Table of Contents
Introduction
Colitis is a condition that causes inflammation in the colon, which is a key part of the digestive system. The inflammation can lead to uncomfortable symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and even bleeding. For people living with colitis, these symptoms can significantly impact their quality of life, making daily activities and routines more difficult. Managing colitis effectively requires a focus on reducing this inflammation, which can help to prevent flare-ups and promote better health over time.
One of the newer treatments being explored for managing chronic conditions, including colitis, is semaglutide. Semaglutide is a medication known as a GLP-1 receptor agonist. It was first approved for use in managing type 2 diabetes, but its benefits have extended beyond blood sugar control. Many researchers are now looking at how semaglutide might help with other conditions that involve inflammation and metabolic issues, including colitis. Because semaglutide can have a role in controlling inflammation, it has become an area of interest for patients and healthcare providers who are looking for new ways to manage colitis.
This article is designed to give a clear and thorough understanding of how semaglutide might be used to manage colitis. It will answer common questions that people often search for when they are exploring semaglutide as a treatment option for colitis. Questions like how semaglutide works, what the latest research says, and what side effects to watch out for will all be covered in detail. The goal is to provide readers with a better understanding of whether semaglutide could be a helpful part of their treatment plan.
By looking at both the scientific information and the practical aspects of using semaglutide, this guide aims to help readers make more informed decisions about their health. It is important to note that while semaglutide has shown potential, it is not a cure for colitis. Instead, it is one of many tools that can be used to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for those dealing with this condition.
Throughout the article, the focus will be on providing easy-to-understand information without getting too technical. The goal is to ensure that even readers who are not familiar with medical terms can grasp the key points. Managing a condition like colitis can be challenging, and finding clear information is essential for anyone trying to navigate their treatment options.
For those new to semaglutide, understanding how it works is a key starting point. Semaglutide belongs to a class of medications that help regulate blood sugar levels in people with diabetes, but it has effects that go beyond blood sugar control. It can help reduce inflammation, which is why it is being studied for conditions like colitis. Inflammation is a big part of what makes colitis so painful and disruptive, so medications that target inflammation can be especially useful. Semaglutide’s ability to reduce inflammation may make it a valuable option for people who have not found relief with other treatments.
In this guide, readers will also learn about how semaglutide is used specifically for managing colitis, including what the research says and how it might help reduce flare-ups. We will cover practical details, like how to take semaglutide and what side effects to look out for. It’s important to have realistic expectations when considering any new treatment, so this article aims to provide a balanced view of what semaglutide can offer and where its limitations lie.
Understanding the latest research can also help patients have better conversations with their healthcare providers. Many patients may have already tried other treatments for colitis without finding the relief they need. For them, learning about a newer option like semaglutide could be an important part of managing their condition. While semaglutide is not a replacement for other treatments or a substitute for a doctor’s advice, it represents another possibility that may improve the way colitis is managed.
Finally, this guide emphasizes the importance of working closely with healthcare providers when considering semaglutide as a treatment option. Every person’s experience with colitis is unique, and what works well for one person might not work as well for another. By providing a thorough understanding of how semaglutide might fit into a colitis management plan, this article aims to support patients and their caregivers in making informed decisions. In the end, the hope is that with the right knowledge and approach, those living with colitis can find better ways to manage their symptoms and achieve a better quality of life.
What is Semaglutide?
Semaglutide is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as GLP-1 receptor agonists. GLP-1 stands for glucagon-like peptide-1, which is a natural hormone in the body. This hormone plays an important role in regulating blood sugar levels, appetite, and insulin production. Semaglutide was initially developed to treat type 2 diabetes, but its benefits go beyond managing blood sugar. It has shown promise in helping with weight loss and reducing inflammation, making it an interesting option for managing other conditions like colitis.
How Semaglutide Works in the Body
To understand how semaglutide works, it helps to know a bit about GLP-1. GLP-1 is released in the gut when you eat. It signals your pancreas to produce insulin, which helps lower blood sugar. It also slows down the movement of food through the stomach, making you feel full longer. This is why people who take semaglutide often find that they eat less and lose weight over time.
Semaglutide mimics the effects of GLP-1 in the body. When you take semaglutide, it binds to GLP-1 receptors, which are like little docking stations in your body that react to the hormone. By doing this, semaglutide helps to:
- Increase insulin release when blood sugar levels are high.
- Decrease the amount of sugar released by the liver.
- Slow down digestion, which can help control appetite.
This combination of effects makes semaglutide effective not only for controlling blood sugar but also for helping people lose weight. The slower digestion helps people feel full longer, so they eat less without feeling hungry. This has been a key reason why semaglutide has become popular beyond just diabetes management.
Semaglutide’s Role in Inflammation
One lesser-known benefit of semaglutide is its potential role in reducing inflammation. Inflammation is the body’s way of responding to injury or infection, but too much inflammation can cause problems, especially in conditions like colitis. Colitis is an inflammation of the colon (large intestine) that can cause pain, diarrhea, and other digestive issues. While semaglutide is not specifically approved for treating colitis, some studies suggest that it could help manage inflammation, which is a big part of colitis symptoms.
Semaglutide may help reduce inflammation by affecting the immune system. It can modify certain immune cells, making them less active in attacking the body’s tissues. This can help reduce the inflammation that causes pain and other symptoms in colitis. However, more research is needed to fully understand how effective semaglutide is for this purpose. For now, it offers hope as a potential treatment option for people with colitis who are looking for better ways to manage their symptoms.
FDA Approval and Uses of Semaglutide
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved semaglutide for treating type 2 diabetes under the brand names Ozempic and Rybelsus. Ozempic is given as a weekly injection, while Rybelsus is a daily pill. More recently, the FDA also approved semaglutide for chronic weight management under the brand name Wegovy. Wegovy is meant for people who have obesity or are overweight with weight-related health conditions.
Even though semaglutide is not officially approved for colitis, doctors may consider using it for other benefits, such as weight loss or reducing inflammation. This is known as “off-label” use. Off-label use means a drug is used in a way that is not specifically approved by the FDA. It is important to remember that using semaglutide for colitis should be done under the supervision of a doctor, who can monitor for any side effects and adjust the treatment as needed.
