Table of Contents
Introduction
Tirzepatide is a medication that has become an important tool in managing type 2 diabetes and obesity. It was designed to help people control their blood sugar levels and achieve significant weight loss. Over time, it has shown promise in improving both these aspects when combined with a healthy lifestyle. As with any medication, getting the right dose is crucial to make sure it works as intended. When dosing tirzepatide properly, patients are more likely to experience the best possible results with fewer side effects.
Understanding how to dose tirzepatide is essential because it helps in managing blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss. This process involves starting with a low dose and then gradually increasing it based on the patient’s response. The goal is to find the right balance between effectiveness and minimizing side effects. If the dose is too high, it can lead to unwanted side effects like nausea or diarrhea. If it is too low, it may not be as effective in controlling blood sugar or promoting weight loss.
The importance of getting the dose right cannot be overstated. When prescribed correctly, tirzepatide can offer significant benefits for people with type 2 diabetes and those struggling with obesity. The goal of dosing is to not only control the patient’s blood sugar levels but also help them lose weight, which is an important factor in managing diabetes. Achieving a healthy weight can improve overall health and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease and kidney problems.
Throughout this article, various aspects of tirzepatide dosing will be explored in detail. Many people have questions about how to use this medication effectively. Some may wonder about the recommended starting dose, how to adjust it over time, or what to do if side effects occur. Others may be concerned about how their lifestyle, other health conditions, or medications may affect the dosing. Addressing these questions helps to guide healthcare providers and patients toward the most effective treatment plan.
In the following sections, common questions about dosing tirzepatide will be answered, focusing on topics such as the initial dose, titration schedule, adjustments based on side effects or lifestyle factors, and the long-term management of the medication. This information is crucial for those who want to make the most of tirzepatide’s benefits while minimizing risks.
The starting dose and how it is adjusted over time can make a significant difference in how well the medication works. It is important to recognize that every individual is different. What works for one person may not work for another, so dosing adjustments are often needed based on each patient’s specific needs. For example, some people may tolerate a higher dose without issues, while others might need a slower increase to avoid side effects.
Monitoring blood sugar levels, weight, and overall health regularly is an important part of the process. Healthcare providers will likely recommend regular follow-up appointments to track progress and make any necessary changes to the treatment plan. This personalized approach to dosing helps to achieve the best outcomes.
In summary, optimizing tirzepatide dosing is essential for achieving better results in managing type 2 diabetes and obesity. By starting with the right dose, carefully adjusting as needed, and monitoring the patient’s response, healthcare providers can help ensure that the medication works as effectively and safely as possible. This article will explore the key aspects of dosing tirzepatide, answering common questions to guide patients and healthcare providers in maximizing the benefits of this powerful treatment.
What is Tirzepatide and How Does It Work?
Tirzepatide is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity. It is a relatively new drug that was developed to help people control their blood sugar levels and, in some cases, support weight loss. Tirzepatide has been shown to be highly effective in managing both of these conditions, making it an important option for many patients who are struggling to control their blood sugar or reduce excess weight.
The key to tirzepatide’s effectiveness lies in its unique mechanism of action. Unlike many other diabetes medications, tirzepatide works by targeting two important hormone receptors in the body: the GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor and the GIP (gastric inhibitory peptide) receptor. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels and appetite.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonism
The GLP-1 receptor is involved in controlling insulin secretion. When blood sugar levels rise after eating, GLP-1 helps the pancreas release insulin to bring the blood sugar down to a normal range. It also helps to reduce the release of glucagon, a hormone that can increase blood sugar levels. By mimicking the action of GLP-1, tirzepatide enhances insulin release when blood sugar is high and helps lower glucagon secretion, improving overall blood sugar control.
In addition to improving blood sugar control, GLP-1 receptor activation also slows the emptying of the stomach. This slowing effect can help people feel full longer after meals, which can lead to reduced food intake. As a result, tirzepatide can also help with weight loss by reducing hunger and cravings, which is particularly beneficial for individuals who are also overweight or obese.
GIP Receptor Agonism
Tirzepatide also targets the GIP receptor, which plays a role in regulating fat metabolism and insulin sensitivity. GIP is another hormone released in response to food intake, particularly when carbohydrates and fats are consumed. When GIP binds to its receptor, it helps promote insulin secretion, just like GLP-1. However, GIP also has effects on fat metabolism. By activating the GIP receptor, tirzepatide can help improve the body’s ability to process and store fat. This may explain why tirzepatide is effective in promoting weight loss, in addition to lowering blood sugar levels.
The dual action on both GLP-1 and GIP receptors makes tirzepatide different from other medications used for type 2 diabetes. Most other drugs only target one of these pathways. By combining both actions, tirzepatide is able to achieve better control over blood sugar and body weight compared to treatments that focus on just one of these hormones.
Benefits of Tirzepatide
The primary benefits of tirzepatide are its ability to lower blood sugar levels and help with weight management. Clinical trials have shown that tirzepatide can significantly reduce A1C levels (a marker of long-term blood sugar control) in people with type 2 diabetes. In fact, some studies suggest that tirzepatide may provide better blood sugar control than other popular diabetes medications, including GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide.
In addition to improving blood sugar control, tirzepatide has shown to help reduce body weight. This is a particularly valuable benefit for people with type 2 diabetes, as obesity is a common risk factor for the condition and can make managing blood sugar even more difficult. Many people with diabetes struggle with weight loss, but tirzepatide’s dual action on the GLP-1 and GIP receptors can make it easier to lose weight. In clinical trials, patients who used tirzepatide lost more weight compared to those on other diabetes medications or placebo.
Besides these primary benefits, tirzepatide may also have other positive effects, such as improving heart health. While studies are still ongoing, some research suggests that tirzepatide may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, by improving cholesterol levels and reducing blood pressure. These secondary benefits could make tirzepatide an even more valuable treatment option for people with type 2 diabetes who also have cardiovascular risk factors.
FDA Approval and Indications for Use
Tirzepatide was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2022 for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It is available as a weekly injection, which makes it convenient for many patients who may not want to take oral medications every day. In addition to type 2 diabetes, tirzepatide has also been studied for its use in weight management, and it may be prescribed for this purpose in certain patients.
Tirzepatide is typically prescribed when other diabetes medications, such as metformin, have not been effective enough in controlling blood sugar levels. It is often used as part of a broader treatment plan that includes dietary changes, exercise, and weight management strategies.
Tirzepatide is a medication that targets both the GLP-1 and GIP receptors to help regulate blood sugar and promote weight loss. By using these two mechanisms, tirzepatide offers a more comprehensive approach to managing type 2 diabetes and obesity compared to other medications. The benefits of tirzepatide, including its ability to lower A1C, promote weight loss, and potentially improve cardiovascular health, make it a promising treatment option for many patients.
How Should Tirzepatide Be Dosed?
