B12 weight loss shots really work, or is it just a trend?
Vitamin B12 is an essential vitamin. It plays a key role in how the body makes red blood cells, keeps the nerves healthy, and turns food into energy. It is a water-soluble vitamin, which means it dissolves in water and does not stay in the body for long. Extra amounts of B12 are usually passed out in urine. Because it helps with energy and cell function, some believe it may help the body burn calories faster or improve weight loss results. However, the science behind these claims is not always clear.
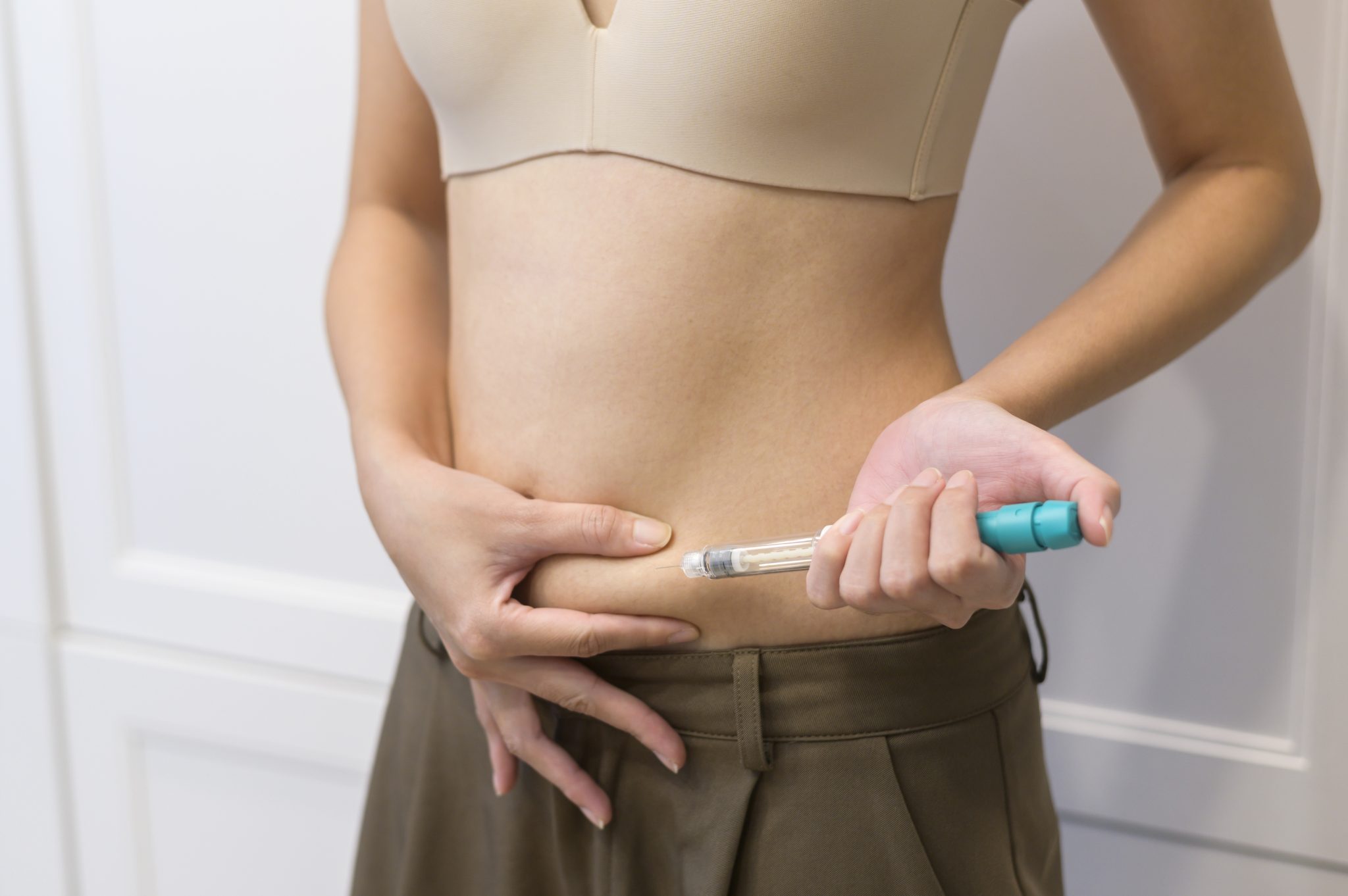
Weight loss is a common health goal, and people often try many methods to reach it. Some try diets, exercise plans, supplements, or medications. Others look to newer treatments like injections. Vitamin B12 shots are one example. They are usually given by a nurse or doctor, although some people use self-injection kits at home. These shots go into the muscle, often in the arm or thigh. They may be given once a week, every few weeks, or as needed, depending on the program.
One of the reasons B12 shots are so popular is that many people feel tired or low on energy. A lack of energy can make it harder to stick to a healthy diet or to stay active. Since vitamin B12 plays a role in energy production, the idea is that getting more of it might help people feel more energetic and motivated to exercise or make healthy choices. Some also believe that the vitamin may help the body break down fat more easily. However, it is important to look at what medical research says about these effects.
Another reason for the popularity of B12 injections is that they are often included in “lipotropic” injections. These are special combinations of nutrients that claim to help the liver process fat more efficiently. Many of these injections contain vitamin B12 along with other ingredients like methionine, inositol, and choline. Together, these are said to help the body burn fat faster. But not all of these claims have strong scientific support.
There are some people who may truly benefit from vitamin B12 shots, especially those with a B12 deficiency. A deficiency means the body does not have enough of the vitamin, which can lead to tiredness, weakness, nerve problems, and trouble thinking clearly. Certain groups are more at risk, such as older adults, people who follow a strict vegan or vegetarian diet, and those who have had stomach surgery or digestive problems. In these cases, B12 shots can help restore healthy levels of the vitamin. But for people who already have enough B12, the added benefit of more may be very small.
This article explores the real facts behind B12 weight loss shots. It explains what B12 is, how it works in the body, and whether it can truly help with weight loss. It also looks at the risks, costs, and possible side effects. While B12 is a key nutrient for health, it is important to understand whether these shots are helpful or just another quick fix. Scientific evidence, medical advice, and safe practices all play a role in making smart health choices.
What Are B12 Weight Loss Shots?
Vitamin B12 weight loss shots are injections that contain a concentrated dose of vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin. This vitamin is essential for the body’s health and plays a key role in making red blood cells, supporting the nervous system, and helping convert food into energy. Some weight loss programs include B12 shots as part of a larger plan, with the idea that they may help increase energy levels, improve metabolism, and support weight loss.
What Is Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin. This means it dissolves in water and travels through the bloodstream. The body cannot make B12 on its own, so it must come from food or supplements. Foods rich in B12 include meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy. People who eat very little or no animal products may have trouble getting enough B12 from their diet alone.
