Table of Contents
Introduction
Sleep apnea is a common yet serious health condition that affects millions of people around the world. It causes people to stop breathing temporarily while they sleep, often multiple times a night. These pauses in breathing, known as apneas, can last from a few seconds to over a minute. Sleep apnea disrupts sleep, making people feel tired during the day and putting them at risk for several health issues like high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, and even stroke. While there are different types of sleep apnea, the most common one is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). In OSA, the airway becomes partially or completely blocked during sleep, usually because of the soft tissues in the throat relaxing and collapsing.
One of the biggest risk factors for sleep apnea is being overweight or obese. Excess fat, especially around the neck and throat, can press on the airway and make it harder to breathe. This connection between weight and sleep apnea has led to a growing focus on weight loss as a way to improve the condition. Research has shown that even losing a small amount of weight can significantly reduce the severity of sleep apnea symptoms for many people. Weight loss can help lower the pressure on the airway, reduce inflammation, and improve overall breathing during sleep.
In recent years, a new class of medications has emerged to help people lose weight more effectively. Tirzepatide is one such medication that is gaining attention. Tirzepatide works by targeting hormones in the body that control appetite and blood sugar levels, making it easier for people to eat less and lose weight. Originally developed to treat type 2 diabetes, tirzepatide has also been shown to cause significant weight loss in people who are overweight or obese. One brand of tirzepatide, marketed under the name Mounjaro®, has already been approved for managing type 2 diabetes, and studies are underway to explore its potential benefits for weight loss and related health conditions.
The link between weight loss and better sleep is well-established. When people lose weight, they often experience improvements in sleep apnea and other sleep-related problems. This is why researchers are now looking at medications like tirzepatide to see if they could indirectly improve sleep apnea by helping patients shed excess weight. While tirzepatide is not currently approved as a direct treatment for sleep apnea, its ability to help people lose weight could make it a valuable tool for managing the condition.
This article will explore the connection between tirzepatide, weight loss, and sleep apnea in detail. It will answer common questions people ask, such as how tirzepatide works, whether it can help with sleep apnea, and what the risks and benefits are. We will also look at the role of weight loss in improving sleep apnea and discuss how tirzepatide fits into the broader picture of sleep apnea treatment. By the end, readers will have a clear understanding of the potential for tirzepatide to make a difference for those struggling with both obesity and sleep apnea.
While tirzepatide shows promise, it’s important to remember that sleep apnea is a complex condition with many causes and contributing factors. For example, not everyone with sleep apnea is overweight, and not everyone who loses weight will see their symptoms disappear completely. Other treatments, such as CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) therapy, oral appliances, or surgery, may still be necessary for many people. Lifestyle changes, like eating a healthier diet, exercising regularly, and improving sleep hygiene, are also crucial parts of managing sleep apnea.
This article will focus on what we know about tirzepatide so far and how it could help people who are living with sleep apnea. While the research is still ongoing, the connection between weight loss and better sleep is a hopeful area of study. With more data, we may better understand how medications like tirzepatide can complement existing treatments and improve the quality of life for many patients.
What is Tirzepatide and How Does It Work?
Tirzepatide is a groundbreaking medication used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity. It belongs to a new class of drugs that work by targeting specific hormones in the body to regulate blood sugar and appetite. Tirzepatide is sold under the brand name Mounjaro® by Eli Lilly and Company, though its benefits extend beyond diabetes management. Understanding how tirzepatide works and why it is being studied for conditions like sleep apnea starts with its unique action in the body.
Dual Action: GLP-1 and GIP Agonist
Tirzepatide is a dual agonist, which means it works on two hormone receptors at the same time:
- GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1): This hormone helps control blood sugar by increasing insulin production after meals. It also slows down how quickly the stomach empties, making people feel full for longer. GLP-1 agonists are already used in other weight-loss medications like semaglutide (Ozempic® and Wegovy®).
- GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide): This hormone complements GLP-1 by improving how the body uses sugar and fat. It also appears to have a direct effect on reducing appetite and promoting fat breakdown.
By targeting both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, tirzepatide provides a more powerful effect on weight loss compared to medications that work on GLP-1 alone.