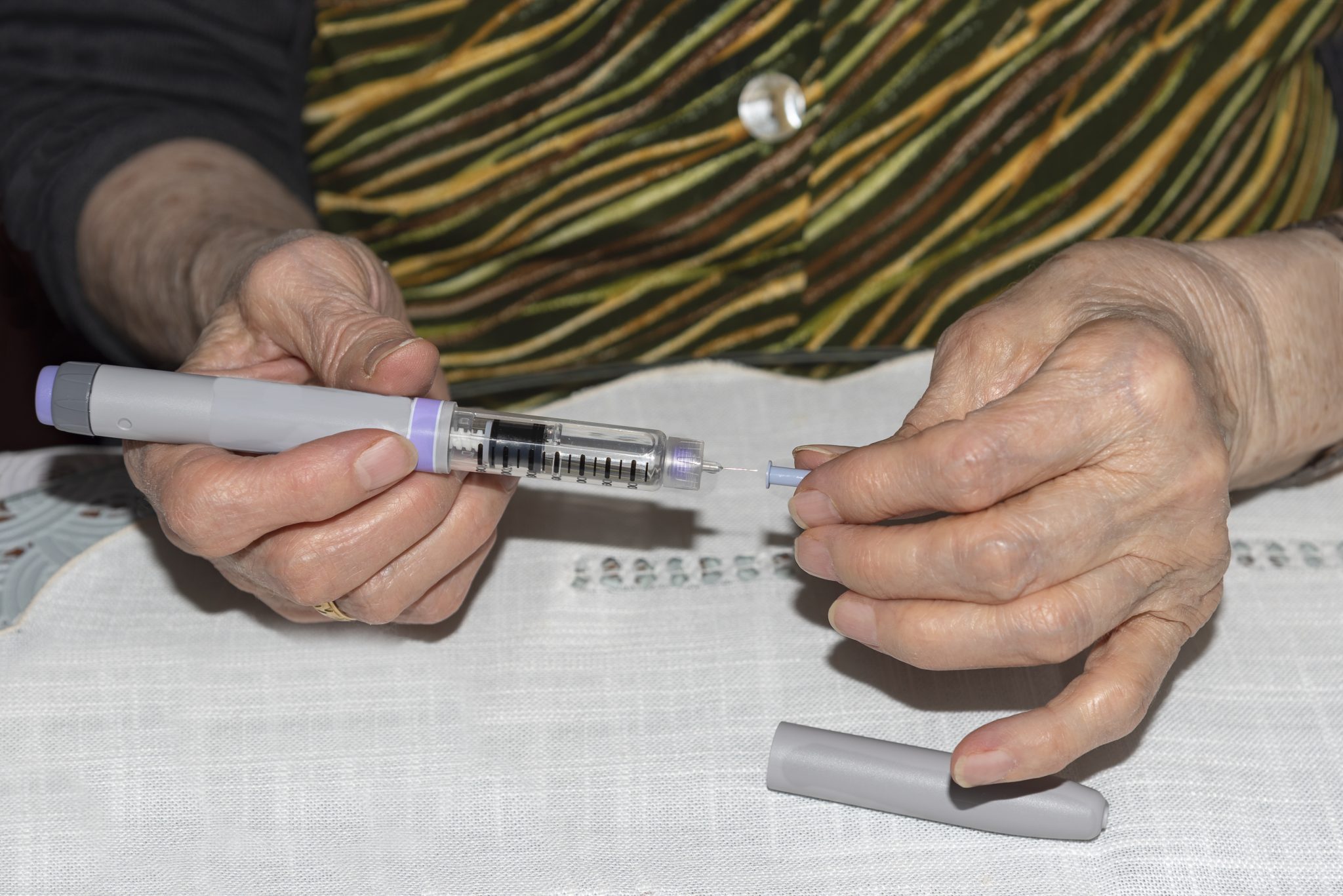
Tirzepatide is a medication that is typically administered via subcutaneous injection once a week. The correct dosing of tirzepatide is essential for achieving the best results, whether for managing type 2 diabetes or assisting with weight loss. It is important to follow the guidelines closely to ensure both safety and effectiveness.
The recommended dosing for tirzepatide is based on clinical trials and expert recommendations. The starting dose is generally low to help patients adjust to the medication and to reduce the likelihood of side effects, especially gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea. After starting at the initial dose, the dose can be gradually increased over time.
Starting Dose
For most adults, the initial dose of tirzepatide is 2.5 mg once a week. This low dose is intended to minimize potential side effects while still providing some benefit. The starting dose may feel mild at first, but it helps the body adjust to the medication. Beginning with a lower dose also reduces the likelihood of nausea, which is one of the most common side effects of tirzepatide.
The decision to start at this dose is based on how tirzepatide works in the body. Tirzepatide mimics two natural hormones, GLP-1 and GIP, that help regulate blood sugar and appetite. Introducing these hormones gradually allows the body to adapt without overwhelming the system, which can lead to fewer side effects.
Titration Schedule
After the initial dose, tirzepatide is typically increased to 5 mg once a week after 4 weeks of treatment. If the patient tolerates this dose well, the dose can then be further increased to 7.5 mg after another 4 weeks. The dose can continue to increase in increments of 2.5 mg until a maximum dose of 15 mg once a week is reached. The maximum dose is generally recommended for patients who need optimal control of blood sugar or significant weight loss.
It is important to note that this titration schedule may vary depending on the patient’s specific needs and how they respond to the medication. Some patients may require a slower increase in dosage if they experience side effects, such as nausea or gastrointestinal discomfort. Adjustments should always be made under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
The rate of titration should be individualized based on the patient’s tolerance and response to the medication. For example, if a patient experiences significant side effects at any dose, the increase in dose can be delayed, or the dose may be lowered to help the patient adjust more comfortably.
Factors Influencing Dosing Decisions
Several factors can influence how the dosing schedule is adjusted for different patients. One of the most significant factors is the patient’s blood sugar levels. In patients with type 2 diabetes, tirzepatide’s primary role is to improve glycemic control. If blood sugar levels are not adequately controlled after starting on the 2.5 mg dose, the dose may need to be increased more quickly.
In addition to blood sugar levels, other factors such as body weight and overall health play a role in determining the optimal dose. For patients who are also trying to lose weight, tirzepatide can help reduce hunger and promote weight loss. In such cases, a higher dose may be more beneficial in achieving both blood sugar control and significant weight loss. However, this should be done carefully and gradually to avoid discomfort.
For patients with specific health conditions, such as kidney problems or severe gastrointestinal issues, the dosing schedule may need to be modified. These patients may need to start at a lower dose and increase it more slowly. Special caution is necessary when treating elderly patients, as their bodies may react differently to medications. Regular monitoring is essential for these patients to ensure safety while achieving therapeutic goals.
Adjusting Dose Based on Side Effects
If a patient experiences side effects like nausea or vomiting, it may be necessary to adjust the dose. It is common for patients to experience some gastrointestinal discomfort when first starting tirzepatide or after increasing the dose. However, these side effects often lessen as the body adjusts. If they persist or are intolerable, the dose may need to be reduced or the titration schedule may need to be slowed down.
Some patients might experience more serious side effects, such as pancreatitis or kidney issues, though these are rare. If any severe side effects occur, the medication should be discontinued immediately, and the healthcare provider will assess the situation to decide on the best course of action.
The dosing of tirzepatide should be tailored to each individual, starting with a low dose and gradually increasing over time. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, side effects, and overall health is essential in determining the most appropriate dose. Working closely with a healthcare provider ensures the best chance of achieving the desired results while minimizing the risk of side effects.

What Are the Dosing Schedules for Tirzepatide?
Tirzepatide is administered once a week and has a specific dosing schedule to ensure its effectiveness in controlling blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss. A well-managed dosing schedule is key to maximizing the benefits of the medication while minimizing side effects.