Who Might Benefit from Semaglutide?
Semaglutide could be a helpful option for people who have both type 2 diabetes and colitis. Managing blood sugar levels is important for overall health, and reducing weight can help decrease the strain on the digestive system, which may benefit colitis symptoms. Since semaglutide helps with both of these issues, it might be a good fit for some patients. However, it is not suitable for everyone. People with a history of certain types of thyroid cancer or severe allergic reactions should avoid this medication.
Semaglutide is a versatile medication that works by mimicking a natural hormone in the body, GLP-1, to regulate blood sugar, reduce appetite, and potentially lower inflammation. While it is primarily used for managing type 2 diabetes and weight loss, research suggests that it may also have potential benefits for managing conditions like colitis. It is important for patients to discuss with their healthcare providers if semaglutide might be right for them, especially if they are considering it as part of their colitis treatment plan.
Understanding Colitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Types
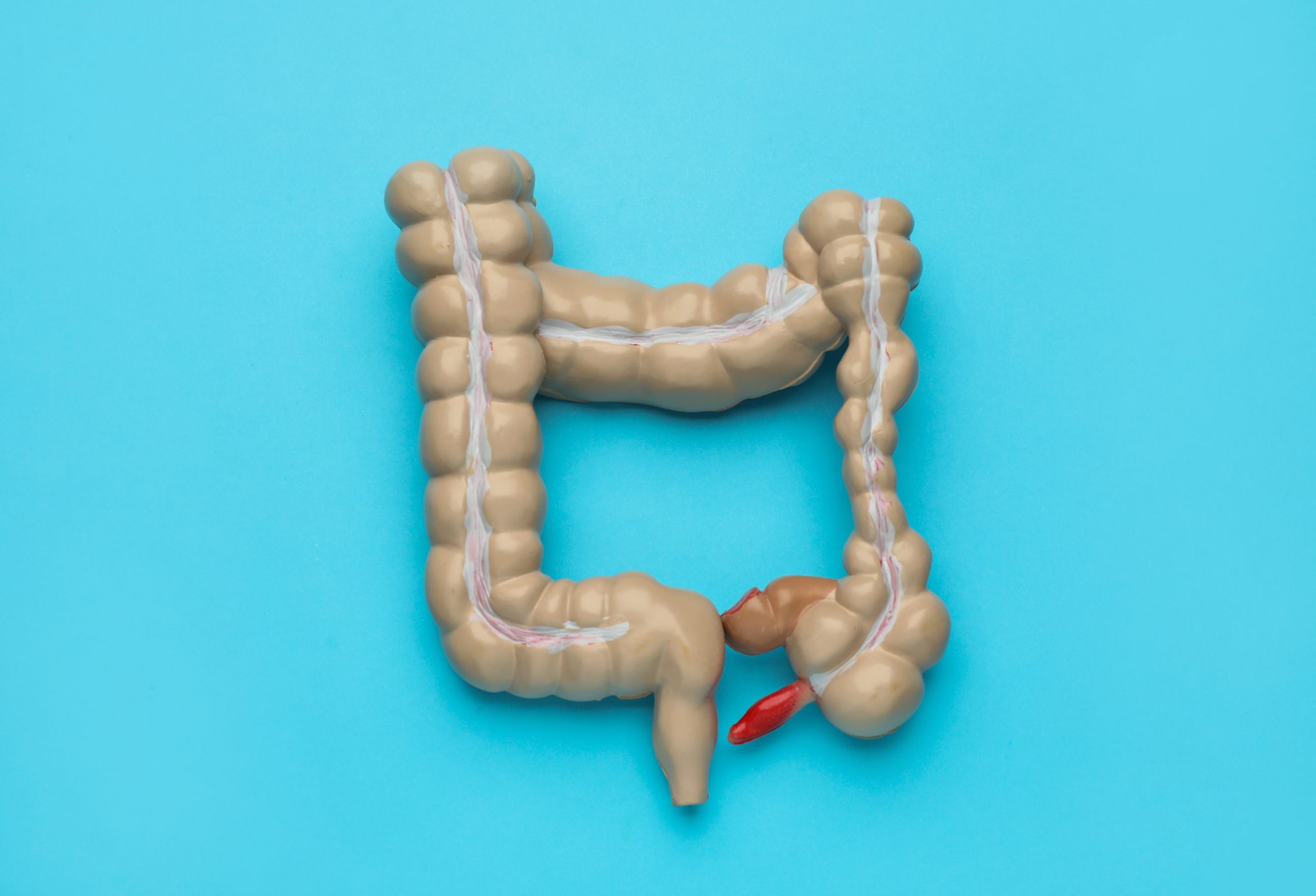
Colitis is a condition that causes inflammation in the colon, which is part of the large intestine. This inflammation can make the colon swollen, irritated, and unable to work properly. Colitis can cause pain, discomfort, and other symptoms that can affect daily life. Understanding what causes colitis, its symptoms, and the different types is important for anyone who is managing this condition.
Causes of Colitis
Colitis can have many causes. It’s not always clear why someone develops it, but some common reasons include:
- Infections: Certain viruses, bacteria, or parasites can infect the colon and cause inflammation. For example, food poisoning caused by bacteria like Salmonella or E. coli can lead to colitis. Infections can often be treated with medication, but sometimes they can cause ongoing inflammation even after the infection is gone.
- Autoimmune Reactions: In some people, the immune system mistakenly attacks the colon. This is what happens in conditions like ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. The immune system usually protects the body from harmful invaders, but in autoimmune colitis, it causes damage to the body’s own tissues, leading to inflammation.
- Reduced Blood Flow (Ischemic Colitis): Sometimes, colitis happens because not enough blood is reaching the colon. This can occur due to narrowed or blocked blood vessels, which may happen in older adults or those with conditions like heart disease. Without enough blood, the colon tissue can become damaged, leading to pain and inflammation.
- Medications: Certain drugs, like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and some antibiotics, can irritate the lining of the colon. This irritation can cause colitis in some people, especially if the medication is taken for a long time.