The body uses vitamin B12 to help with many important tasks. These include making red blood cells, supporting brain and nerve function, and breaking down fat and protein for energy. Without enough B12, people may feel tired, weak, or confused. They may also have trouble with memory or balance.
What Are B12 Shots Made Of?
B12 weight loss shots are injections that contain a form of vitamin B12. There are different types of B12 used in shots. The most common forms are:
- Cyanocobalamin – This is a man-made form of B12 often used in supplements and injections. It is stable and works well for many people.
- Methylcobalamin – This is a natural form of B12 that the body can use directly. It is sometimes used in shots for people who need higher absorption.
- Hydroxocobalamin – This form stays in the body longer and may be used to treat more serious B12 deficiency.
Some B12 injections may contain only vitamin B12, while others include extra ingredients. These are sometimes called lipotropic injections. They may include substances like methionine, inositol, and choline, which are believed to help break down fat. These combination shots are often used in weight loss clinics, although their effects are still being studied.
How Are the Shots Given?
B12 shots are usually given with a small needle into the muscle (intramuscular injection) or under the skin (subcutaneous injection). The most common site is the upper arm or hip. In a medical clinic, a nurse or doctor usually gives the shot. Some people who use B12 regularly may be trained to give themselves the shot at home.
The dose and schedule can vary. Some people get B12 shots once a week. Others may get them every few weeks or monthly, depending on their needs and health status. When used as part of a weight loss program, shots may be given more often in the beginning and then spaced out over time.
Who Gets B12 Shots?
B12 injections are often given to people who have a B12 deficiency. This means their B12 levels are too low. Deficiency can be caused by:
- Poor diet (especially in people who avoid animal products)
- Problems absorbing B12 from food (common in older adults)
- Certain medical conditions, like celiac disease or Crohn’s disease
- Weight loss surgery that affects the stomach or intestines
- Use of certain medications like metformin or acid-reducing drugs
Some people may not have a true deficiency but may still feel tired or low on energy. They may choose to get B12 shots hoping for an energy boost. In weight loss programs, B12 injections are sometimes offered to help increase energy and improve mood, especially when people are eating fewer calories.
It is important to note that not everyone needs B12 shots. Many people get enough B12 from food or oral supplements. A blood test can show whether B12 levels are low and if injections are needed. Health care providers usually decide if shots are appropriate based on a person’s symptoms, diet, and lab results.
B12 weight loss shots are injections that deliver a high dose of vitamin B12 directly into the body. They are used for treating low B12 levels and are also included in some weight loss programs to support energy and metabolism. The shots can be given by a healthcare provider or, in some cases, at home. While helpful for people with low B12 levels, not everyone needs these shots. A medical evaluation is the best way to know if B12 injections are right for any health or weight-loss plan.
How Does Vitamin B12 Affect Metabolism and Energy?
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a key role in many body functions. It helps the body use food for energy, keeps the nervous system healthy, and is needed to make red blood cells. Although it does not directly cause weight loss, it supports several processes in the body that are important for energy and metabolism.
Vitamin B12 Helps the Body Turn Food Into Energy
One of the most important jobs of vitamin B12 is helping the body break down food. The body needs B12 to convert carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into fuel. This process happens in all cells, especially in cells with high energy needs, like muscles and the brain.
Vitamin B12 is involved in a process called the citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle. This cycle helps the body release energy stored in food. Without enough B12, the body may not work as efficiently when turning nutrients into energy. People who are low in B12 might feel tired or weak because their cells are not getting the energy they need.
Supports Red Blood Cell Production
Vitamin B12 also plays a role in making red blood cells. These cells carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. When the body doesn’t have enough B12, it can’t make red blood cells properly. This can lead to megaloblastic anemia, a condition where red blood cells are too large and do not work well.
When oxygen delivery is reduced, it can make a person feel tired and slow. Low oxygen also makes it harder for muscles to perform during exercise. When people correct a B12 deficiency, they often feel more energetic. This extra energy may help with exercise and staying active, which are both important for weight management.
Important for Nervous System Health
Vitamin B12 helps maintain the health of the nervous system. It protects the myelin sheath, a layer that covers and protects nerves. Myelin helps nerve signals travel quickly and properly. If B12 levels are too low for too long, nerve damage can occur.
Symptoms of low B12 can include numbness, tingling, memory problems, and trouble walking. People may also have mood changes, like feeling depressed or anxious. When B12 levels are brought back to normal, these symptoms often improve. Feeling better mentally and physically may lead to more physical activity, which can support weight control.
Helps With DNA Synthesis
B12 is needed to make DNA, the genetic material in every cell. This is especially important in cells that divide often, such as those in the bone marrow that produce red blood cells. Without enough B12, cells cannot divide properly. This affects how well the body can repair and grow tissues.
Although DNA synthesis does not directly affect weight, it is part of keeping the body functioning well. A healthy body is more likely to have normal metabolism and energy use.
Indirect Link to Weight Management
There is no strong evidence that vitamin B12 directly burns fat or speeds up metabolism to cause weight loss. However, when B12 levels are low, people may feel tired, weak, or mentally foggy. These symptoms can make it harder to exercise, stay motivated, or make healthy food choices. After B12 levels are corrected, some people report more energy and better mood. This may lead to increased physical activity and improved habits, which could help with weight control over time.
Some people without a deficiency also take B12 shots, hoping to feel more energetic. However, studies show that people with normal B12 levels may not get extra energy from injections. The body will remove extra B12 through the urine if it doesn’t need it.
Vitamin B12 is essential for energy production, red blood cell health, nerve function, and DNA creation. These functions support a healthy metabolism. While B12 does not directly cause weight loss, having the right level of B12 can help the body feel better and work more efficiently. This may make it easier to stay active and maintain a healthy weight. Still, B12 is not a substitute for a balanced diet, physical activity, and other proven weight loss strategies.

Do B12 Shots Really Help with Weight Loss?
Many people are curious if vitamin B12 injections can help with weight loss. B12 shots are often advertised as energy boosters or fat burners. Some clinics and weight loss centers include them as part of a larger program. However, it is important to look at what science says about whether B12 actually causes weight loss.
What the Research Says
There is no strong scientific proof that B12 injections by themselves lead to weight loss. Most research on B12 focuses on its role in treating deficiency, supporting energy levels, or helping with certain health conditions. While some people who receive B12 shots say they feel more energetic or lose weight, there is not enough clinical evidence to show that B12 directly causes fat loss or reduces appetite.
Some small studies have looked at B12 levels in people with obesity. In some of these studies, people with lower B12 levels were more likely to have higher body weight. However, this does not mean that low B12 causes weight gain, or that taking more B12 will lead to weight loss. Correlation does not mean causation. Many people who are overweight or obese also have health conditions, such as diabetes or digestive problems, that can affect how the body absorbs or uses B12.