Starting Dose of Tirzepatide
When beginning treatment with tirzepatide, the recommended starting dose is 2.5 mg per week. This lower dose is chosen to allow the body to adjust gradually to the medication. Starting with a small dose reduces the chances of experiencing side effects, such as nausea or stomach upset, that are more common in the early stages of treatment.
Titration Schedule
After the initial starting dose of 2.5 mg, the dose is usually increased by 2.5 mg every four weeks, based on the patient’s response to the medication. This gradual increase allows the healthcare provider to monitor how well the patient tolerates the medication. The goal is to reach the maintenance dose, which can be up to 15 mg per week. The specific dose that is right for each patient depends on their individual needs, including how well their blood sugar levels are controlled and whether they experience any side effects.
How Dose Adjustments are Made
The adjustment of the tirzepatide dose depends on several factors, including the patient’s blood glucose control, weight loss progress, and how well they tolerate the medication. Regular follow-up visits and blood tests help healthcare providers determine when and how to adjust the dose. If side effects are severe or the patient is struggling with the medication, the healthcare provider may slow the titration process or temporarily stop the dose increase. For patients who do not experience significant side effects, the dose may be increased more quickly.
Consistency in Dosing Schedule
One of the key aspects of using tirzepatide effectively is maintaining a consistent dosing schedule. The medication should be injected on the same day each week. Patients can choose any day of the week to take the injection, but once chosen, that day should remain consistent for each weekly dose. This regular schedule helps ensure that the medication maintains a steady level in the bloodstream, which is essential for optimal blood sugar control and weight loss.
Missed Doses
If a patient misses a dose of tirzepatide, it is important to take the missed dose as soon as possible, but only within four days of the missed injection. If more than four days have passed since the missed dose, the patient should skip it and wait for the next scheduled dose. Patients should not double the dose to make up for a missed injection, as this could increase the risk of side effects. In the case of frequent missed doses, it is important to discuss strategies with a healthcare provider to ensure better adherence to the treatment plan.
Injection Technique and Administration
Tirzepatide is given as a subcutaneous injection, which means it is injected under the skin. The injection can be administered in the thigh, abdomen, or upper arm. Patients are typically trained on how to perform the injection properly during their healthcare appointments. Proper injection technique is crucial to avoid complications like injection site irritation or infection.
Patients who are uncomfortable with self-injection or who find it difficult to administer the medication may prefer to have the injection given by a healthcare professional. In these cases, regular visits to the healthcare provider may be necessary to maintain the dosing schedule.
Injection Site Considerations
To reduce the chances of irritation or discomfort, patients should rotate the injection site each week. This helps prevent soreness or buildup of tissue at the injection site. Rotating the injection sites ensures that the body has time to heal between injections and reduces the risk of reactions to the medication.
Combining Tirzepatide with a Healthy Lifestyle
While tirzepatide helps manage blood sugar levels and supports weight loss, it is most effective when combined with a healthy lifestyle. This includes a balanced diet and regular physical activity. Healthcare providers often recommend lifestyle changes to support tirzepatide’s effects, improving both glucose control and weight management.
Incorporating these lifestyle changes helps enhance the benefits of tirzepatide, making the medication more effective in the long term. A healthcare provider can offer guidance on nutrition, exercise, and other lifestyle factors to improve outcomes.
Potential Side Effects and Their Impact on Dosing
As tirzepatide is gradually increased, patients may experience side effects. The most common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These side effects are generally mild and tend to lessen over time as the body adjusts to the medication. However, if side effects persist or become severe, the healthcare provider may adjust the dose more slowly or temporarily stop increasing the dose until the side effects subside.
Patients are encouraged to communicate openly with their healthcare provider about any side effects they experience, so the dosing plan can be adjusted to ensure comfort while still achieving therapeutic benefits.
Long-Term Dosing and Maintenance
Once the optimal dose is reached, patients typically remain on this maintenance dose, which can be as high as 15 mg per week, depending on individual needs. The long-term goal is to maintain stable blood glucose levels and support ongoing weight management. Ongoing monitoring is important to assess the effectiveness of the medication and to make adjustments if necessary. If a patient reaches their target goals, the healthcare provider may consider adjusting the dosage to maintain the most effective balance between benefits and side effects.
The dosing schedule for tirzepatide is designed to be gradual, starting with a low dose and increasing based on the patient’s tolerance and response. Consistent weekly injections, proper administration techniques, and regular monitoring are essential to ensure the best outcomes. Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations for dose adjustments and adhere to a consistent dosing schedule to optimize the medication’s effectiveness.
What Is the Recommended Initial Dose of Tirzepatide?
Tirzepatide is usually started at a low dose to help the body adjust to the medication. This approach helps reduce the risk of side effects, especially gastrointestinal issues. Understanding the recommended initial dose and how to adjust it over time is crucial for optimizing treatment.
Starting Dose of Tirzepatide
The recommended starting dose of tirzepatide for most patients is 2.5 mg once a week. This initial dose is important for minimizing the risk of side effects, particularly gastrointestinal discomfort, which is common when beginning new diabetes treatments. By starting with a low dose, the body can gradually adjust to the medication without being overwhelmed. This gradual approach helps ensure the patient can tolerate the drug while still gaining its benefits for blood sugar control and weight loss.
Gradual Dose Increase
After the first four weeks of treatment with the 2.5 mg dose, the dose can be increased to 5 mg once a week if the patient is tolerating the medication well. This step is typically done if there have been no significant side effects at the 2.5 mg dose and if further blood sugar control or weight loss is desired. Once the 5 mg dose has been maintained for four weeks, the dose can be further increased to 7.5 mg per week, based on the patient’s response.
Maximum Dose and Its Benefits
The maximum recommended dose of tirzepatide is 15 mg per week. For most patients, this higher dose is used to achieve optimal blood sugar control and to maximize weight loss. However, it is important to note that not all patients will need or tolerate this maximum dose. Most patients will achieve sufficient benefits with doses ranging from 5 mg to 10 mg per week, depending on their individual treatment goals and how well they tolerate the medication. The goal is to find the dose that balances effectiveness and tolerability.
Factors Influencing Dose Adjustment
Several factors influence when and how the dose should be adjusted. These include:
- Tolerability of the Medication: If the patient experiences significant side effects, such as nausea or gastrointestinal distress, it may be necessary to either stay at the current dose or proceed with a slower titration. The body’s ability to tolerate the drug is a key consideration in determining when to increase the dose.
- Blood Sugar Control: The primary purpose of tirzepatide is to control blood sugar levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. If the patient’s blood sugar is not within the desired range, it may be necessary to increase the dose. Higher doses, such as 7.5 mg or 10 mg, have been shown to be more effective in lowering blood glucose levels compared to lower doses.
- Weight Loss Goals: Tirzepatide also aids in weight loss, which can be an important treatment goal for many patients with type 2 diabetes. If weight loss is a primary goal and the patient is not seeing the desired results at a lower dose, the dose may be increased to 10 mg or 15 mg to enhance weight loss.
Adjusting the Dose for Special Populations
Some patients may require special dosing considerations. For example, elderly patients or those with kidney impairment may need a slower titration to minimize the risk of side effects. Healthcare providers will adjust the starting dose and how quickly the dose is increased depending on these individual needs. These patients are often started on a lower dose and monitored closely to ensure that the medication is both safe and effective.