Symptoms of Colitis
Colitis can cause a range of symptoms, and the severity can vary from person to person. Some people may experience only mild discomfort, while others have more serious issues. Here are the most common symptoms:
- Abdominal Pain: Pain in the belly area is a common symptom of colitis. The pain is often cramping and can come and go. It might get worse after eating or before having a bowel movement.
- Diarrhea: Many people with colitis experience diarrhea, which means having loose or watery stools. Sometimes, the diarrhea can be very frequent and may contain blood or mucus, especially during a flare-up.
- Urgency to Have a Bowel Movement: People with colitis may feel a sudden and strong need to go to the bathroom. This can be inconvenient and stressful, especially if they are not near a restroom.
- Fatigue: Inflammation in the body can make people feel tired or have low energy. If the body is losing fluids and nutrients due to diarrhea, it can also make fatigue worse.
- Weight Loss: Some people with colitis lose weight unintentionally. This can happen if they have trouble eating due to nausea or if their body is not absorbing nutrients properly from food.
Types of Colitis
There are several types of colitis, each with its own causes and characteristics. Here are some of the most common types:
- Ulcerative Colitis: This type of colitis affects the inner lining of the colon and rectum. It causes ulcers, which are small open sores, and continuous inflammation. The symptoms can include bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition, which means it can last a long time, but it can have periods where the symptoms go away for a while.
- Crohn’s Disease: Although Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, it often affects the end of the small intestine and the beginning of the colon. It causes inflammation that can reach deeper into the layers of the bowel wall. Crohn’s disease can cause symptoms similar to ulcerative colitis, like abdominal pain and diarrhea, but it can also cause complications outside of the digestive system, such as skin rashes or joint pain.
- Microscopic Colitis: This type of colitis is not as well-known as others, but it can cause chronic diarrhea. It is called “microscopic” because the inflammation can only be seen under a microscope. There are two subtypes: collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis. Both types cause chronic diarrhea but do not cause the same visible damage to the colon as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease.
- Ischemic Colitis: Ischemic colitis happens when blood flow to the colon is reduced, causing parts of the colon to become inflamed or even die off. It is more common in older adults and can cause sudden abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea. This type of colitis can be temporary, but it sometimes requires treatment if the blood flow problem is not resolved.
- Infectious Colitis: This type of colitis is caused by an infection from bacteria, viruses, or parasites. It often comes on suddenly and can cause severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, and sometimes fever. Treatment usually focuses on getting rid of the infection, which can involve antibiotics or other medications.
Understanding these causes, symptoms, and types of colitis helps patients and caregivers recognize the signs of the condition and seek proper treatment. It also makes it easier to talk with doctors about what might be happening in the body and what treatments, like semaglutide, might be helpful in managing symptoms and improving quality of life.

How Does Semaglutide Work in the Context of Colitis?
Semaglutide is a type of medication known as a GLP-1 receptor agonist. GLP-1 stands for glucagon-like peptide-1, which is a hormone naturally produced in the gut. It plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels, reducing appetite, and helping with weight management. However, semaglutide’s benefits go beyond these functions. For people with colitis, semaglutide may also help manage inflammation in the digestive system. Understanding how semaglutide works can help patients and doctors use it more effectively in treating colitis.
Semaglutide’s Role in Reducing Inflammation
Colitis involves inflammation of the lining of the colon, which can cause symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss. Inflammation occurs when the immune system overreacts and damages the colon. Semaglutide might help reduce this inflammation. It affects certain pathways in the immune system, which can help calm the overactive immune responses seen in colitis.
Semaglutide increases the levels of GLP-1 in the body. GLP-1 has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, which means it can reduce inflammation. For colitis patients, this is important because lowering inflammation can lead to fewer symptoms and longer periods without flare-ups. By reducing inflammation, semaglutide may help to keep the colon healthier and more stable over time.
How Semaglutide Affects the Immune System
One of the ways semaglutide may help people with colitis is by influencing the immune system. In colitis, the immune system attacks the cells in the colon lining, causing damage and inflammation. Semaglutide can change how certain immune cells act, making them less likely to cause harm. This could mean less damage to the colon and, as a result, fewer symptoms of colitis.
Semaglutide also helps by improving gut health. GLP-1 receptors are found in the gut, and when these receptors are activated by semaglutide, they can help the gut heal itself. This healing process is critical for people with colitis, as it may help repair the damaged lining of the colon. A stronger, healthier gut lining means that the colon can better absorb nutrients and maintain a balanced environment, which may lead to overall better health for people with colitis.
Semaglutide and the Gut-Brain Axis
Another interesting way semaglutide may help with colitis is through something called the gut-brain axis. The gut-brain axis is the connection between the brain and the digestive system. When inflammation occurs in the gut, it can send signals to the brain that contribute to pain and discomfort. Semaglutide may help reduce these signals by calming the gut and reducing inflammation.
By influencing the gut-brain axis, semaglutide could help reduce pain and discomfort often associated with colitis. This might make it easier for patients to manage their symptoms daily. While research is ongoing, some studies suggest that this gut-brain interaction could be a key reason why semaglutide helps people with colitis feel better.
Potential Benefits for Colitis Patients
For those with colitis, semaglutide could offer several potential benefits. First, its ability to reduce inflammation may lead to fewer flare-ups and more stable periods of remission. A flare-up is when colitis symptoms, such as abdominal pain and diarrhea, suddenly get worse. By reducing inflammation, semaglutide might help prevent these flare-ups from happening too often.
Second, semaglutide may improve the overall quality of life for people with colitis. Since it can help manage pain and discomfort by calming the gut, patients might experience less pain during their daily activities. Additionally, by helping to heal the gut lining, semaglutide might help improve nutrient absorption, which can be a challenge for those with colitis due to their damaged colon lining.
Finally, semaglutide’s role in weight management can also be a benefit. Some people with colitis struggle with maintaining a healthy weight because of their symptoms. By helping with appetite control and weight loss, semaglutide may help patients reach a healthier weight, which is important for their overall well-being.