No Proven Fat-Burning Effect
Vitamin B12 does not act as a stimulant or thermogenic. It does not raise the body’s temperature or increase how many calories are burned at rest. B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a role in how the body turns food into energy. It helps with the breakdown of fats and proteins, but this is a normal process in everyone. Getting extra B12 does not speed up metabolism unless the body is deficient to begin with.
Unlike medications used for weight loss, such as appetite suppressants or GLP-1 receptor agonists, B12 has no direct impact on hunger or cravings. It also does not block fat absorption or increase the feeling of fullness. That’s why B12 is not approved as a weight loss drug by health agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Possible Indirect Benefits
Even though B12 may not directly cause weight loss, it can play a supportive role, especially in people who are low in B12. When someone has a B12 deficiency, they may feel tired, weak, or foggy. These symptoms can make it harder to exercise or stay active. Fixing a deficiency with B12 shots can improve energy, alertness, and mood. This may help some people become more physically active, which could lead to weight loss over time.
In addition, B12 supports the production of red blood cells and helps keep the nervous system working properly. If these systems are not functioning well due to low B12, overall health can suffer. A person with better energy and mental focus may find it easier to follow a healthy eating plan or complete a workout routine.
Combining B12 with Other Strategies
Many clinics give B12 shots along with a full weight loss program that includes diet changes, physical activity, behavior support, and sometimes other medications. In these cases, it is difficult to know if weight loss is from the B12, from the overall plan, or from both. Most likely, any weight loss seen during these programs is due to a combination of healthy lifestyle changes, not just the injection.
Some B12 injections also include lipotropic compounds like methionine, inositol, and choline. These are said to help the body process fat more efficiently. However, there is limited research on how well these combinations work. Most studies on lipotropic injections are small or not well-designed.
Vitamin B12 shots do not melt away fat or cause dramatic weight loss. They do not replace the need for healthy eating, regular physical activity, or other medical treatments. However, correcting a B12 deficiency can improve energy levels and overall well-being. For some people, this may help support long-term weight management, but B12 alone is not a magic solution for losing weight.
Who Might Benefit from B12 Injections in a Weight Loss Context
Vitamin B12 plays an important role in how the body produces energy and processes fats and proteins. For this reason, B12 is sometimes included in weight loss programs. But not everyone needs extra B12, and it does not work the same way for all people. Certain groups are more likely to benefit from B12 injections, especially those with low levels of this vitamin. Understanding who is more likely to respond to B12 shots can help avoid unnecessary treatments and focus on real needs.
People With a Vitamin B12 Deficiency
People with a true vitamin B12 deficiency are the most likely to benefit from B12 shots. A deficiency means that the body does not have enough B12 to carry out normal functions. This can lead to problems such as fatigue, weakness, poor memory, nerve issues, or anemia.
A lack of B12 can also make it harder to stay active or maintain a healthy metabolism. In these cases, B12 injections may improve energy levels and overall well-being. This may help people feel more able to exercise or follow a diet plan, which can lead to weight loss over time. However, the weight loss is usually an indirect result, not a direct effect of the injection.
A deficiency can be confirmed by a simple blood test. If blood levels of B12 are low, a doctor may recommend injections to quickly raise them. This is often more effective than taking pills, especially when the body has trouble absorbing the vitamin.
Older Adults
Older adults are more likely to have lower B12 levels. This is because, with age, the body produces less stomach acid. Stomach acid helps release B12 from food during digestion. Without enough acid, the body cannot absorb enough B12.
In addition, many older adults take medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or metformin, which can also lower B12 absorption. These people may feel tired or weak, and sometimes these symptoms are wrongly blamed on aging.
B12 injections may help improve energy and mental sharpness in older adults with low levels. When combined with a balanced diet and regular activity, this can support weight management goals.
People With Digestive Conditions or Surgeries
Some health problems can make it harder for the body to absorb vitamin B12 from food. These include digestive disorders like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or atrophic gastritis. People who have had certain types of weight loss surgery, such as gastric bypass, are also at risk. These surgeries change the stomach and intestines in a way that limits how nutrients, including B12, are absorbed.
Even if these individuals eat enough B12, their bodies may not absorb it well through the gut. Injections go directly into the muscle and bypass the digestive system, which can help restore healthy levels faster. Improving B12 levels may boost energy and help support long-term weight loss efforts when part of a full health plan.
Vegetarians and Vegans
Vitamin B12 is found mostly in animal products such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy. People who follow vegetarian or vegan diets may not get enough B12 through food alone. Over time, this can lead to a deficiency, especially if no supplements are taken.
In such cases, B12 injections may be used to correct low levels and prevent symptoms like fatigue or weakness. These symptoms can affect physical activity and reduce motivation to stay on a healthy routine. Raising B12 levels may support better energy, which can help with weight management.
People With Low B12 but Normal Lab Results
Sometimes, a person may feel tired or sluggish even if their B12 blood level is technically within the normal range. These levels can vary from person to person, and what is “normal” on a lab test may still be low for some individuals. Doctors may consider a trial of B12 injections if other causes of fatigue have been ruled out.
However, there is little strong evidence that B12 shots help people who already have healthy levels. For people with normal B12, injections are unlikely to lead to weight loss. That’s why it’s important to focus on proven causes of low energy before using injections as a general fix.
People who benefit most from B12 injections are those with low levels due to diet, age, digestion problems, or certain medications. For these individuals, improving B12 levels may lead to more energy and better physical function, which can support healthy weight loss when combined with other lifestyle changes. However, for people with normal B12 levels, injections are unlikely to make a big difference in weight on their own. Proper testing and medical advice can help determine who truly needs them.
What Are the Typical Ingredients in B12 Lipotropic Injections?
B12 lipotropic injections are often marketed as a way to boost metabolism and support weight loss. These injections usually include vitamin B12 along with other compounds called lipotropics. The word “lipotropic” means “fat-loving,” and it refers to substances that help the liver process fat more efficiently. Lipotropic injections are often given in weight-loss clinics as part of larger medical weight loss programs.
The exact ingredients in these injections can vary depending on where they are made. However, most lipotropic injections used for weight loss contain a combination of vitamin B12 and three common fat-processing compounds: methionine, inositol, and choline. These are often called MIC injections, based on the first letters of each of the lipotropic ingredients. Some formulations may also contain L-carnitine, B-complex vitamins, or other amino acids.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a key role in energy production, brain function, and the formation of red blood cells. In weight-loss injections, the most common forms of B12 are methylcobalamin, hydroxocobalamin, and cyanocobalamin.
Methylcobalamin is a natural, active form of B12 and is often used because it is well absorbed and stays in the body longer. Hydroxocobalamin is a longer-lasting form that is often used in clinical settings. Cyanocobalamin is a synthetic version that is stable and inexpensive but must be converted by the body before it becomes active.
B12 is included in these injections because it helps the body convert food into energy. It also supports nerve function and the production of DNA. Although B12 is essential for health, most research shows that it does not directly lead to weight loss in people who already have normal B12 levels.