How Tirzepatide Promotes Weight Loss
Tirzepatide’s weight-loss benefits stem from its ability to:
- Reduce appetite: By acting on parts of the brain that control hunger, tirzepatide helps people eat less.
- Improve insulin sensitivity: It makes the body’s cells more responsive to insulin, reducing fat storage.
- Slow gastric emptying: This delays how fast food leaves the stomach, leading to a feeling of fullness and fewer cravings.
In clinical trials, patients using tirzepatide lost an average of 15% to 20% of their body weight over the course of several months. These results are particularly promising for people with obesity, as even modest weight loss can lead to significant health improvements.
FDA Approval and Current Uses
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved tirzepatide in 2022 for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It is currently under investigation for weight management in individuals with or without diabetes. The approval process for weight-loss use is ongoing, but early studies have shown remarkable results, leading experts to call tirzepatide a “game-changer” in obesity treatment.
While tirzepatide is not yet specifically approved for sleep apnea, its effects on weight loss make it a promising candidate for improving this condition. Excess weight is a major risk factor for sleep apnea, so any treatment that promotes weight reduction could have positive effects on sleep quality.
Benefits Beyond Weight Loss
Tirzepatide offers more than just weight loss:
- Improved blood sugar control: Patients with diabetes see significant reductions in their HbA1c levels (a measure of long-term blood sugar control).
- Cardiovascular benefits: Tirzepatide may lower the risk of heart attack and stroke by improving cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
- Fat distribution changes: The drug specifically reduces visceral fat (fat stored around internal organs), which is more dangerous than fat stored under the skin.
These benefits are especially relevant for people with sleep apnea, as they often face an increased risk of heart disease and metabolic disorders.
How Tirzepatide is Taken
Tirzepatide is administered as a once-weekly injection. It comes in pre-filled pens, making it easy for patients to use at home. The medication is typically started at a low dose and gradually increased over several weeks to reduce side effects. Most people tolerate tirzepatide well, though some experience nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, especially during the early stages of treatment.
Why Tirzepatide Stands Out
Tirzepatide’s unique dual-action mechanism sets it apart from other medications. While traditional GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide have been highly effective, tirzepatide’s added action on GIP receptors makes it even more potent. This dual effect not only enhances weight loss but also improves metabolic health, which could indirectly benefit conditions like sleep apnea.
Future Potential
As researchers continue to study tirzepatide, its applications may expand. While current studies focus on weight loss and diabetes, future trials may explore its direct effects on sleep apnea and other obesity-related conditions. Early results suggest that the medication could play a vital role in comprehensive treatment plans aimed at improving sleep, reducing cardiovascular risk, and enhancing overall quality of life.
Tirzepatide is a revolutionary medication that combines weight-loss benefits with broader health improvements. Its dual-action mechanism makes it a powerful tool in managing obesity and related conditions, paving the way for potential use in sleep apnea treatment.
Understanding Sleep Apnea: Causes and Risk Factors
Sleep apnea is a common condition that affects millions of people around the world. It is a sleep disorder that causes breathing to repeatedly stop and start during sleep. This can lead to poor-quality sleep, daytime tiredness, and serious health problems if not treated. Understanding the causes and risk factors of sleep apnea is essential to recognizing its symptoms and finding effective treatments.
Types of Sleep Apnea
There are three main types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most common form. It happens when the muscles in the throat relax too much, blocking the airway. This leads to interrupted breathing and can cause snoring.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): This type is less common. It occurs when the brain does not send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. Unlike OSA, there is no physical blockage of the airway.
- Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Also called treatment-emergent central sleep apnea, this is a combination of obstructive and central sleep apnea.
This article focuses on obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), as it is strongly linked to weight and body composition.
What Causes Sleep Apnea?
The primary cause of obstructive sleep apnea is the physical collapse or blockage of the airway during sleep. Here are the main factors that contribute to this condition:
- Throat and Neck Anatomy
Some people are more likely to develop sleep apnea because of the shape and size of their airway. For example:
- Narrow airway: If the airway is naturally small, it can collapse more easily.
- Enlarged tonsils or adenoids: These tissues can block the airway, especially in children.
- Fat deposits around the throat: In overweight or obese individuals, excess fat can press against the airway, making it harder to stay open during sleep.