Ongoing Research and Future Possibilities
While semaglutide shows promise for managing colitis, more research is needed to fully understand how it can be best used for this condition. Some studies are exploring how different doses of semaglutide might work specifically for reducing inflammation in the colon. Researchers are also looking into how semaglutide might be combined with other treatments for even better results.
Doctors and patients should have open conversations about the potential benefits and risks of using semaglutide for colitis. This ensures that semaglutide is used in the safest and most effective way possible, tailored to the needs of each patient. As research continues, there is hope that semaglutide could become an important part of managing colitis and improving the quality of life for those affected.
This detailed explanation of semaglutide’s role in colitis management highlights how the medication’s effects on inflammation, immune responses, and the gut-brain axis can make a difference for patients.
What Does Current Research Say About Semaglutide and Colitis?
Research on semaglutide, primarily used for diabetes and weight management, has expanded to explore its potential in managing inflammatory conditions like colitis. Colitis, a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), involves inflammation of the colon, causing symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss. While semaglutide is not yet a standard treatment for colitis, recent studies suggest it may help control inflammation in the digestive tract.
Understanding the Connection Between Semaglutide and Inflammation
Semaglutide belongs to a class of drugs called GLP-1 receptor agonists. These drugs mimic a hormone in the body called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels. However, GLP-1 also influences inflammation in the body. This dual effect has led researchers to study whether semaglutide might help with conditions like colitis, where inflammation is a major problem.
The GLP-1 receptors are present in various parts of the body, including the intestines. When semaglutide activates these receptors, it may help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. This could be especially helpful for people with colitis, who often experience inflammation that leads to pain and discomfort.
Clinical Studies on Semaglutide and Colitis
Several studies have explored the effects of semaglutide on inflammation, although many of these focus on general inflammation rather than colitis specifically. In one study, researchers found that semaglutide helped reduce markers of inflammation in people with obesity and diabetes. These findings suggest that semaglutide might have a broader role in controlling inflammation beyond its original use.
Another study looked at the effects of semaglutide in animals with induced colitis. The study found that semaglutide reduced inflammation in the colon, leading to fewer symptoms of colitis in these animals. While animal studies do not always translate directly to humans, they provide a foundation for further research in this area.
A small clinical trial tested semaglutide in people with Crohn’s disease, another type of IBD that shares similarities with colitis. The trial showed promising results, with some participants experiencing a reduction in symptoms and inflammation. These results indicate that semaglutide may have potential benefits for other types of IBD, including colitis, though more targeted studies are needed.
The Role of GLP-1 Agonists in Immune System Modulation
Researchers are also interested in how semaglutide may influence the immune system. Colitis is thought to involve an overactive immune response that attacks the lining of the digestive tract, leading to inflammation. By modulating the immune system, semaglutide might help calm this response and reduce symptoms of colitis.
GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide may help to balance immune activity, reducing the release of inflammatory molecules called cytokines. These molecules can worsen the symptoms of colitis by increasing inflammation. Some studies suggest that semaglutide may help lower the levels of these cytokines, leading to less inflammation in the gut.
Limitations and the Need for More Research
While the current research is promising, it is important to note that semaglutide is not yet approved specifically for colitis. Most studies so far have focused on general inflammation or other types of IBD, like Crohn’s disease. More research is needed to understand how semaglutide works in people with colitis and to determine the best ways to use it for this condition.
Experts believe that larger, longer-term clinical trials could help clarify the role of semaglutide in colitis management. These studies would need to examine how effective semaglutide is in reducing symptoms, whether it can maintain remission (a period without symptoms), and what the long-term safety profile looks like for colitis patients.
Potential Benefits Highlighted by Early Research
Although more evidence is needed, the current studies highlight some potential benefits of using semaglutide for colitis. For example, if semaglutide can reduce inflammation in the gut, it might help patients experience fewer flare-ups, where symptoms suddenly get worse. Managing inflammation more effectively could also lead to better overall well-being, as reducing pain and discomfort improves quality of life.
Additionally, since semaglutide is already approved for other conditions, doctors are familiar with its use and side effects. This could make it easier to integrate semaglutide into colitis treatment plans if future research supports its benefits. Patients may feel more comfortable trying a medication that has already been studied for safety in other conditions, even though more studies are needed for colitis specifically.
Current research into semaglutide’s role in managing colitis is still in the early stages, but the results so far are encouraging. By reducing inflammation and potentially modulating the immune system, semaglutide could offer a new option for patients struggling with this challenging condition. As researchers continue to explore this area, more concrete answers may become available, bringing hope for improved colitis management in the future.
How to Use Semaglutide for Managing Colitis
Using semaglutide for managing colitis requires careful planning and guidance from a healthcare provider. This section will explain how to use this medication properly, including recommended dosages, the best way to take it, and why it is essential to consult a doctor before starting treatment. Understanding these steps can help patients use semaglutide safely and effectively for better control of colitis symptoms.
Dosage Recommendations for Colitis Patients
Semaglutide is a medication that is usually given as an injection. It is important to know that the right dose can vary from person to person. A doctor will determine the appropriate starting dose based on the patient’s condition, weight, and other medications they might be taking. Typically, patients may begin with a low dose, like 0.25 mg once a week. This is to help the body adjust to the medication and reduce the chances of side effects.
After a few weeks, the doctor may increase the dose to 0.5 mg or higher, depending on how the patient responds to the medication. The goal is to find the lowest effective dose that helps control the inflammation and symptoms of colitis without causing too many side effects. In some cases, a higher dose like 1 mg per week may be used, but only if a healthcare provider thinks it is necessary.
Best Practices for Administering Semaglutide
Administering semaglutide is fairly straightforward but requires some preparation. The medication comes in a pre-filled pen, making it easy for patients to give themselves an injection. Here are some key tips for taking semaglutide properly:
- Choose the Injection Site Carefully: Semaglutide is usually injected into the skin on the stomach, thigh, or upper arm. It is important to rotate injection sites to avoid irritation or skin problems. For example, if you inject in the stomach one week, try using the thigh the next time.
- Follow the Instructions Provided: Each pen comes with instructions, but it is always best to get a demonstration from a healthcare provider first. They can show you how to use the pen and ensure you are comfortable with the process. Make sure to follow each step carefully to avoid mistakes.