Methionine
Methionine is an essential amino acid, meaning the body cannot make it and it must come from food. It plays a role in breaking down fats and removing heavy metals from the body. Methionine helps the liver process fats by reducing fat buildup and supporting the flow of bile, which helps carry fats away from the liver.
It also helps with the production of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that protects the liver from damage. Methionine is thought to support weight loss by improving fat metabolism and liver function, although more research is needed to confirm this effect.
Inositol
Inositol is a sugar-like substance that plays a part in how cells respond to insulin and process fats. It is often grouped with B vitamins, although it is not officially classified as one. Inositol supports nerve function and may help regulate mood.
Some studies suggest that inositol can improve insulin sensitivity, especially in people with conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Better insulin control may lead to better fat metabolism and reduced fat storage. This is why inositol is sometimes included in fat-burning injections.
Choline
Choline is an essential nutrient that helps transport fats and cholesterol from the liver to other parts of the body. Without enough choline, fat can build up in the liver and lead to liver damage. Choline is also important for nerve function, muscle control, and memory.
Choline plays a key role in fat metabolism. It helps break down fats during digestion and moves them into the bloodstream to be used for energy. Choline may not cause weight loss directly, but it supports a healthy liver, which is essential for burning fat efficiently.
Other Possible Ingredients
Some lipotropic injections may include L-carnitine, a compound that helps transport fatty acids into the cells to be burned for energy. Others may contain B-complex vitamins, which include B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid), and B6 (pyridoxine). These vitamins help the body use carbohydrates, proteins, and fats more effectively.
Regulatory Considerations
It is important to note that most of these lipotropic injections are not approved by the FDA as weight-loss treatments. Many of them are made in compounding pharmacies, where ingredients are mixed based on a doctor’s prescription. Because they are compounded, the strength and purity can vary. Some clinics offer these injections as part of weight-loss programs, but the quality and safety may depend on the provider.
While the ingredients in B12 lipotropic injections support healthy body functions, especially liver health and fat metabolism, there is limited scientific evidence that these combinations lead to significant weight loss in people who do not have nutritional deficiencies.
When used under medical supervision and as part of a complete weight-loss plan, lipotropic injections may support other treatments, but they are not a substitute for healthy eating, regular exercise, and other proven methods for long-term weight management.
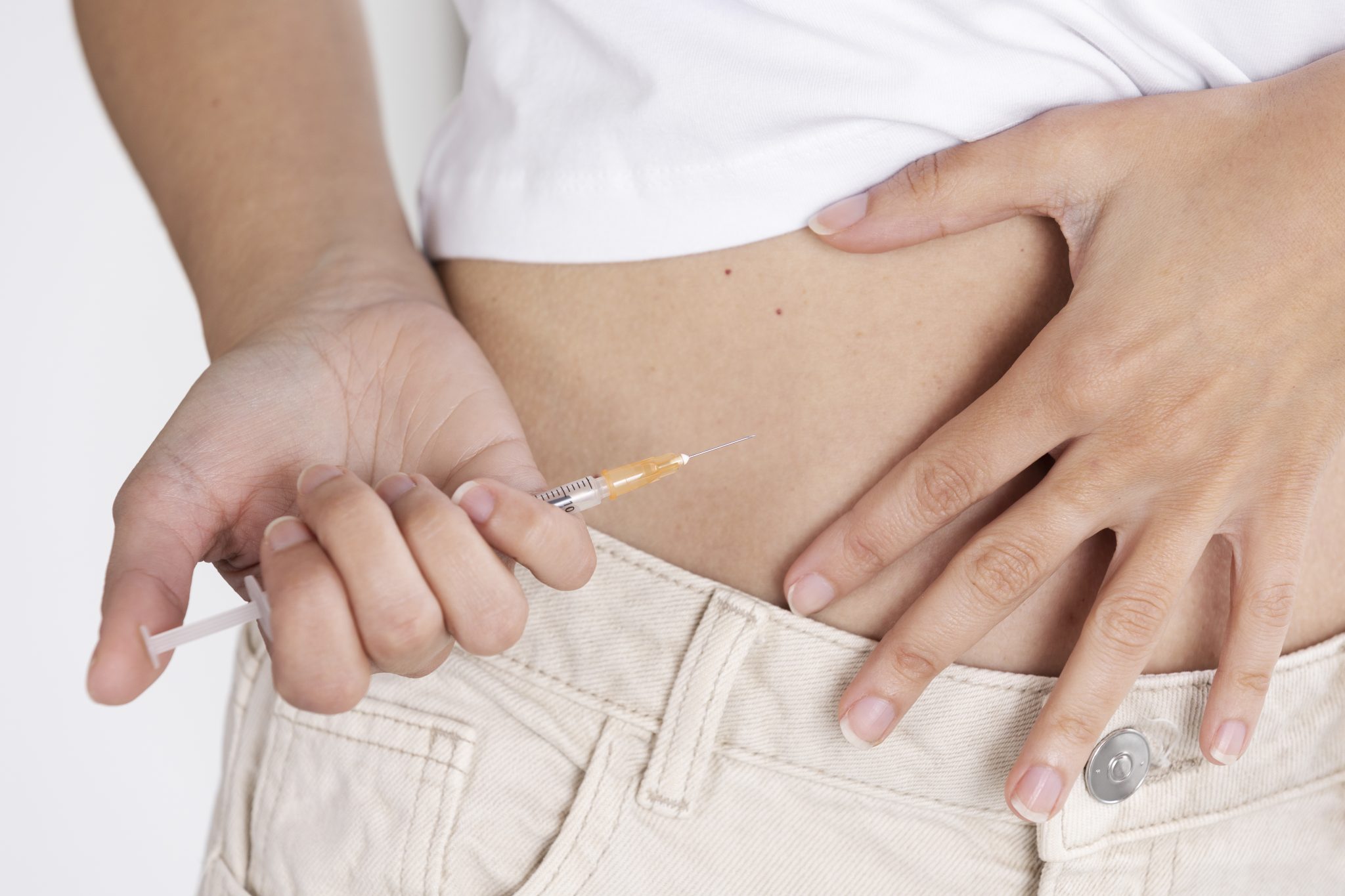
Are B12 Shots Safe? Potential Risks and Side Effects
Vitamin B12 injections are usually considered safe, especially when given by a healthcare provider and used for medical reasons. However, like all medical treatments, they can sometimes cause side effects. These side effects can range from mild and short-term to rare and more serious. Understanding the risks and how the body might react can help people make informed choices before starting B12 shots as part of a weight loss plan.
Common Side Effects
Most people who get B12 shots do not have serious problems. The most common side effects are mild and do not last long. These can include:
- Pain at the injection site: After the shot, there may be a small amount of pain, redness, or swelling where the needle went in. This is normal and usually goes away within a few hours or days.
- Mild diarrhea: Some people report loose stools or mild stomach discomfort. This side effect often improves without treatment.