- Muscle Relaxation During Sleep
When you sleep, the muscles in your body relax, including the ones in your throat. For people with sleep apnea, this relaxation can cause the airway to collapse or become blocked. This is why episodes of apnea often occur during the deepest stages of sleep.
- Obesity
Obesity is one of the most significant risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea. Carrying extra weight, especially around the neck and upper body, increases the likelihood of the airway collapsing during sleep. Studies have shown that even modest weight loss can significantly reduce the severity of sleep apnea in many patients.
- Aging
As people age, their muscles lose tone and strength, including those in the throat. This natural weakening can increase the risk of airway collapse, leading to sleep apnea.
- Genetic Factors
Sleep apnea can run in families. If your parents or siblings have sleep apnea, you may be at a higher risk of developing the condition. Genetic factors may influence airway anatomy, muscle tone, and weight distribution.
Who Is at Risk for Sleep Apnea?
Certain groups of people are more likely to develop sleep apnea. Below are the key risk factors:
- Excess Weight
Obesity is the leading risk factor for sleep apnea. A high body mass index (BMI) is strongly associated with the condition. People with excess fat around their neck, chin, and abdomen are particularly at risk because this fat can compress the airway.
- Gender
Men are more likely than women to develop sleep apnea. However, the risk increases for women after menopause, likely due to hormonal changes that affect muscle tone and fat distribution.
- Age
Sleep apnea is more common in adults over the age of 40. As mentioned earlier, aging weakens muscles, which can contribute to airway problems during sleep.
- Lifestyle Factors
Certain habits and lifestyle choices can increase the risk of sleep apnea, including:
- Smoking: Smoking can inflame and irritate the airways, making blockages more likely.
- Alcohol use: Alcohol relaxes the throat muscles, which can worsen sleep apnea symptoms.
- Sedative medications: These drugs have similar effects to alcohol, relaxing the throat muscles too much.
- Medical Conditions
Certain health conditions can increase the risk of sleep apnea, such as:
- High blood pressure (hypertension): Many people with sleep apnea also have hypertension, and the two conditions often worsen each other.
- Diabetes: Sleep apnea is common in people with type 2 diabetes, possibly due to shared risk factors like obesity.
- Heart disease and stroke: These conditions are linked to central and obstructive sleep apnea.
- Asthma: Studies suggest that having asthma may raise the risk of sleep apnea.
Why Does Obesity Matter in Sleep Apnea?
Obesity directly contributes to sleep apnea by:
- Increasing fat deposits around the throat and tongue, which can narrow the airway.
- Adding pressure on the chest and lungs, making it harder to breathe during sleep.
- Contributing to systemic inflammation, which may affect the airway and breathing control.
Research shows that reducing weight through diet, exercise, or medications like tirzepatide can significantly improve sleep apnea symptoms in overweight individuals. Weight loss reduces the pressure on the airway, lowers inflammation, and helps normalize breathing patterns during sleep.
Understanding sleep apnea’s causes and risk factors highlights the importance of managing conditions like obesity to improve symptoms. By addressing these underlying issues, patients can reduce their risk of complications and enjoy better-quality sleep. In the following sections, we will explore how tirzepatide may play a role in achieving these goals.