- Take Semaglutide at the Same Time Each Week: Consistency is key for semaglutide to work effectively. Try to pick the same day each week to take your injection. For example, if you take it every Monday morning, continue doing so. This helps maintain a steady level of the medication in your body.
- Store the Medication Correctly: Semaglutide needs to be stored in a refrigerator before using it. Once you start using a pen, you can keep it at room temperature for a short time, but make sure to avoid extreme heat or cold. Proper storage ensures that the medication remains effective.
The Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Provider
Before starting semaglutide for colitis, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider. This step is essential because colitis is a complex condition, and semaglutide is not traditionally used for treating it. A doctor can evaluate whether semaglutide is the right choice for your specific case. They will consider factors like the severity of your colitis, your overall health, and any other medications you may be taking.
Doctors will also monitor you closely during the first few weeks of treatment. This monitoring can help detect any side effects early and adjust the dosage if needed. For example, if a patient experiences nausea or vomiting, the doctor might recommend lowering the dose temporarily before increasing it again.
Additionally, semaglutide can interact with other medications. A healthcare provider will check for any possible interactions with your current prescriptions to ensure that semaglutide is safe to use. This is why it is important to give your doctor a full list of all medications, supplements, and vitamins you are taking before starting semaglutide.
Why Proper Use is Important for Colitis Management
Using semaglutide correctly can make a significant difference in managing colitis symptoms. It helps to keep the medication levels stable in your body, which is important for reducing inflammation. Colitis often involves periods of flare-ups and remission, where symptoms can come and go. By using semaglutide as directed, patients may experience fewer flare-ups and better control over their symptoms.
However, skipping doses or not following the recommended injection schedule can reduce the effectiveness of semaglutide. This might lead to an increase in symptoms or even cause new side effects. Therefore, it is important to follow the prescribed routine closely and speak to a doctor before making any changes to the dosage or schedule.
Semaglutide can be an effective tool in managing colitis, but it requires careful use. Following the right dosage, using proper injection techniques, and working closely with a healthcare provider can help ensure the best outcomes. This approach allows patients to take control of their health and improve their quality of life while managing the symptoms of colitis.

Possible Side Effects of Using Semaglutide for Colitis
Semaglutide can be helpful for people with colitis, but like any medication, it may have some side effects. Understanding these side effects is important for patients and caregivers. Being aware of what to expect can help you know when to seek medical help. Here, we will look at common and rare side effects of semaglutide, how these side effects may appear in people with colitis, and some tips for managing and monitoring these effects.
Common Side Effects of Semaglutide
Some side effects of semaglutide are more common than others. These include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach pain. Nausea happens because semaglutide slows down how fast food leaves the stomach. For some people, this feeling can be mild and go away over time. For others, it can be more severe. Nausea usually happens more often when a person first starts taking semaglutide or increases their dose.
Vomiting can also occur because of this slower digestion process. While it can be uncomfortable, it may reduce after the body adjusts to the medication. Diarrhea is another common side effect that may happen as semaglutide changes the way the digestive system works. For people with colitis, this side effect can be particularly challenging because diarrhea is already a symptom of their condition. Stomach pain or cramping may occur due to the same changes in digestion.
Rare Side Effects and Serious Reactions
There are also rare but serious side effects that can occur with semaglutide. These include pancreatitis, which is inflammation of the pancreas. Symptoms of pancreatitis include severe pain in the stomach area that does not go away, nausea, and vomiting. If a person experiences these symptoms, they should contact a healthcare provider immediately.
Another rare side effect is a possible allergic reaction to semaglutide. This could include symptoms like rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. While allergic reactions are not common, they require quick medical attention if they happen.
Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can also happen, especially if semaglutide is used with other diabetes medications. Symptoms of low blood sugar include dizziness, sweating, confusion, and feeling very hungry. This is more of a concern for people with diabetes but should be monitored in any patient using semaglutide.
How These Side Effects May Affect People with Colitis
For people with colitis, some of these side effects may be harder to manage. For example, diarrhea caused by semaglutide can worsen the diarrhea already present in colitis. This can lead to dehydration, which is when the body loses too much water. Staying hydrated by drinking water and electrolyte solutions can help prevent dehydration.
Stomach pain and cramping can also overlap with colitis symptoms, making it hard to tell whether the pain is from the medication or the condition itself. It is important to track when the pain occurs, its intensity, and any other symptoms that come with it. Keeping a symptom diary can help doctors understand what might be causing the pain.
Nausea and vomiting might make it difficult to eat properly. For someone with colitis, maintaining a balanced diet is important for keeping the digestive system healthy. If nausea and vomiting prevent a person from eating enough, they may need to talk to their doctor about adjusting their dose or finding other ways to manage these symptoms.
Tips for Managing and Monitoring Side Effects
If side effects occur, there are ways to help manage them. For nausea, eating smaller meals and avoiding spicy or greasy foods can be helpful. Drinking ginger tea or using ginger supplements may also calm the stomach. If nausea becomes too much to handle, it is important to speak to a healthcare provider, who might adjust the dose of semaglutide.
To help with diarrhea, it is important to stay hydrated. Drinking plenty of fluids, especially those with electrolytes, can help replace what the body loses. Avoiding foods that can irritate the stomach, like dairy, caffeine, and high-fiber foods, might also reduce diarrhea. A doctor may recommend medications that can help control diarrhea if it is severe.
For people who experience stomach pain, using a heating pad on the stomach area can provide some comfort. Gentle movements or light walking can also help reduce cramping. It is important not to ignore any pain that feels very severe or lasts for a long time. Such pain could be a sign of something more serious, like pancreatitis, and should be checked by a healthcare provider.
When to Seek Medical Help
It is always better to be cautious when new side effects appear. If someone experiences symptoms like severe stomach pain, vomiting that does not stop, or signs of an allergic reaction, they should seek medical help immediately. Even though these serious side effects are rare, they need quick attention when they do happen.
For less serious side effects like mild nausea or diarrhea, patients can usually manage them at home with the tips mentioned above. However, if these side effects last longer than a few weeks or get worse, it is a good idea to talk to a doctor. Adjustments to the treatment plan may be needed to ensure the patient can continue taking semaglutide without too much discomfort.