- Headache: A headache may occur after the injection. It is usually short-lived and goes away without medication.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: A few individuals may feel dizzy shortly after the shot. Resting for a short time often helps.
These side effects are not dangerous for most healthy people. They are usually the body’s way of adjusting to the new level of vitamin B12 in the system.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
Although uncommon, there are some side effects that are more serious and need medical attention. These include:
- Allergic reactions: Some people may have an allergy to one of the ingredients in the injection. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can include swelling of the face, tongue, or throat, skin rash, itching, or trouble breathing. This is an emergency and requires immediate care.
- Low potassium levels (hypokalemia): In rare cases, B12 injections can lower potassium in the blood. This can cause muscle cramps, weakness, irregular heartbeat, or fatigue. A doctor can check potassium levels with a blood test.
- Blood clots or vein inflammation: If the injection is not given correctly or if the person has certain medical conditions, there may be a risk of swelling or clotting in the veins.
- Heart or chest problems in people with pre-existing conditions: B12 may change how the heart or blood pressure responds in certain individuals, especially if there are heart conditions already present. Though this is rare, it should be considered before starting injections.
Drug Interactions
Vitamin B12 can also interact with certain medications. This means the vitamin or the medicine may not work as well, or unexpected side effects could happen. Important examples include:
- Metformin: This common diabetes drug may lower B12 levels in the body over time. A person taking metformin and receiving B12 shots should have B12 levels checked regularly.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): These drugs are used to treat acid reflux or stomach ulcers. They can lower the amount of B12 absorbed from food, which is one reason B12 injections may be recommended. However, any ongoing use should be monitored.
- Certain antibiotics or seizure medications: Some of these drugs may interfere with how the body uses or absorbs B12. A healthcare provider should be aware of all medicines being taken.
Who Should Avoid or Be Cautious with B12 Injections
B12 shots are not right for everyone. Some people need to be extra cautious or avoid them completely:
- People with Leber’s disease: This rare inherited condition affects the eyes. Vitamin B12 injections, especially in high doses, may cause vision loss in people with this disorder.
- Individuals with allergies to cobalt or B12: Since B12 contains cobalt, anyone allergic to these substances should not receive B12 injections.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: While B12 is safe and often needed during pregnancy, high doses should only be given under medical supervision.
- People with kidney problems or blood disorders: Injections might need to be adjusted for those with certain health issues. It is important for these individuals to be closely monitored.
Importance of Medical Supervision
Vitamin B12 injections should not be used without a proper diagnosis and medical guidance. Blood tests can confirm if there is a deficiency. A doctor can also check for other causes of low energy or slow weight loss before starting treatment. Regular follow-up helps make sure the injections are working as expected and that side effects are not developing.
While most people handle B12 shots well, it is important to understand both the common and rare risks. Safe use means getting the right dose, being aware of possible side effects, and making sure there is a real need for the treatment. This helps reduce unnecessary risks and improves health outcomes.
How Often Should You Get B12 Shots for Weight Loss?
Vitamin B12 shots are often used in medical and wellness settings for people trying to lose weight. The timing and frequency of these injections can vary. How often they are given depends on the person’s health, their vitamin B12 levels, and the goals of their weight loss plan. It’s important to understand how these shots are used and why regular monitoring is necessary.
Common Schedules for B12 Injections
B12 shots are usually given as intramuscular injections. This means the vitamin is injected into a muscle, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream over time. In most weight loss clinics, these shots are given once a week. Some people may get them every other week or once a month, depending on how their body responds.
Weekly injections are common for people who are starting a new weight loss program or have low energy levels. These weekly doses may continue for 4 to 6 weeks in a row. After this starting phase, some doctors may reduce the shots to once or twice a month for maintenance.
People who have a diagnosed B12 deficiency often need shots more often in the beginning. For example, someone with a serious deficiency may receive injections every day for a week, then weekly for a month, and later switch to monthly injections. These medical cases are not just for weight loss but to treat the deficiency itself.
For healthy people without a deficiency, there is no one-size-fits-all schedule. The decision often depends on how the person feels after the injection and if there is any improvement in energy levels or mood. Still, it is important to follow medical advice rather than simply guessing how often to use them.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Use
B12 shots are sometimes used for a short period as a boost during weight loss programs. This short-term use may last a few weeks or a couple of months. The idea is to increase energy, improve focus, and support the body during calorie restriction and increased physical activity.
Other people may choose to use B12 injections long-term. However, using these shots for many months without checking blood levels can be risky. Taking more vitamin B12 than needed does not always give more benefits. While the vitamin is water-soluble and extra amounts are usually passed in urine, unnecessary injections can still cause side effects or waste money.
Long-term use should be based on a real medical need. It should also be guided by a healthcare provider who checks blood levels and makes sure the body is responding well.
Importance of Medical Supervision
It is not safe to take B12 injections without medical advice. A doctor should first test blood to check B12 levels. This will help show if there is a deficiency or not. A person with normal levels may not need the injections at all.
Doctors also check for other health problems that may affect B12 absorption. For example, people who take certain medications like metformin or proton pump inhibitors may have trouble absorbing B12 from food. People with digestive issues like celiac disease or those who had weight loss surgery may also need regular injections.
After starting B12 shots, the doctor may repeat the blood test after a few weeks or months. This helps to see if the levels are going up and if the body is using the vitamin properly.
Self-injecting B12 at home is sometimes allowed if the person has a prescription and proper training. Even then, regular follow-up is needed. A healthcare provider should still track progress and watch for side effects or signs of overdose.
The frequency of B12 shots for weight loss depends on many factors, including blood levels, health history, and treatment goals. Weekly shots are common at the start, but the schedule can change based on how the body reacts. Long-term use should always involve a doctor’s care, blood tests, and proper follow-up. While B12 injections are generally safe, they must be used the right way to avoid problems and ensure the best results.