Importance of Monitoring During the Initial Phase
During the first few months of treatment, it is crucial to monitor the patient’s response to tirzepatide. This includes checking blood sugar levels and tracking weight loss progress. Monitoring helps guide decisions on whether to increase the dose and ensures that side effects are managed. If a patient experiences severe side effects at any point, the healthcare provider may decide to adjust the dose or delay further increases.
What to Do If a Dose is Missed
If a patient misses a dose of tirzepatide, it is important to follow the guidance of the healthcare provider. In general, if a dose is missed, the patient should take the dose as soon as possible, provided it is within five days of the missed dose. If more than five days have passed, the patient should skip the missed dose and resume the regular dosing schedule. It is important not to take two doses at the same time to make up for a missed dose, as this can lead to unwanted side effects.
The recommended initial dose of tirzepatide is 2.5 mg once a week, with gradual increases based on the patient’s response and tolerance. The dose can be increased every four weeks, with a maximum dose of 15 mg per week. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and weight loss progress is essential to determine the right dose for each patient. Dose adjustments should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider to ensure the best balance of effectiveness and tolerability. By starting at a low dose and increasing gradually, tirzepatide treatment can be optimized for each individual.
How to Adjust Tirzepatide Dosing for Optimal Effectiveness?
Adjusting the dose of tirzepatide is an essential part of ensuring its effectiveness for each patient. Since every person’s response to the medication can be different, the goal is to find the right dose that balances controlling blood sugar, promoting weight loss, and minimizing side effects. Understanding when and how to adjust the dose can help healthcare providers achieve the best results for their patients.
When starting tirzepatide, doctors usually begin with a low dose. This helps the body adjust to the medication and reduces the likelihood of side effects, particularly gastrointestinal issues like nausea. The starting dose for most patients is typically 2.5 mg once a week. From there, the dose can be gradually increased based on how well the patient is managing with the medication and how their body is responding.
Monitoring Response and Adjusting Dose
One of the key factors in adjusting the dose is regular monitoring. Doctors will typically check blood sugar levels and track the patient’s weight during the first few weeks of treatment. If blood sugar levels are not at the desired target or if weight loss is slower than expected, the doctor might increase the dose to a higher level.
The usual process for increasing the dose involves waiting at least four weeks before making any changes. This allows enough time to assess how the body is responding to the current dose and whether any side effects, like nausea or diarrhea, are becoming a problem. A typical dose escalation schedule would be to start at 2.5 mg per week, and then move to 5 mg, 7.5 mg, and up to 10 mg over time. The dose increase can vary based on individual needs and the patient’s ability to tolerate the medication.
If a patient experiences significant side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, the doctor might decide to hold off on increasing the dose or may decrease it temporarily. In some cases, the dose may be reduced to help the patient adjust to the medication before trying to increase it again.
Individualizing Dosing for Different Patients
Every patient’s situation is unique, so dosing should be tailored to meet individual needs. This is especially important for people with comorbid conditions like heart disease, kidney issues, or gastrointestinal problems. For example, patients with kidney disease may need a slower increase in dose or may be started on a lower dose to prevent excessive buildup of the drug in the body. It is important for healthcare providers to carefully consider any pre-existing conditions when adjusting tirzepatide dosing.
Another factor to consider is the patient’s weight and how it affects the medication’s impact. Tirzepatide is used both for managing blood sugar and promoting weight loss, so its effectiveness may vary based on a person’s current weight. A patient who has a lot of weight to lose might need a higher dose for better results, while someone closer to their ideal weight might need a lower dose to avoid excessive weight loss.
Adjusting Based on Blood Sugar Control
Tirzepatide is most commonly prescribed for patients with type 2 diabetes to help control blood sugar levels. Monitoring blood glucose regularly is essential to determine whether the current dose is sufficient. If blood sugar levels remain high after several weeks on a dose, the healthcare provider may choose to increase the dose to improve blood sugar control.
However, it is important to note that excessively low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, is not a common side effect of tirzepatide when used alone. This is because tirzepatide helps regulate insulin levels in a way that lowers blood sugar only when necessary. Nevertheless, if blood sugar control is still not optimal, increasing the dose may be necessary. Careful monitoring and communication between the patient and healthcare provider are key during this process.
Adjusting Based on Weight Loss
Another major benefit of tirzepatide is its ability to support weight loss, particularly in people with obesity or those who are overweight. Weight loss should be closely monitored during the treatment. If the patient is not losing weight at the expected rate, this might suggest that the dose is too low. Increasing the dose may help improve the effects on weight reduction.
However, weight loss should be gradual. Rapid weight loss can sometimes cause problems like nutritional deficiencies, muscle loss, or other health issues. For this reason, the doctor might adjust the dose slowly and keep track of any changes in the patient’s diet or exercise habits. Ensuring that the patient’s weight loss is both safe and effective is a top priority in dosing adjustments.
Adjusting the dose of tirzepatide requires careful attention to the patient’s blood sugar levels, weight loss progress, and the potential for side effects. Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to fine-tune the dosage to achieve the best possible outcomes. Patients may need dose increases, decreases, or adjustments based on their individual responses to the medication. Regular check-ups and communication between patients and healthcare providers are essential to optimizing tirzepatide dosing for maximum effectiveness.

What Are the Key Side Effects to Monitor During Tirzepatide Treatment?
Tirzepatide is generally well-tolerated, but like any medication, it can cause side effects. It’s important to understand both the common and rare side effects, as this helps ensure the medication is working effectively without causing harm. Monitoring side effects is a key part of optimizing the treatment to get the best results for each individual.
Common Side Effects
The most common side effects of tirzepatide are gastrointestinal in nature. These side effects typically happen when the medication is first started or when the dose is increased. They usually become less severe over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
- Nausea is the most frequently reported side effect. It can be mild to moderate and is often temporary. Some patients may feel queasy or experience an upset stomach after taking the injection. This side effect can usually be managed by starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it. Additionally, taking the injection after eating a light meal may help reduce nausea. If nausea continues or becomes severe, adjusting the dose or taking anti-nausea medication may be recommended by the doctor.
- Diarrhea is another common side effect. Some people may experience loose stools or frequent bowel movements when starting tirzepatide. Similar to nausea, diarrhea often improves with continued use of the medication, but staying hydrated is important. If diarrhea becomes persistent or troublesome, it may be necessary to adjust the dose or switch to a different medication.
- Vomiting can also occur, although it is less common. For patients who experience vomiting regularly, the dosage may need to be adjusted or additional treatment may be considered. It’s important to note that if vomiting is severe or ongoing, it should be reported to a healthcare provider to assess the situation.
- Loss of appetite is another side effect that many patients report. While this may seem beneficial for weight loss, it can sometimes lead to unintentional weight loss or poor nutrition. A decrease in appetite can make it difficult for patients to maintain an adequate intake of calories and nutrients, which can be harmful in the long term. Monitoring food intake and weight is important, especially in the first few weeks of treatment.
Serious Side Effects
Though less common, some serious side effects need to be carefully monitored. These are rare but can be dangerous, so it’s important to contact a healthcare provider immediately if any of the following occur.
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) is a serious condition that can sometimes develop with tirzepatide use. Symptoms of pancreatitis include severe stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. If a patient experiences any of these symptoms, medical attention is needed right away. Pancreatitis is a known risk with GLP-1 receptor agonists, a class of drugs to which tirzepatide belongs. Although this side effect is rare, it’s important to be aware of the symptoms so it can be addressed quickly.