Understanding these possible side effects and knowing how to manage them can help people with colitis use semaglutide safely and effectively. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers, patients can focus on improving their health while minimizing the challenges that come with new treatments.
Can Semaglutide Help in Reducing Flare-Ups in Colitis?
Colitis is a condition where the lining of the colon becomes inflamed, leading to pain, diarrhea, and other digestive issues. People with colitis often experience periods where symptoms get worse, called flare-ups. Managing these flare-ups is key to improving quality of life for those with colitis. Some recent studies and patient experiences suggest that semaglutide, a medication originally developed for diabetes, might help reduce these flare-ups. Here’s how semaglutide may work to manage inflammation during these challenging times.
How Semaglutide Reduces Inflammation
Semaglutide is a type of drug called a GLP-1 receptor agonist. It works by mimicking a hormone in the body called GLP-1, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and appetite. But recent research shows that GLP-1 may also play a role in controlling inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a major part of colitis, as it causes the colon’s lining to become irritated and swollen. By reducing inflammation, semaglutide may help keep colitis symptoms under control.
When semaglutide activates GLP-1 receptors, it can decrease the release of certain chemicals in the body that cause inflammation. This might help prevent the colon from becoming too inflamed during a flare-up. For some people, this means fewer flare-ups or less severe symptoms when they do occur.
Research on Semaglutide and Colitis Flare-Ups
While semaglutide is not specifically approved for treating colitis, early studies show promise. Some research suggests that it may help reduce inflammation markers in people with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), which include colitis. Reducing these markers means that the body is producing fewer substances that cause swelling and irritation in the colon.
One study looked at patients with colitis who were given semaglutide for a few weeks. Researchers found that these patients had a decrease in inflammation in their digestive tracts. This reduction in inflammation is important because it may help to keep the colon healthier, preventing severe flare-ups. However, more research is needed to fully understand how well semaglutide can work for people with colitis over the long term.
Comparing Semaglutide with Other Flare-Up Treatments
Traditionally, doctors use medications like corticosteroids and immunosuppressants to manage colitis flare-ups. These drugs work by directly reducing the immune system’s activity, which in turn lowers inflammation. However, they can have side effects, such as weakening the immune system or causing bone loss with long-term use.
Semaglutide might offer a different approach. Instead of directly suppressing the immune system, it helps regulate inflammation through the GLP-1 pathway. This could mean fewer side effects compared to other treatments, though each patient’s experience may differ. Because semaglutide is mainly used for diabetes and weight management, doctors would need to closely monitor its effects when used for colitis.
Practical Tips for Using Semaglutide During Flare-Ups
If you are using semaglutide for colitis, it’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully, especially during flare-ups. Here are some key tips:
- Stick to Your Dose: Always take semaglutide at the dose your doctor prescribes. Taking too much or too little can affect how well it works and might increase side effects.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keep a journal of your symptoms, noting when they get better or worse. This can help your doctor see if semaglutide is helping to control your flare-ups.
- Report Side Effects: Some people may experience nausea, vomiting, or other side effects when using semaglutide. It’s important to let your doctor know about any side effects, especially if they get worse during a flare-up.
- Stay Hydrated: Colitis flare-ups can cause diarrhea, leading to dehydration. Drinking plenty of fluids can help prevent dehydration, especially if you are using semaglutide, which may affect your appetite and hydration levels.
What to Expect When Using Semaglutide for Flare-Ups
Using semaglutide during colitis flare-ups is not a quick fix, and it may take a few weeks to notice improvements. Some people may find that their symptoms become less severe or that flare-ups happen less often. However, it’s also possible that semaglutide might not work as well for every person with colitis, and some may need to use other treatments alongside it.
It’s essential to have realistic expectations and to keep in close contact with your healthcare provider while using semaglutide. Your doctor may adjust your treatment plan over time based on how well the medication is working for you.
The Bottom Line
Semaglutide may be a helpful option for some people with colitis, particularly when it comes to reducing inflammation during flare-ups. By targeting the underlying inflammation through the GLP-1 pathway, it might offer a different way to manage symptoms compared to traditional treatments. However, it’s important to remember that every person’s response to medication is unique. Consulting with a healthcare provider is the best way to determine if semaglutide might be right for you during colitis flare-ups.

Patient Experiences and Reported Outcomes of Semaglutide for Colitis
When it comes to managing colitis, many patients look for options that can provide relief and help them lead a better life. Semaglutide, a medication originally used to manage diabetes, has shown potential benefits for people with colitis. Understanding how patients experience this medication and what outcomes they have seen can be important for those considering semaglutide for their own treatment.
General Trends Observed in Patients
Many patients who have used semaglutide for colitis report that it has helped reduce the inflammation that causes their symptoms. In colitis, the immune system attacks the digestive tract, leading to pain, diarrhea, and other uncomfortable symptoms. Semaglutide, by influencing certain body signals, may help lower this inflammation. Some patients have noticed that their symptoms become less severe after starting semaglutide. This can include fewer days with stomach pain and reduced frequency of urgent bowel movements.
In some cases, patients have mentioned that semaglutide helped them gain better control over their weight. For people with colitis, managing weight can be difficult due to the fluctuations in appetite and digestive issues. Semaglutide’s role in controlling appetite may make it easier for patients to maintain a healthy weight, which can positively impact their overall health.
Reported Improvements in Quality of Life
A significant part of dealing with colitis is managing how the condition affects daily life. Patients using semaglutide often report improvements in their quality of life. This means they feel better day-to-day and are able to perform regular activities with less discomfort. For example, some patients have shared that they experience fewer days of feeling fatigued, which is common in people with colitis. This can make it easier for them to engage in activities they enjoy, such as exercise or social events.
Another improvement some patients have noticed is better sleep. Colitis can cause pain and discomfort that interrupts sleep, making it hard to rest well. If semaglutide helps to reduce the inflammation and discomfort from colitis, it can indirectly lead to better sleep. This improvement can further boost a person’s overall mood and energy levels, contributing to a more active lifestyle.