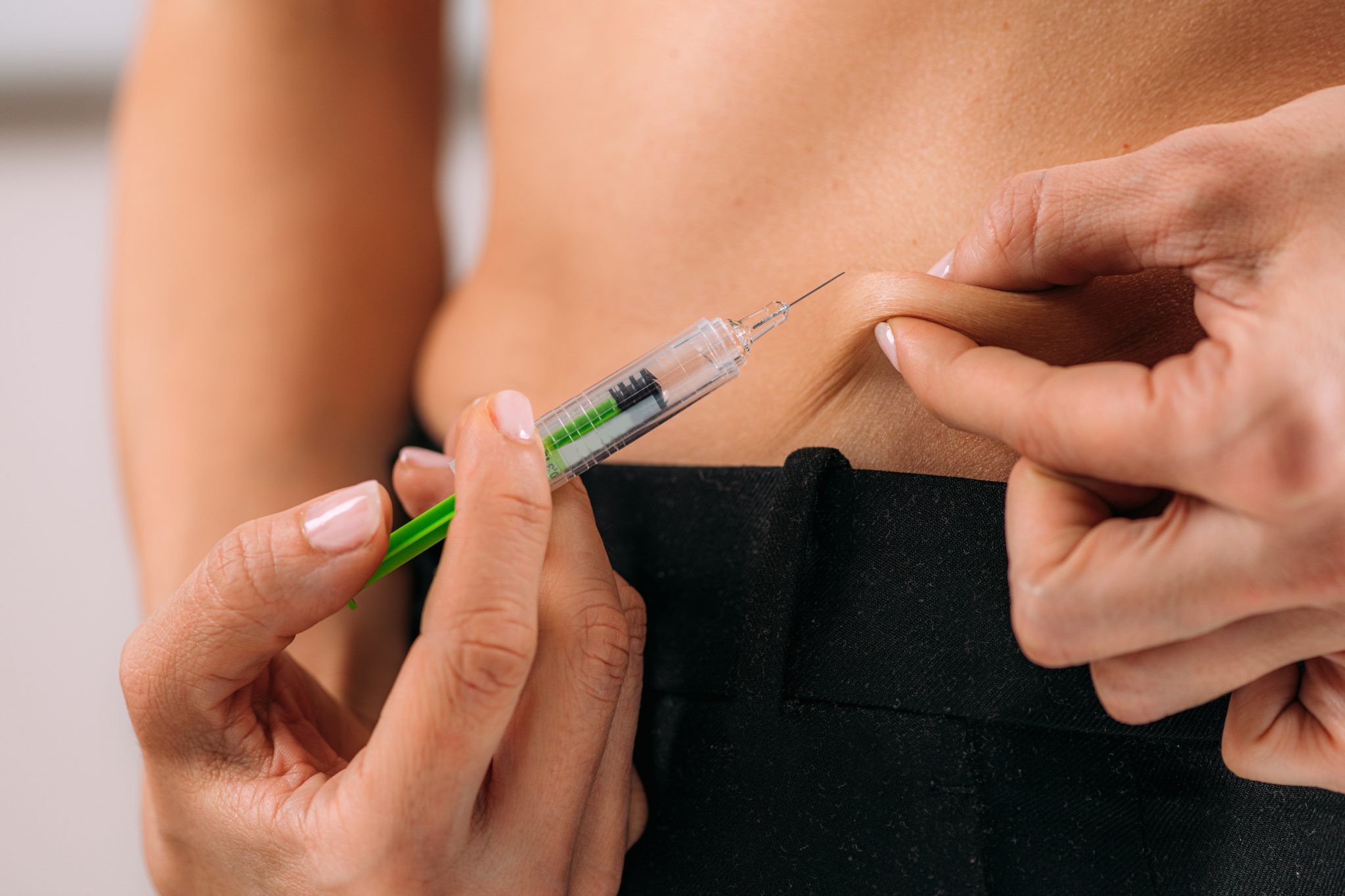
What Do Medical Guidelines Say About B12 for Weight Loss?
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that helps the body make red blood cells, maintain a healthy nervous system, and produce energy. While some weight loss clinics and online sources promote B12 injections as a way to boost metabolism or burn fat, major medical organizations have not approved Vitamin B12 as a primary treatment for weight loss. This section looks closely at what professional medical guidelines say about B12 shots, especially in relation to weight management.
No Approval for Weight Loss by the FDA
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved Vitamin B12 as a drug for weight loss. The FDA only approves medicines after strong evidence shows they are both safe and effective for a specific condition. So far, no high-quality research has shown that B12 alone causes significant weight loss in people who are not deficient in the vitamin. Because of this, B12 is not classified as a weight-loss drug.
National Institutes of Health (NIH)
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) offers clear guidelines on Vitamin B12. According to the NIH Office of Dietary Supplements, there is no evidence that B12 supplements or injections help with weight loss in people who already have normal B12 levels. The main use for B12 is to treat or prevent deficiency. Symptoms of deficiency can include fatigue, weakness, numbness in hands or feet, and memory problems. When someone with a B12 deficiency receives treatment, they may feel more energetic. That extra energy might help them become more active, which could support weight loss. However, the weight loss is a result of increased activity, not a direct effect of the B12 itself.
American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP)
The American Academy of Family Physicians also states that B12 injections are not a standard treatment for obesity or weight loss. The organization encourages a focus on healthy lifestyle habits, such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and getting behavioral support when needed. The AAFP supports using B12 shots only in cases of diagnosed deficiency, which can be found through a blood test. Giving B12 without testing or clear need is not recommended, especially when used only for weight loss.
Obesity Medicine Association (OMA)
The Obesity Medicine Association is a professional group that creates guidelines for doctors who help patients manage their weight. According to their clinical tools, weight loss medications should only be used when they are FDA-approved and prescribed as part of a full treatment plan. This includes a proper diet, physical activity, and behavior changes. B12 is not listed among the drugs recommended by the OMA for weight loss, because it does not meet the evidence requirements. The OMA does mention that patients with low B12 levels may benefit from correcting the deficiency, but it does not claim that B12 helps burn fat or suppress appetite.
Role of B12 in Supervised Weight Loss Programs
In some medical weight loss programs, B12 is used as a supportive therapy. This is often the case when patients are following a very low-calorie diet or have had weight loss surgery. In these cases, B12 may be given to prevent deficiency because the body is receiving fewer nutrients from food. This use is different from using B12 to lose weight. It is used to keep the body healthy while losing weight through other means.
All major medical guidelines agree on one point: Vitamin B12 should not be used as a weight-loss treatment unless a person is deficient in it. Giving extra B12 to someone who already has normal levels is not likely to result in weight loss. Instead, it may lead to unnecessary costs or even side effects. Medical experts recommend checking B12 levels with a blood test before starting any injections. If levels are normal, there is usually no benefit in taking more.
Doctors and health professionals support weight loss plans that are safe, science-based, and individualized. These plans may include dietary changes, exercise, counseling, and, in some cases, prescription medications. Vitamin B12 injections are only helpful when part of a medically supervised program and when deficiency is present. Using B12 as a stand-alone weight-loss method is not supported by science or clinical guidelines.
What Are the Realistic Outcomes of Using B12 Shots for Weight Loss?
Vitamin B12 shots are often promoted as a way to lose weight quickly. Many clinics and wellness centers offer B12 injections as part of a weight loss program. Some people believe that getting these shots will help burn fat, boost energy, and reduce appetite. But it is important to understand what B12 shots can and cannot do.
B12 Shots and Fat Loss
Vitamin B12 plays an important role in how the body turns food into energy. It helps break down fats and proteins and supports the health of nerve cells and red blood cells. Because of this, some people believe that more B12 will speed up fat burning. However, studies have not shown that B12 injections directly lead to fat loss in people who already have normal B12 levels.