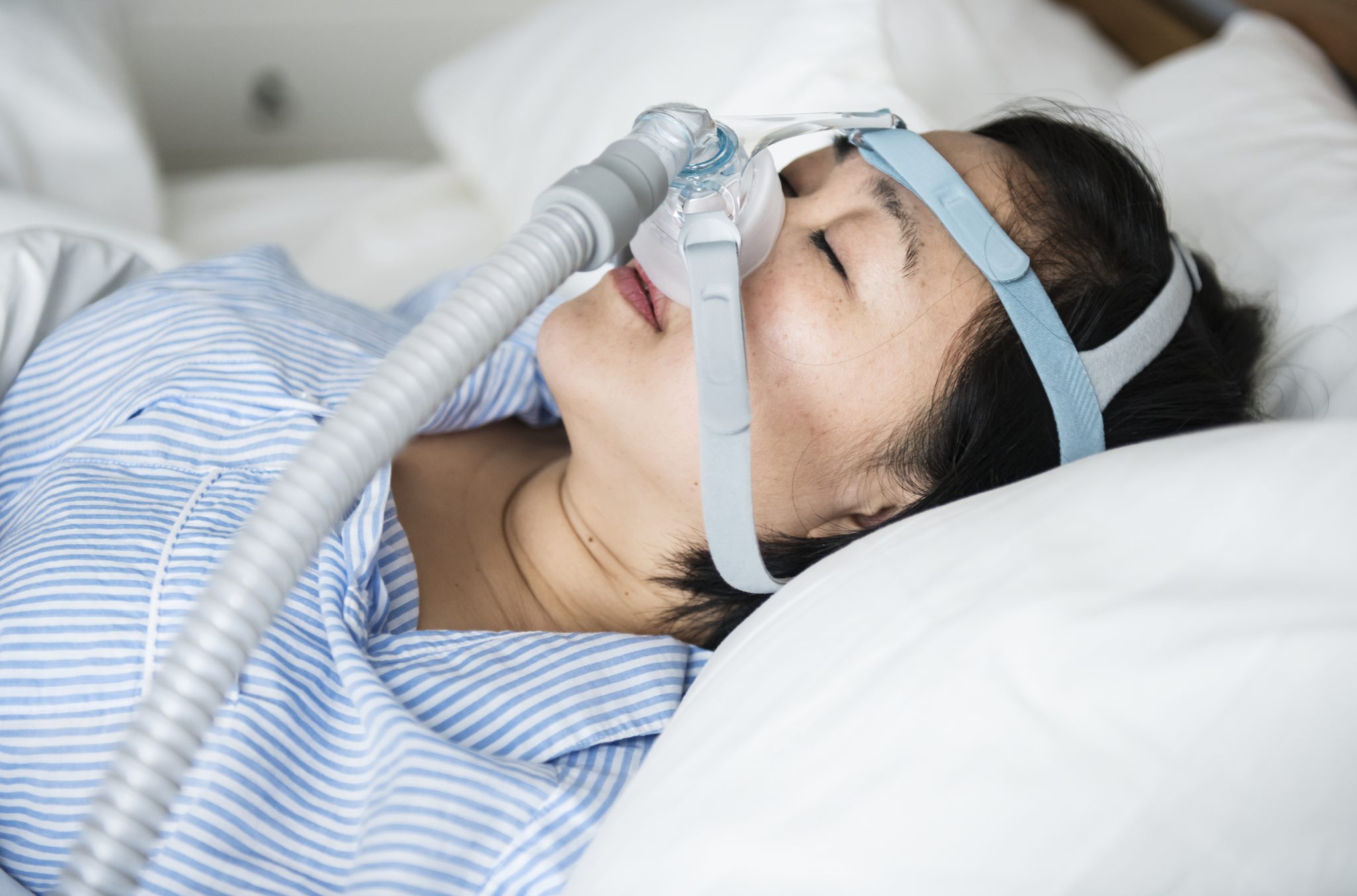
Can Weight Loss Improve Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a common condition where breathing stops and starts repeatedly during sleep. It can lead to poor sleep quality, daytime fatigue, and serious health problems. Obesity is one of the most significant risk factors for developing sleep apnea. Losing weight, therefore, is often recommended as a key strategy to improve sleep apnea symptoms. In this section, we will explore why weight loss matters, how it impacts sleep apnea, and what science says about this relationship.
The Link Between Obesity and Sleep Apnea
Obesity contributes to sleep apnea in several ways. People with excess body fat, particularly in the neck and upper body, are more likely to experience airway obstruction during sleep. Fat deposits around the neck can compress the upper airway, making it narrower. This increases the likelihood that the airway will collapse when the muscles relax during sleep, leading to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Additionally, abdominal fat increases pressure on the chest and lungs, which can reduce lung capacity and worsen breathing problems. Obesity is also linked to inflammation and hormonal changes that may weaken the muscles controlling the airway, further contributing to sleep apnea symptoms.
Studies show that more than 70% of individuals with OSA are overweight or obese. For this reason, many doctors encourage weight loss as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for sleep apnea.