- Kidney Problems can also arise, especially in people who already have kidney disease or those at risk. Tirzepatide can affect kidney function, sometimes leading to dehydration or kidney injury. Symptoms of kidney problems include changes in urination, swelling in the legs or feet, and fatigue. Dehydration caused by side effects like nausea and vomiting can increase the risk of kidney problems, so it’s important for patients to stay hydrated throughout treatment.
- Thyroid Tumors: In animal studies, tirzepatide has been associated with an increased risk of thyroid tumors. While there is no direct evidence linking tirzepatide to thyroid cancer in humans, patients with a history of thyroid disease or family members with medullary thyroid carcinoma should discuss this risk with their doctor. Symptoms of thyroid issues, such as a lump in the neck, trouble swallowing, or voice changes, should be monitored.
Managing Side Effects
Most side effects associated with tirzepatide are manageable and typically improve over time. When starting the medication, it’s advised to begin with a lower dose and gradually increase it to minimize gastrointestinal discomfort. This approach allows the body to adjust to the medication at a more comfortable pace.
In addition to adjusting the dosage, healthcare providers may recommend other strategies to help manage side effects. For instance, drinking plenty of water can help prevent dehydration caused by diarrhea or vomiting. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can ease nausea and help with the loss of appetite. If side effects become severe, the healthcare provider may decide to temporarily lower the dose or discontinue tirzepatide in favor of other treatments.
When to Seek Medical Help
While most side effects are mild and temporary, it’s important to seek medical help if any of the following signs occur:
- Severe stomach pain or persistent nausea
- Vomiting that does not stop
- Dark-colored urine or changes in urine output
- Swelling in the legs or feet
- Difficulty swallowing or a lump in the neck
- Persistent dizziness or fainting
These symptoms could indicate more serious complications, and immediate medical attention may be necessary to ensure safety and proper care.
Monitoring side effects is an essential part of tirzepatide treatment. While gastrointestinal issues like nausea, diarrhea, and loss of appetite are the most common and typically improve with time, more serious side effects such as pancreatitis, kidney problems, and thyroid issues should not be ignored. Regular check-ups and clear communication with a healthcare provider will help ensure the treatment is as effective and safe as possible. Adjusting the dose, managing side effects, and keeping track of any symptoms that arise are all part of the process in getting the most benefit from tirzepatide.
How Can Dosing Be Optimized in Patients with Comorbid Conditions?
Tirzepatide is a powerful medication that works to help control blood sugar and promote weight loss in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity. However, when a person has other health problems, called comorbid conditions, the dosing of tirzepatide might need to be adjusted. These conditions can include kidney disease, heart disease, gastrointestinal issues, and others. Understanding how these conditions affect tirzepatide dosing is crucial for getting the best results while also keeping patients safe.
Impact of Kidney Disease on Dosing
Kidney disease is one of the most important factors to consider when deciding the right dose of tirzepatide. The kidneys help the body remove excess fluids and waste. When the kidneys are not working well, these processes slow down, and medications may stay in the body longer than expected. This could increase the risk of side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, or dehydration.
Currently, there is no official recommendation to reduce tirzepatide doses specifically for patients with kidney disease, even those with moderate to severe kidney problems. However, it is essential to monitor kidney function regularly, especially when starting tirzepatide treatment or adjusting doses. If kidney function worsens, it may be necessary to reassess the treatment approach, which could include lowering the dose or using other medications to help manage the patient’s conditions.
For patients who already have kidney disease, doctors may choose to start with a lower dose of tirzepatide and increase it slowly. This approach helps minimize the risk of side effects and ensures that the body can handle the medication appropriately.
Adjusting Dosing in Patients with Heart Disease
Heart disease is another condition that can affect how tirzepatide works in the body. Research has shown that tirzepatide can be beneficial for patients with heart disease by lowering blood sugar and aiding in weight loss, which can improve heart health. However, heart disease may require special dosing considerations. For example, patients with heart failure or other heart conditions might be more sensitive to changes in blood pressure, fluid balance, and electrolyte levels.
In most cases, tirzepatide can still be used in people with heart disease, but careful monitoring is essential. If a patient experiences side effects like low blood pressure, dizziness, or swelling, doctors may adjust the dose or suggest a slower titration schedule. Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it gives the body time to adapt and reduces the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Gastrointestinal Issues and Tirzepatide Dosing
Gastrointestinal problems, such as nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain, are common side effects of tirzepatide. For patients with pre-existing gastrointestinal conditions, such as gastroparesis (a condition where the stomach empties too slowly), the starting dose of tirzepatide might need to be adjusted. These conditions could make the symptoms of tirzepatide more severe, so doctors may decide to begin with the lowest possible dose and increase it very slowly.
If gastrointestinal symptoms become problematic, patients may need to take a break from the medication or adjust the dose. In some cases, doctors may recommend other strategies, like dietary changes or additional medications, to help manage side effects and ensure the treatment remains effective.
Other Chronic Conditions
In addition to kidney disease, heart disease, and gastrointestinal issues, there are other chronic conditions that may require adjustments in tirzepatide dosing. For example, patients with liver disease may also experience slower clearance of the medication. While there is no official guideline for adjusting tirzepatide dosing in people with liver problems, doctors may consider starting with a lower dose and carefully monitoring the patient’s response.
Similarly, patients with a history of pancreatitis or other pancreatic problems may need to be monitored more closely when using tirzepatide. Though pancreatitis is a rare side effect, individuals with a history of the condition might be at higher risk. Regular checkups and discussions about any discomfort or changes in health are important for these patients.
Monitoring and Adjusting Dosing for Special Populations
It is important to remember that dosing for tirzepatide is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Each patient’s unique health history, including comorbid conditions, must be taken into account. For people with multiple health issues, doctors often recommend a tailored approach. This might mean starting with lower doses, adjusting doses slowly over time, and carefully monitoring the patient’s response to treatment.
Regular follow-ups, lab tests, and physical exams are essential when treating patients with comorbid conditions. Healthcare providers should also ensure that patients are well-educated on how to monitor for any side effects and what to do if they experience any concerning symptoms.
The goal of dosing tirzepatide in patients with comorbid conditions is to provide effective treatment while minimizing risks. Adjustments based on kidney function, heart health, gastrointestinal issues, and other chronic conditions are necessary to ensure safety and optimize the medication’s benefits. Working closely with healthcare providers to monitor health status and adjust doses as needed can help patients get the most out of tirzepatide while managing their other medical conditions.
Can Tirzepatide Be Used with Other Medications?
Tirzepatide is often prescribed alongside other medications to manage type 2 diabetes and obesity. However, when combining treatments, it is important to carefully consider how these medications interact with each other. Knowing which drugs can be used safely with tirzepatide, as well as how to adjust doses, can help improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of side effects.
Potential Drug Interactions with Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide works by mimicking two important hormones in the body, GLP-1 and GIP. These hormones are involved in controlling blood sugar levels, appetite, and digestion. While tirzepatide is effective on its own, it may interact with other diabetes medications or treatments for other conditions, which could either reduce its effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects.
For instance, tirzepatide may interact with medications that affect the stomach or digestive system. Drugs that slow down gastric emptying (how fast food moves through the stomach) might add to tirzepatide’s natural effects, increasing the risk of nausea or bloating. People who are already prone to gastrointestinal issues should be cautious when using tirzepatide alongside these medications.