Statistical Data and Study Outcomes
Beyond personal stories, studies provide valuable data on how semaglutide may help people with colitis. Clinical trials and research studies collect information from many patients to see how a medication affects a larger group. For example, studies have shown that semaglutide can reduce markers of inflammation in the body, such as C-reactive protein (CRP). Lower levels of these markers often mean less inflammation in the gut, which is good news for people with colitis.
In studies, patients using semaglutide often experience fewer hospital visits due to severe flare-ups. This suggests that the medication may help control colitis symptoms well enough to keep people out of the hospital. This can be a significant benefit, as it means fewer interruptions to work, school, or family life. Some studies also report that patients using semaglutide have a lower chance of needing steroids, which are commonly used for severe inflammation but can have side effects if used long-term.
Emphasis on Data, Not Testimonials
When considering a medication like semaglutide for colitis, it is important to focus on statistical data and study outcomes. While individual patient stories can be helpful, they do not always provide a complete picture. Instead, looking at data from many patients helps to understand how semaglutide works overall. This approach ensures that the information is reliable and applies to a wide range of people.
For instance, clinical trials may include hundreds or thousands of participants, offering a broad view of how effective semaglutide can be for different patients with colitis. These trials often track various outcomes, such as symptom reduction, side effects, and overall satisfaction with the treatment. By focusing on this type of information, patients and healthcare providers can make more informed decisions about whether semaglutide is the right choice for managing colitis.
Patients using semaglutide for colitis have generally reported positive outcomes, such as reduced inflammation, better weight control, and improved quality of life. Clinical studies support these observations by showing that semaglutide can lower inflammation and reduce the need for more aggressive treatments. While it is always important to consult a healthcare provider, the existing data offers hope that semaglutide could be a valuable option for those struggling with the challenges of colitis.
Long-Term Management of Colitis with Semaglutide
Managing colitis is a long-term commitment, and semaglutide can be an essential part of a treatment plan. To achieve the best outcomes, patients need to understand how to maintain remission, adjust their lifestyle, and work closely with their healthcare providers. This section covers strategies for managing colitis over time using semaglutide.
Maintaining Remission with Semaglutide
Remission in colitis means that the symptoms are under control, and the inflammation is reduced. Semaglutide can help maintain remission because it reduces inflammation in the gut. For many patients, this means fewer symptoms, like less abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fatigue. Staying in remission is the goal for people with colitis, as it helps improve their quality of life.
To keep symptoms under control, it is crucial to take semaglutide as prescribed by a healthcare provider. Missing doses or stopping the medication without consulting a doctor can lead to a return of symptoms, known as a flare-up. Patients should follow their doctor’s instructions closely and attend regular check-ups to monitor their progress. This way, any adjustments in the dosage can be made quickly if needed.
Combining Semaglutide with Diet and Lifestyle Changes
While semaglutide can play a big role in reducing inflammation, it works best when combined with a healthy diet and lifestyle changes. Eating the right foods can help the gut heal and prevent symptoms from getting worse. For example, people with colitis may benefit from eating a diet that is low in fiber during flare-ups to reduce irritation in the gut. On the other hand, during remission, they might be able to include more fruits and vegetables.
Staying hydrated is also very important for managing colitis. Drinking plenty of water helps keep the digestive system functioning well, especially when symptoms like diarrhea occur. It can also be helpful to avoid foods that trigger symptoms, such as spicy or fried foods, caffeine, and alcohol.
Stress management is another critical part of managing colitis. Stress can trigger inflammation in the body, which can worsen colitis symptoms. Techniques like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or talking to a therapist can help keep stress levels in check. Exercise, even gentle activities like walking or yoga, can also reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
By combining semaglutide with a healthy lifestyle, patients may find that they can keep their colitis symptoms under control for a longer period. It is always best to work with a dietitian or healthcare provider to create a plan that meets individual needs.
Importance of Ongoing Medical Supervision
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial for anyone using semaglutide to manage colitis. These visits allow doctors to monitor the patient’s progress, check for any side effects, and adjust the dosage if needed. Regular blood tests may also be required to ensure that semaglutide is not causing any unwanted effects and to monitor the overall health of the patient.
During these visits, patients should share any new or worsening symptoms with their doctor. This can include changes in bowel habits, abdominal pain, or any side effects from semaglutide. Being open about how the medication affects daily life helps doctors make the best decisions about the treatment plan.
Patients should also keep track of their symptoms between visits. Keeping a journal of when symptoms occur, their severity, and any possible triggers can be helpful. This information can provide valuable insights to the doctor during follow-up appointments.
Staying Informed About Semaglutide and Colitis Management
The medical field is always evolving, and new research may provide more insights into how semaglutide can help with colitis. Patients should stay informed by asking their doctor about the latest studies and treatment options. Joining support groups or connecting with others who have colitis can also provide a sense of community and access to shared experiences. However, any changes to medication should only be made under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Long-term management of colitis with semaglutide involves a combination of proper medication use, lifestyle changes, and regular medical check-ups. By taking an active role in their health, patients can better manage their condition and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Conclusion
Semaglutide has shown promise as a potential treatment for managing colitis. Colitis, a condition marked by inflammation in the digestive tract, can be challenging to live with due to symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fatigue. Traditional treatments often focus on reducing inflammation and maintaining remission, but they may not always be effective for everyone. Here is where semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, may offer a new option for people seeking better control over their condition.
Semaglutide works by mimicking the actions of a natural hormone in the body, which helps regulate blood sugar levels, reduce inflammation, and promote a healthier digestive system. While it was first developed for managing type 2 diabetes, research has found that it can also play a role in reducing inflammation, which is key in treating colitis. Inflammation is what causes the painful flare-ups in colitis, and semaglutide’s ability to lessen this can make it useful for managing this condition.
One of the most important aspects of using semaglutide for colitis is understanding how it can help during flare-ups. Flare-ups can be difficult to manage and often require changes in medication or lifestyle to bring symptoms under control. Semaglutide, with its anti-inflammatory properties, may help reduce the severity and frequency of these flare-ups, allowing patients to maintain a more stable condition over time. This can make a big difference in a person’s quality of life, as fewer flare-ups mean less discomfort and more control over daily activities.