If someone has a B12 deficiency, they may feel tired, weak, and slow. This can make it harder to exercise or stay active. In these cases, getting B12 shots can help restore energy levels, which may support physical activity and better eating habits. That, in turn, could lead to weight loss. But for people who already have healthy B12 levels, extra B12 usually does not make the body burn more fat.
Water Weight vs. Fat Loss
Some people report losing a few pounds after starting B12 shots. But this early weight loss is often due to a drop in water weight, not fat. Water weight can change quickly because of changes in diet, sodium intake, or how much fluid the body holds. Real fat loss usually takes more time and happens slowly with regular physical activity and fewer calories.
Fat loss means the body is using stored fat as energy, and it usually shows up over weeks or months. B12 shots alone do not cause this kind of steady fat loss unless they are combined with lifestyle changes like healthy eating and exercise.
B12 and Muscle Retention
When losing weight, it is important to keep as much muscle as possible. Muscle helps the body burn more calories, even at rest. B12 supports muscle function by helping the body make red blood cells, which carry oxygen to muscles. It also supports nerve health, which helps muscles work well.
If a person is low in B12, they may have poor muscle function or weakness. In this case, B12 shots can help support the body during exercise. This can help maintain or build muscle while losing fat. But again, this benefit is more likely to help people who were already lacking B12 before starting injections.
Energy and Motivation
Another common belief is that B12 shots increase energy and improve mood. Some people feel more alert or less tired after getting a B12 shot. This can help them move more, stay active, and stick to a weight loss routine. However, this boost only happens in people who were low in B12. If energy levels were already normal, extra B12 likely will not change much.
Also, the energy boost is usually mild and may not last long. It should not be confused with the kind of strong effect that stimulant medications give. B12 is a natural vitamin, not a fat burner or appetite suppressant.
B12 as Part of a Bigger Plan
The best outcomes happen when B12 shots are used as part of a full weight loss program. This means eating fewer calories, choosing healthy foods, getting regular exercise, and having medical support. B12 injections alone are unlikely to cause major weight loss. They may help with energy or mood, but they are not a replacement for other changes.
In many medical weight loss programs, B12 shots are given along with counseling, meal plans, and fitness advice. In these settings, B12 may play a supportive role. The real weight loss, though, comes from the combined effort of lifestyle changes, not from the vitamin shot itself.
What to Expect
For most people, the results from B12 shots will be mild unless there is a true B12 deficiency. Any weight loss is likely to be small and gradual. B12 can support energy and health, but it should not be seen as a quick fix. It works best when paired with a full plan that includes diet and exercise.
Expectations should be realistic. While B12 is important for many functions in the body, it is not a magic solution for weight problems. Lasting results come from steady changes over time.
How Much Do B12 Weight Loss Injections Cost?
The cost of B12 weight loss injections can vary a lot depending on where they are given, how often they are needed, and what ingredients are included. These injections may be offered in medical clinics, weight loss centers, or online through self-injection kits. Some B12 shots include only vitamin B12, while others combine B12 with other substances that are believed to help with fat metabolism. These are often called “lipotropic” injections and may cost more.
Average Cost Per Injection
For a basic B12 injection without any added ingredients, the cost usually ranges between $20 and $80 per shot. This price is common at clinics or doctor’s offices. Some clinics may charge more depending on the location or whether other services are included, such as a health check or weight-loss consultation.
When B12 is combined with lipotropic agents such as methionine, inositol, and choline (often called “MIC + B12”), the price can increase. These lipotropic injections usually cost between $50 and $150 per shot. The higher price is because the injections contain more ingredients and are often marketed as premium fat-burning treatments.
Cost of Injection Programs
Some weight-loss clinics or wellness centers offer injection programs or packages. These packages may include weekly or twice-weekly injections for a set number of weeks. A one-month program with four B12 injections may cost between $100 and $400, depending on the clinic and whether any extra services (like diet counseling or lab work) are included.
Longer programs, such as 3-month or 6-month packages, can cost over $1,000, especially if they include regular visits, progress tracking, or personalized nutrition plans. Some clinics offer discounts if patients pay upfront for a package instead of paying per visit.
Online Self-Injection Kits
B12 injections are also available as self-injection kits from online retailers or telehealth platforms. These kits may come with a vial of B12, sterile syringes, and instructions for how to inject the vitamin at home. The cost of these kits usually ranges from $60 to $200, depending on the amount of B12, the brand, and whether the kit includes medical consultation or ongoing support.
Some online providers require a quick health screening or a prescription before selling B12 injection kits. Others may offer kits directly, but it’s important to make sure the provider is licensed and that the product is safe and properly stored.
Insurance Coverage
In some cases, insurance may cover the cost of B12 injections. This usually happens only if there is a confirmed vitamin B12 deficiency, which can be shown through blood tests. For example, people with anemia caused by low B12, or those with certain medical conditions like pernicious anemia or gastrointestinal disorders, may qualify for insurance coverage.
However, B12 injections given for weight loss are rarely covered by insurance. Insurance companies usually consider these injections as elective or cosmetic, especially if the person does not have a diagnosed deficiency. Patients may have to pay the full cost out of pocket if they are using B12 shots only as part of a weight-loss plan.
Cost vs. Value
It’s important to think about the value of the treatment compared to its cost. While B12 is a necessary vitamin for health, many people can meet their needs through diet or oral supplements, which are much cheaper than injections. A bottle of B12 tablets or lozenges may cost $10 to $30 for a month’s supply, and may be just as effective for people who do not have absorption problems.
Some people choose injections because they believe they work faster or give better results. However, for people who are not truly deficient in B12, injections may not give noticeable benefits. Spending hundreds of dollars on shots that do not produce real weight loss can be costly in the long run.
Before starting B12 injections, especially those used for weight loss, it’s helpful to speak with a healthcare provider. A medical professional can test B12 levels, review health history, and help decide whether injections are needed. This can help avoid unnecessary spending and ensure the safest and most effective approach to health and weight management.
The price of B12 weight loss shots can vary widely based on ingredients, location, and how the treatment is delivered. Insurance usually does not cover them unless there is a medical reason. Weighing the cost against the actual benefits can help people make informed decisions about whether these injections are worth it.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 plays a key role in many important body functions. It helps make red blood cells, supports nerve health, and helps turn food into energy. Because of these roles, many people believe that B12 shots can help with weight loss. These shots are often advertised as a way to boost energy, burn fat, and improve metabolism. However, there is limited scientific proof that B12 shots directly cause people to lose weight—especially for those who are not deficient in the vitamin.
Some people may benefit from B12 injections, especially if they have low B12 levels. Deficiency is more common in older adults, people who follow a vegan or vegetarian diet, and those with stomach or bowel conditions such as celiac disease or after weight-loss surgery. In these cases, B12 shots can help restore healthy levels. This may lead to more energy, better mood, and the ability to be more physically active, which could support weight loss efforts. But these benefits come from correcting the deficiency—not from the B12 shot causing weight loss on its own.