Additionally, tirzepatide is usually combined with oral diabetes medications like metformin, SGLT2 inhibitors, and sulfonylureas, which all have different ways of lowering blood sugar. However, when using multiple medications, blood sugar levels must be monitored carefully. If blood sugar becomes too low, it may require reducing doses of one or more of the medications.
Dosing Adjustments for Other Medications
When tirzepatide is used alongside other diabetes treatments, dosing adjustments may be necessary. For example, insulin is sometimes prescribed along with tirzepatide to help control blood sugar levels. Insulin can lower blood sugar quickly, which can sometimes result in hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Because tirzepatide also lowers blood sugar, combining the two medications can increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
To avoid this, doctors may recommend reducing the dose of insulin when starting tirzepatide. The goal is to find a balance where blood sugar is controlled, but the risk of hypoglycemia is minimized. This is especially important for people who already use insulin regularly to manage their diabetes.
In addition to insulin, other diabetes medications such as sulfonylureas or glinides, which work by stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin, can also increase the risk of low blood sugar when combined with tirzepatide. In these cases, healthcare providers may recommend lowering the dose of these drugs to prevent hypoglycemia.
It is also important to monitor blood sugar levels regularly when starting tirzepatide with other drugs. By adjusting the doses of medications based on regular testing, a healthcare provider can help maintain blood sugar control while reducing the risk of side effects.
Combination with Non-Diabetes Medications
Tirzepatide is not limited to use with just diabetes medications. It is sometimes used in patients with obesity, even if they do not have diabetes. This could involve combining tirzepatide with other types of medications, such as those used to treat high blood pressure, cholesterol, or other conditions. In these cases, there is generally no direct interaction between tirzepatide and these medications, but each patient’s individual health needs must be considered.
For example, people using tirzepatide who also take medications for high blood pressure may experience changes in blood pressure. Tirzepatide’s effects on weight loss and blood sugar may have secondary benefits on blood pressure levels, so blood pressure should be monitored regularly. Any changes might lead to adjustments in antihypertensive medications to avoid dizziness or fainting.
People who take statins or other cholesterol-lowering medications while using tirzepatide do not typically need to adjust their cholesterol medications. However, as with all treatments, regular check-ups and monitoring are essential to ensure that medications are working effectively together.
Monitoring for Potential Side Effects
When combining tirzepatide with other medications, it is critical to watch for any side effects or changes in health status. One of the most common side effects of tirzepatide is nausea, especially during the initial phase of treatment. When combined with other medications that affect the stomach or digestion, such as metformin or certain antibiotics, this side effect may be more pronounced. If nausea becomes severe, adjusting the dose of tirzepatide or other medications may be necessary.
In addition, because tirzepatide affects blood sugar regulation, it can sometimes cause hypoglycemia, particularly when used with other blood sugar-lowering medications. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include shaking, sweating, dizziness, and confusion. It is essential to have a plan for treating low blood sugar if it occurs, which may involve adjusting the doses of insulin or other medications.
Overall, any time tirzepatide is combined with another medication, it is important to work closely with a healthcare provider. Regular monitoring of blood sugar, side effects, and overall health is key to ensuring that the treatment plan remains effective and safe.

How Do Lifestyle Factors Affect Tirzepatide Dosing?
Lifestyle factors play a crucial role in how well tirzepatide works for managing type 2 diabetes and obesity. Tirzepatide is a medication that can help lower blood sugar levels and support weight loss, but it works best when combined with healthy lifestyle habits. Proper diet, regular exercise, and managing body weight can influence how the body responds to tirzepatide and may affect the way the dosage should be adjusted over time.
The Role of Diet in Dosing
Diet is one of the most important lifestyle factors to consider when using tirzepatide. A balanced, healthy diet supports the medication’s effectiveness by improving blood sugar control and helping with weight loss. Diet changes can lead to more stable blood sugar levels, which in turn can impact how much tirzepatide is needed. For example, if a patient adopts a diet that lowers blood sugar levels more effectively, they may need a lower dose of tirzepatide to maintain optimal control of their blood glucose.
A diet rich in vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can enhance the effects of tirzepatide, while processed foods, excessive sugars, and unhealthy fats may reduce its effectiveness. In some cases, changes in diet may also help reduce common side effects of tirzepatide, such as nausea or gastrointestinal discomfort. For instance, eating smaller, more frequent meals or avoiding foods that are particularly hard to digest might make the treatment more tolerable.
On the other hand, if someone is following a high-calorie diet, especially one that leads to weight gain, the effectiveness of tirzepatide might be diminished. Weight gain can make blood sugar control more challenging, and it may require adjustments in dosing or the addition of other lifestyle modifications to achieve the desired therapeutic outcomes.
Exercise and Physical Activity Impact on Dosing
Physical activity is another lifestyle factor that can greatly affect tirzepatide treatment. Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, making the body more efficient at using glucose. This means that people who exercise regularly may find that they need a lower dose of tirzepatide to control their blood sugar levels. Exercise also supports weight loss, which is often a key goal for patients taking tirzepatide. As weight decreases, insulin sensitivity improves, and blood sugar control becomes easier.
Exercise can also help counteract some of the side effects of tirzepatide, such as fatigue or mild nausea. Being active boosts overall energy levels and can improve mood, which helps maintain motivation to stay on track with the medication and treatment plan. However, exercise should be tailored to the individual’s ability and fitness level. It is important to start with activities that are safe and gradually increase the intensity as the body adapts.
For patients who are not regularly active, starting with light exercises such as walking or swimming can be a good way to improve overall health and support the effectiveness of tirzepatide. For those who are already active, adjusting the intensity or duration of exercise might further enhance the benefits of the medication and may even allow for dosing adjustments to be made.
Weight Management and Dosing Adjustments
Weight loss is often a key goal of tirzepatide treatment, especially for individuals who are obese or overweight. Tirzepatide itself is designed to help patients lose weight by improving satiety and reducing appetite. As patients lose weight, they may find that their body’s response to the medication changes. In some cases, the dose of tirzepatide may need to be adjusted over time to continue to support optimal blood sugar levels and weight loss.
It is essential to monitor progress closely during weight loss to ensure that the dosing remains effective. For patients who lose a significant amount of weight, a dose reduction may be considered to avoid hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or other side effects. Regular follow-up visits with a healthcare provider are key to determining if dose adjustments are needed as weight changes.
On the other hand, if weight loss plateaus or a person gains weight, the dose of tirzepatide might need to be increased or other interventions may be necessary to address blood sugar control and weight management. Changes in lifestyle, such as adopting a more structured exercise plan or modifying diet, may help resolve these issues and support the goal of weight loss.
Combining Lifestyle Factors with Medication for Best Results
When tirzepatide is used alongside other healthy habits, such as a nutritious diet and regular physical activity, the likelihood of achieving and maintaining good blood sugar control and weight loss increases. It is important for patients to understand that while tirzepatide is an effective medication, it is most successful when used as part of a holistic approach to managing diabetes and obesity.
A balanced diet and regular exercise will not only help optimize the effects of tirzepatide but may also reduce the risks of long-term complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease and nerve damage. Additionally, these lifestyle factors help improve the overall quality of life and support mental health, which is crucial for maintaining motivation and adherence to a treatment plan.
Diet, exercise, and weight management all play a significant role in how tirzepatide works in the body. By making thoughtful and consistent changes to these lifestyle factors, patients can maximize the effectiveness of their medication, reduce the need for frequent dosing adjustments, and achieve better long-term outcomes in managing both blood sugar levels and body weight.