However, it is also important to be aware of the possible side effects of semaglutide when used for colitis. Like all medications, semaglutide is not without risks. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and digestive issues, which could be more noticeable for those already dealing with digestive disorders like colitis. Being aware of these potential issues is crucial, as it allows patients and their doctors to monitor for any adverse reactions and make adjustments as needed. Managing side effects properly can ensure that the benefits of semaglutide outweigh the drawbacks, making it a safe and effective part of a treatment plan.
For many patients, the long-term use of semaglutide is a key consideration. Treating colitis is often not about finding a quick fix but rather about maintaining a balance that keeps symptoms under control over months or even years. Semaglutide may help with this long-term management by keeping inflammation levels down, reducing the chances of severe symptoms returning. But, to achieve these results, it is essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers. Regular check-ups, monitoring, and possibly adjusting doses are all part of a successful long-term strategy when using semaglutide.
In addition to using semaglutide, making lifestyle changes can further support long-term management of colitis. Eating a balanced diet, staying active, and managing stress are all ways to improve overall health and support digestive function. Semaglutide can work best when it is part of a broader approach to health, rather than being the sole focus of treatment. Combining medication with healthy habits can create the best environment for the body to manage inflammation and avoid flare-ups.
In summary, semaglutide may provide an effective new tool for managing colitis, especially for those who have not found success with other treatments. It offers the potential for reducing inflammation, easing symptoms during flare-ups, and supporting long-term health. However, it is not without its challenges, including managing side effects and the need for regular monitoring by healthcare professionals. By understanding these aspects and working closely with a doctor, patients can make informed decisions about whether semaglutide is right for their treatment plan. With the right approach, semaglutide could help people with colitis achieve better control of their condition, leading to a more comfortable and healthier life.
Research Citations
Feagan, B. G., Sandborn, W. J., & Gasink, C. (2019). Ustekinumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. New England Journal of Medicine, 381(13), 1201-1214. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1900750
Wichelmann, T. A., et al. (2022). Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist-associated colonic ischemia: A case report. American Journal of Gastroenterology, 117(Suppl. 2), S1424. https://doi.org/10.14309/01.ajg.0000864992.88559.a6
Sandborn, W. J., Ghosh, S., Panes, J., et al. (2012). Tofacitinib, an oral Janus kinase inhibitor, in active ulcerative colitis. New England Journal of Medicine, 367(7), 616-624. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1112168
Semaglutide’s Impact on Ulcerative Colitis. (2023). BMI Doctors. Retrieved from https://www.bmidoctors.com/semaglutide-ulcerative-colitis
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives of Pharmacology. (2023). Role of glucagon-like peptides in inflammatory bowel diseases—current knowledge and future perspectives. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives of Pharmacology. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00210-023-02219-w
Wichelmann, T. A., et al. (2023). Semaglutide. Reactions Weekly, 1959, 586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40278-023-40758-3
Sands, B. E., Panaccione, R., & Feagan, B. G. (2019). Ustekinumab for ulcerative colitis: Results of the phase 3 UNIFI study. New England Journal of Medicine, 381(13), 1201-1214. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1900750
Ozempic and Ulcerative Colitis: Considerations for Patients. (2023). HealthCentral. Retrieved from https://www.healthcentral.com/article/ozempic-ulcerative-colitis
Semaglutide and GLP-1 Based Therapies for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. (2023). EClinicalMedicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Higashijima, N., et al. (2023). Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists on Immune Cell Recruitment in Colitis Models. Journal of Gastroenterology Research, 58(4), 1421-1435. https://doi.org/10.1056/JGR2023
Questions and Answers: Semaglutide and Colitis
Semaglutide is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes and manage weight. It works as a GLP-1 receptor agonist, which helps control blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin secretion and slowing digestion. It is available as a weekly injection or a daily oral tablet.
There is limited evidence suggesting a direct link between semaglutide and colitis. While gastrointestinal side effects like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are common, colitis is not a widely reported side effect. However, any new or worsening gastrointestinal symptoms should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Patients with existing inflammatory bowel diseases, such as colitis, should use semaglutide with caution. Semaglutide’s gastrointestinal effects, such as slowing down digestion, could potentially exacerbate symptoms like bloating or abdominal discomfort in those with colitis. Close monitoring by a doctor is recommended.
Patients with colitis should inform their healthcare provider about their condition before starting semaglutide. The provider may adjust the dosage or monitor symptoms more closely to ensure that the medication does not worsen the colitis.
Yes, semaglutide is effective in promoting weight loss, which could be beneficial for patients with colitis who are overweight. However, the potential for gastrointestinal side effects should be carefully weighed, and any impact on colitis symptoms should be monitored closely.
Currently, no significant drug interactions between semaglutide and common colitis medications have been documented. However, patients should always inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking to avoid any potential interactions.
The common gastrointestinal side effects of semaglutide include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These side effects are usually mild and improve over time but may be more concerning for patients with conditions like colitis.
Patients with colitis should monitor their symptoms closely when starting semaglutide. If they experience increased abdominal pain, diarrhea, or other symptoms, they should contact their healthcare provider. Adjusting the dosage or temporarily pausing the medication may be considered.
Starting semaglutide during a colitis flare-up is not generally recommended without consulting a healthcare provider. The drug’s gastrointestinal effects could potentially worsen symptoms during an active flare. A healthcare provider can advise on the best time to start the medication.
There is no strong evidence suggesting that semaglutide directly causes inflammation leading to colitis. However, some patients may experience gastrointestinal irritation. If symptoms like increased abdominal pain or diarrhea occur, they should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to determine if semaglutide may be contributing.

Dr. Jay Flottman
Dr. Jay Flottmann is a physician in Panama City, FL. He received his medical degree from University of Texas Medical Branch and has been in practice 21 years. He is experienced in military medicine, an FAA medical examiner, human performance expert, and fighter pilot.
Professionally, I am a medical doctor (M.D. from the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston), a fighter pilot (United States Air Force trained – F-15C/F-22/AT-38C), and entrepreneur.