Many clinics and wellness centers offer lipotropic injections, which are shots that include B12 along with other substances like methionine, inositol, and choline. These are known as MIC injections. These ingredients are thought to help the liver process fat more efficiently, but studies supporting this are small and limited. These kinds of shots are not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a treatment for weight loss. That means there is not enough strong evidence to prove they are safe or effective for this use.
B12 injections are usually safe when given by a healthcare provider. Common side effects include soreness at the injection site, mild diarrhea, or dizziness. Serious side effects are rare but can happen, especially in people who have certain health problems or take specific medicines. For example, people with Leber’s disease should avoid B12 shots because of the risk of vision loss. Some medicines, such as metformin or proton pump inhibitors, can affect how the body absorbs B12. Because of this, it is important that B12 injections are only used under medical care.
People who get B12 shots for weight loss are often told to take them once a week or every few weeks. This may continue for several months. There is no standard schedule, and how often the shots are given depends on the person’s needs and lab results. Without regular monitoring, there is a risk of getting too much B12, even though it is a water-soluble vitamin. That means the body usually removes extra B12 in urine, but very high levels over time may cause problems.
Several respected medical organizations have reviewed the use of B12 for weight loss. These include the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), and the Obesity Medicine Association (OMA). None of these organizations recommend B12 shots as a stand-alone method for losing weight. They support its use only when there is a proven deficiency or as part of a medical weight-loss plan that includes diet, exercise, and behavior changes.
When used correctly and for the right reasons, B12 shots may offer some benefits. People with a deficiency may feel better and more energized. This can help them become more active and stick to a healthy lifestyle. However, for people with normal B12 levels, the shots are unlikely to make a big difference in weight. Claims that B12 melts fat or leads to fast weight loss are not supported by strong science.
The cost of B12 weight loss injections can vary widely. Some clinics charge $20 to $75 per shot, and multiple injections may be needed over several weeks or months. Insurance may cover the shots if they are medically necessary due to a diagnosed deficiency, but not if they are used for general wellness or cosmetic weight loss. This means people could spend a lot of money without seeing much benefit.
Weight loss is a complex process. It depends on many factors like genetics, hormones, lifestyle habits, and emotional health. There is no single treatment or quick fix that works for everyone. The best results come from long-term changes, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, good sleep, and emotional support. B12 shots may be part of this plan for some people, but they are not a magic solution.
Choosing to use B12 shots should be a medical decision based on blood test results and health history. Before starting any injection therapy, it is important to talk with a qualified healthcare provider. This helps make sure the treatment is safe, necessary, and likely to help. Understanding what B12 shots can and cannot do helps set clear expectations and avoids disappointment.
Research Citations
Sun, Y., Sun, M., Liu, B., Du, Y., Rong, S., Xu, G., Snetselaar, L. G., & Bao, W. (2019). Inverse association between serum vitamin B₁₂ concentration and obesity among adults in the United States. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 10, 414. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00414
Nachtigal, M. C., Patterson, R. E., Stratton, K. L., Adams, L. A., Shattuck, A. L., & White, E. (2005). Dietary supplements and weight control in a middle‐age population. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 11(5), 909–915. doi:10.1089/acm.2005.11.909
Saper, R. B., Eisenberg, D. M., & Phillips, R. S. (2004). Common dietary supplements for weight loss. American Family Physician, 70(9), 1731–1738.
Lang, M. (2013). The effect of phentermine and B₁₂ on weight loss among obese patients [Clinical trial registration]. ClinicalTrials.gov. Registration No. NCT01719185.
Wiebe, N., Field, C. J., & Tonelli, M. (2018). A systematic review of the vitamin B₁₂, folate and homocysteine triad across body mass index. Obesity Reviews, 19(11), 1608–1618. doi:10.1111/obr.12724
Schijns, W., van den Berg, M., Wijtvliet, P. M., et al. (2018). Efficacy of oral compared with intramuscular vitamin B₁₂ supplementation after Roux‐en‐Y gastric bypass: A randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 108(1), 6–12. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqy118
Mahawar, K. K., Reid, A., Graham, Y., Callejas‐Diaz, L., Parmar, C., Carr, W. R., Jennings, N., & Singhal, R. (2018). Oral vitamin B₁₂ supplementation after Roux‐en‐Y gastric bypass: A systematic review. Obesity Surgery, 28(7), 1916–1923. doi:10.1007/s11695-017-3102-y
Metaxas, C., Mathis, D., Jeger, C., Schild, H., & Walser, M. (2017). Early biomarker response and patient preferences to oral and intramuscular vitamin B₁₂ substitution in primary care: A randomised parallel‐group trial. Swiss Medical Weekly, 147, w14421. doi:10.4414/smw.2017.14421
Sanz‐Cuesta, T., Escortell‐Mayor, E., Cura‐González, I., et al.; OB12 Group. (2020). Oral versus intramuscular administration of vitamin B₁₂ for vitamin B₁₂ deficiency in primary care: A pragmatic, randomised, non‐inferiority clinical trial (OB12). BMJ Open, 10(8), e033687. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033687
Aasheim, E. T., Bjørkman, S., Sovik, T. T., et al. (2008). Vitamin status in morbidly obese patients: A cross‐sectional study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 87(2), 362–369. doi:10.1093/ajcn/87.2.362
Questions and Answers: Weight Loss Shot B12
A B12 weight loss shot is an injection that delivers a high dose of vitamin B12 directly into the bloodstream. It is often promoted to boost energy, support metabolism, and aid weight loss.
Vitamin B12 helps convert fats and proteins into energy and supports proper metabolism. While it doesn’t directly cause weight loss, it may enhance energy levels and stamina, helping with physical activity and calorie burning.
People with a B12 deficiency, vegetarians, vegans, older adults, or those with absorption issues (like after gastric surgery) may benefit, as the injection bypasses digestive absorption.
No, B12 shots alone do not cause weight loss. They may support a weight loss plan when combined with a healthy diet and exercise.
Yes, for most people, B12 shots are considered safe. The body excretes excess B12 through urine, so toxicity is rare.
Frequency varies based on individual needs, but they are often administered weekly or bi-weekly, especially during weight loss programs.
Mild side effects may include pain at the injection site, headache, dizziness, or nausea. Serious side effects are rare.
Yes, especially for those deficient in B12. Increased energy may indirectly support more physical activity, which can aid weight loss.
They are generally safe for most adults, but it’s best to consult a healthcare provider, especially if you have a medical condition or take medications.
B12 shots deliver the vitamin directly into the bloodstream for better absorption, especially in people with digestive issues, while oral supplements rely on gut absorption, which may be less effective in some individuals.

Dr. Kevin Kargman
Dr. Kevin J. Kargman is a pediatrician in Sewell, New Jersey and is affiliated with multiple hospitals in the area, including Cooper University Health Care-Camden and Jefferson Health-Stratford, Cherry Hill and Washington Township. (Learn More)