What Are the Long-Term Considerations for Tirzepatide Dosing?
Tirzepatide is an effective treatment for managing type 2 diabetes and obesity, offering significant benefits in controlling blood sugar levels and supporting weight loss. However, long-term use of tirzepatide presents a number of important factors to consider when it comes to dosing. These factors ensure that the treatment remains effective, and that any adjustments needed for individual needs and health conditions are made. Below, the long-term considerations for tirzepatide dosing are broken down into distinct areas.
Monitoring the Effectiveness of Tirzepatide Over Time
One of the most important aspects of long-term tirzepatide treatment is ongoing monitoring of its effectiveness. When starting the medication, patients often experience rapid improvements in both blood sugar control and weight loss. However, as time progresses, the body may adapt to the drug, and its effectiveness can begin to plateau. It is essential to regularly monitor blood glucose levels, HbA1c, and weight to evaluate how well the medication continues to work.
Healthcare providers will typically assess the patient’s progress at regular intervals, adjusting the dosage if necessary. If a patient’s blood sugar levels are not as well-controlled as before, or if the weight loss effect slows significantly, increasing the dose might be considered. Alternatively, if blood sugar levels become too low or the patient experiences side effects, the dose may need to be reduced.
Dose Adjustments Based on Patient Progress
As patients continue their tirzepatide regimen, they may notice changes in how their body responds. One common scenario is when patients lose weight during the initial stages of treatment. Over time, weight loss may slow or stabilize. Since tirzepatide is designed to help both manage blood sugar and assist with weight loss, any changes in weight will affect the dosing decisions. For example, a person who has lost a significant amount of weight might no longer require the same dose of tirzepatide to achieve the desired effects.
Additionally, if a patient’s weight stabilizes or starts to increase, a healthcare provider might consider adjusting the dose to help maintain both blood sugar control and further weight loss. In such cases, patients may be asked to track their weight and report any changes to their healthcare provider to ensure optimal dosing.
Side Effects and How They Impact Dosing Decisions
Tirzepatide is generally well tolerated, but like any medication, it can cause side effects. The most common side effects include gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea, diarrhea, or abdominal discomfort. These side effects are often temporary and lessen as the body adjusts to the medication. However, if these symptoms persist or worsen, the dose might need to be adjusted.
In rare cases, more serious side effects like pancreatitis, kidney issues, or thyroid problems may arise. If such side effects occur, immediate medical attention is necessary. In these instances, the healthcare provider may reduce the dose, temporarily discontinue tirzepatide, or consider alternative treatments. Therefore, patients on long-term tirzepatide therapy should be aware of potential side effects and keep regular appointments with their healthcare provider to monitor any changes.
Special Considerations for Patients with Comorbidities
Long-term dosing of tirzepatide must also take into account any comorbid conditions the patient may have. For example, individuals with kidney disease, liver issues, or cardiovascular conditions may require special dosing adjustments. In patients with renal impairment, the medication might need to be started at a lower dose or adjusted during treatment. Likewise, individuals with a history of cardiovascular disease may need to be monitored closely for any changes in heart health.
Healthcare providers should assess the patient’s health status regularly and adjust the dose of tirzepatide if necessary. Collaboration between different specialists, such as nephrologists or cardiologists, can help manage dosing in these patients and ensure that tirzepatide remains a safe and effective treatment.
The Role of Lifestyle Changes in Long-Term Dosing
While tirzepatide is an important part of managing blood sugar and weight, it works best when combined with consistent lifestyle changes. Long-term success with tirzepatide depends not only on the medication but also on maintaining a healthy diet and regular physical activity. As patients progress with their treatment, their lifestyle habits may evolve, which could influence the effectiveness of the medication.
For example, if a patient loses a significant amount of weight, they may find that their blood sugar control improves, and they may no longer need the same dose of tirzepatide. Similarly, if a patient’s exercise routine becomes more consistent or if they adopt a healthier diet, the effects of tirzepatide could be enhanced, potentially requiring a reduction in the dose. Thus, it is essential for patients to communicate their lifestyle changes to their healthcare provider so that their treatment plan, including dosage, can be adjusted accordingly.
Long-Term Effectiveness and the Potential for Dose Adjustments
Long-term treatment with tirzepatide may require ongoing adjustments to ensure continued effectiveness. While the medication offers long-lasting results in many patients, as time goes on, some might notice a decrease in the effectiveness of the drug. As the body adapts, the dose may need to be modified to either enhance or maintain the desired results.
In general, the dose of tirzepatide is titrated gradually based on a patient’s response. For instance, as a patient’s blood sugar levels stabilize or their weight loss plateaus, the dosing schedule might be altered to provide the best long-term benefit. The goal is to find the right balance to continue achieving the desired results without unnecessary side effects.
Addressing Long-Term Side Effects
Some side effects of tirzepatide may emerge after months or even years of use. While gastrointestinal side effects are common early on, patients may also experience other long-term effects. For instance, there may be concerns about kidney function or gastrointestinal health, especially in patients who have pre-existing conditions. Over time, the healthcare provider will need to ensure that any potential side effects are addressed in a timely manner.
Regular testing, including kidney function tests, liver function tests, and monitoring for signs of pancreatitis, is important to catch any long-term side effects early. If significant problems arise, the dosage may be reduced or alternative therapies may need to be considered.
The Importance of Regular Follow-up Appointments
Long-term treatment with tirzepatide requires regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers. These visits are essential for assessing the effectiveness of the medication, making adjustments as needed, and monitoring for potential side effects. During these visits, patients will undergo tests to check their blood sugar levels, kidney function, and other vital health indicators.
It is crucial that patients attend these appointments, as they provide an opportunity to discuss any changes in health or lifestyle that might impact dosing. By staying proactive in their healthcare, patients ensure that their treatment plan remains tailored to their evolving needs.
Patient Education for Ongoing Management
For long-term success with tirzepatide, patient education is key. Patients should be aware of the potential side effects and understand when to seek medical advice. They should also be knowledgeable about how to monitor their blood sugar and weight regularly. Having an open line of communication with healthcare providers allows patients to address any concerns as soon as they arise, ensuring that treatment remains effective.
Patients should also be encouraged to keep track of lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, which may impact the effectiveness of the medication. Educating patients on how these factors influence treatment helps them take an active role in managing their health.
Long-term dosing with tirzepatide requires regular monitoring, dose adjustments, and a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers. By considering factors such as patient progress, side effects, comorbidities, and lifestyle changes, healthcare providers can help ensure that the medication remains effective for the long haul. Regular follow-ups, patient education, and careful dosing adjustments are all vital elements of maintaining the success of tirzepatide therapy over time.
Conclusion
Tirzepatide is a powerful medication that has shown significant promise in treating type 2 diabetes and obesity. It works by acting on two important hormones, GLP-1 and GIP, which help control blood sugar levels and promote weight loss. To get the most benefit from tirzepatide, it is crucial to dose it properly and follow the recommended guidelines. Proper dosing ensures that patients experience the full therapeutic benefits of the medication while minimizing potential side effects. It is also essential to monitor the patient’s response regularly to make adjustments as needed.
One of the main points to remember is the importance of starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it. This approach helps to reduce the chances of side effects, such as nausea or gastrointestinal issues, which are common when starting tirzepatide. The gradual increase in dosage allows the body to adjust to the medication. It is important for patients to follow the prescribed titration schedule, which usually starts at a low dose and is increased weekly, depending on how well the patient is tolerating the medication and their specific treatment goals. This careful approach helps to prevent any complications while giving the medication time to show its full effects.
Another key factor in optimizing tirzepatide treatment is regular monitoring. Blood sugar levels should be checked frequently to ensure the medication is controlling them effectively. For patients using tirzepatide to lose weight, monitoring weight loss progress is also necessary. If a patient is not reaching their goals or experiences side effects, the dose may need to be adjusted. By working closely with a healthcare provider, patients can ensure that their dosage is right for them and that it aligns with their specific health needs.
Special populations, such as older adults or those with kidney problems, may need additional attention when it comes to dosing. Tirzepatide’s effects can vary depending on a person’s age or other health conditions, so doses may need to be lowered or adjusted. In some cases, it might be necessary to start at an even lower dose or increase the dose more slowly. Healthcare providers are trained to make these adjustments based on the patient’s overall health and any other medications they may be taking. It is essential for healthcare providers to consider the full picture of a patient’s health to make sure that tirzepatide is used safely and effectively.
Lifestyle factors also play a significant role in tirzepatide’s effectiveness. Diet, exercise, and weight management can all influence how well tirzepatide works. For example, patients who make healthy changes to their eating habits and get regular exercise may find that they need less medication over time. These lifestyle factors can help control blood sugar and contribute to weight loss, potentially allowing for dose reductions in some cases. Patients who are actively engaged in their health through lifestyle changes are more likely to see long-term success with tirzepatide.
Long-term considerations should also be kept in mind when using tirzepatide. As the patient continues treatment, regular assessments of blood sugar and weight will help healthcare providers determine whether the current dose is still appropriate. Over time, it is possible that the patient’s need for the medication may change, either because their condition improves or because they encounter new health challenges. This is why ongoing monitoring and periodic dose adjustments are necessary. Tirzepatide is a tool that, when used correctly, can lead to significant long-term benefits, but its effectiveness relies on the patient’s ability to work with their healthcare provider to make the necessary adjustments as their treatment progresses.
In conclusion, tirzepatide is a highly effective medication for managing type 2 diabetes and obesity, but proper dosing is key to achieving the best results. Starting with the right dose, monitoring regularly, adjusting based on individual needs, and considering the role of lifestyle changes all contribute to the optimal use of this treatment. Healthcare providers and patients must work together to ensure that dosing is tailored to the individual, taking into account factors such as age, kidney function, and other medical conditions. With careful management, tirzepatide can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life by better controlling blood sugar and promoting weight loss, making it a valuable tool in the fight against diabetes and obesity.
Research Citations
Frias, J. P., Nauck, M. A., Van, J., Kutner, M. E., Cui, X., Benson, C., … Haupt, A. (2018). Efficacy and safety of LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomised, placebo-controlled and active comparator-controlled phase 2 trial. The Lancet, 392(10160), 2180–2193. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32260-8
Frias, J. P., Nauck, M. A., Van, J., Benson, C., Bray, R., Cui, X., … Robins, D. A. (2020). Efficacy and tolerability of tirzepatide, a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate different dose-escalation regimens. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 22(6), 938–946. doi:10.1111/dom.13979
Rosenstock, J., Wysham, C., Frías, J. P., Kaneko, S., Lee, C. J., Fernández Landó, L., … Thieu, V. T. (2021). Efficacy and safety of a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. The Lancet, 398(10295), 143–155. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01324-6
Ludvik, B., Giorgino, F., Jódar, E., Frías, J. P., Fernández Landó, L., Brown, K., … Rodríguez, Á. (2021). Once-weekly tirzepatide versus once-daily insulin degludec as add-on to metformin with or without SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-3): A randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 trial. The Lancet, 398(10300), 583–598. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01443-4
Dahl, D., Onishi, Y., Norwood, P., Huh, R., Bray, R., Patel, H., & Rodríguez, Á. (2022). Effect of subcutaneous tirzepatide versus placebo added to titrated insulin glargine on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: The SURPASS-5 randomized clinical trial. JAMA, 327(6), 534–545. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.0078
Del Prato, S., Kahn, S. E., Pavo, I., Weerakkody, G. J., Yang, Z., Doupis, J., … Wiese, R. J. (2021). Tirzepatide versus insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes and increased cardiovascular risk (SURPASS-4): A randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3 trial. The Lancet, 398(10313), 1811–1824. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02188-7
Heise, T., Mari, A., DeVries, J. H., Urva, S., Li, J., Pratt, E. J., … Milicevic, Z. (2022). Effects of subcutaneous tirzepatide versus placebo or semaglutide on pancreatic islet function and insulin sensitivity in adults with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-arm, phase 1 clinical trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 10(6), 418–429. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00085-7
Heerspink, H. J. L., Sattar, N., Pavo, I., Haupt, A., Duffin, K. L., Yang, Z., … Cherney, D. I. Z. I. (2022). Effects of tirzepatide versus insulin glargine on kidney outcomes in people with type 2 diabetes in the SURPASS-4 trial: Post-hoc analysis of an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 10(11), 774–785. doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00243-1
Feng, P., Sheng, X., Ji, Y., Urva, S., Wang, F., Miller, S., Qian, C., An, Z., & Cui, Y. (2023). A phase 1 multiple dose study of tirzepatide in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. Advances in Therapy, 40(8), 3434–3445. doi:10.1007/s12325-023-02536-8
Furihata, K., Mimura, H., Urva, S., Oura, T., Ohwaki, K., & Imaoka, T. (2022). A phase 1 multiple-ascending dose study of tirzepatide in Japanese participants with type 2 diabetes: Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 24(2), 239–246. doi:10.1111/dom.14572
Questions and Answers: Tirzepatide Dosing
The typical starting dose of tirzepatide for type 2 diabetes management is 2.5 mg once weekly.
Tirzepatide is administered once a week.
Yes, the dose of tirzepatide can be increased after 4 weeks to help improve blood sugar control. The dose can be raised to 5 mg, then to 7.5 mg, and further up to 10 mg depending on the patient’s tolerance and response.
The maximum recommended dose of tirzepatide is 15 mg once weekly.
Tirzepatide is administered via subcutaneous injection, typically in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm.
If a dose of tirzepatide is missed, it should be taken as soon as possible within 4 days of the missed dose. If it is more than 4 days, the patient should wait until the next scheduled dose and then continue the regular dosing schedule.
Tirzepatide can be used in patients with renal impairment, but no dose adjustment is required for mild to moderate renal impairment. It should be used with caution in patients with severe renal impairment, but the dose adjustment guidelines are not specifically altered for this population.
Yes, tirzepatide is also approved for weight loss under the brand name Mounjaro. The dosing for weight loss is similar, starting at 2.5 mg and increasing to 15 mg once weekly, depending on the patient’s response.
Yes, tirzepatide can be used in combination with other antidiabetic medications, including metformin, insulin, and SGLT2 inhibitors, as long as there are no contraindications or specific concerns for the individual patient.
Common side effects of tirzepatide include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, decreased appetite, and constipation, particularly when starting treatment or increasing the dose.

Dr. Judith Germaine
Dr. Jude (Germaine-Munoz) Germaine, MD is a family physician in Springfield, New Jersey. She is currently licensed to practice medicine in New Jersey, New York, and Florida. She is affiliated with Saint Josephs Wayne Hospital.