How Weight Loss Can Help Sleep Apnea
Reduction in Fat Around the Airway
Losing weight reduces fat deposits in the neck and around the throat, which can widen the airway and decrease the chance of blockage during sleep. A wider airway makes it easier to breathe and reduces the number of apnea events during the night. For individuals with moderate to severe sleep apnea, even a small reduction in neck circumference can lead to noticeable improvements in breathing.
Improved Lung Function
Weight loss also lowers abdominal fat, which reduces pressure on the diaphragm—the muscle responsible for helping you breathe. This can improve lung function and oxygen flow during sleep. Better lung capacity means less strain on your body to keep breathing during the night.
Decreased Inflammation
Excess weight is often associated with chronic inflammation, which can weaken the muscles that support the airway. Weight loss helps reduce inflammation throughout the body, including in the airway tissues. This may improve muscle tone and make it easier for the airway to stay open while sleeping.
Better Metabolic Health
Obesity is linked to insulin resistance and other metabolic problems that may worsen sleep apnea. Losing weight can improve blood sugar levels, reduce insulin resistance, and regulate hormones such as leptin and ghrelin, which control hunger and energy balance. These metabolic changes can enhance sleep quality and overall health.
Scientific Evidence on Weight Loss and Sleep Apnea
Research strongly supports the idea that weight loss can improve sleep apnea. A study published in the journal Sleep found that losing just 10% of body weight could reduce the severity of OSA by 20% to 30%. In some cases, significant weight loss has even led to complete remission of sleep apnea symptoms.
Another study looked at individuals who underwent bariatric (weight loss) surgery. The researchers observed that many participants experienced significant improvements in sleep apnea severity after losing weight. For some, the need for continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy was reduced or eliminated entirely.
However, the amount of weight loss needed to improve sleep apnea depends on the individual. For those with severe OSA, losing more weight may be necessary to achieve substantial improvements. Even so, weight loss often leads to better outcomes when combined with other treatments like CPAP or oral appliances.
The Limitations of Weight Loss Alone
While weight loss is highly beneficial, it is not a cure-all for sleep apnea. Some people with sleep apnea are not overweight, and others may continue to experience symptoms even after losing significant weight. This is because sleep apnea can have multiple causes, such as genetic factors, nasal congestion, or structural issues in the airway.
Doctors typically recommend combining weight loss with other treatments to achieve the best results. For example, CPAP therapy remains the gold standard for managing OSA, as it provides immediate relief by keeping the airway open during sleep. Lifestyle changes, including weight loss, can complement these treatments and improve overall health.
Sustainable Weight Loss Matters
For weight loss to improve sleep apnea in the long term, it must be sustainable. Crash diets and rapid weight loss methods are often ineffective because the weight is quickly regained. A combination of healthy eating, regular exercise, and behavior changes is more effective for lasting weight loss. Medications like tirzepatide may also be helpful for individuals who struggle to lose weight through traditional methods.
Weight loss plays a crucial role in reducing sleep apnea symptoms. By decreasing fat around the airway, improving lung function, and enhancing metabolic health, losing weight can significantly improve breathing and sleep quality. While weight loss alone may not cure sleep apnea, it is a vital part of a comprehensive treatment plan. If you have sleep apnea, talk to your doctor about how weight loss could help and whether medications like tirzepatide may be a good option for you.
How Does Tirzepatide Influence Weight Loss?
Tirzepatide is a groundbreaking medication developed to aid in weight loss and improve blood sugar control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. It works by mimicking hormones in the body that regulate appetite and digestion. The effectiveness of tirzepatide in promoting significant weight loss has caught the attention of researchers, especially for its potential benefits for people with obesity-related conditions like sleep apnea. Let’s explore how tirzepatide helps with weight loss and why this matters for health.
What Is Tirzepatide and How Does It Work?
Tirzepatide is a once-weekly injectable medication belonging to a class of drugs known as GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists. However, tirzepatide is unique because it is a dual agonist that also targets another hormone receptor called GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide). Together, these hormones work on parts of the brain involved in hunger and fullness, as well as on metabolic processes that control how the body uses energy.
Here’s how tirzepatide works:
- Reduces Appetite: Tirzepatide sends signals to the brain that make you feel full sooner during meals and reduce cravings between meals. This helps people eat less without feeling deprived.
- Slows Digestion: Tirzepatide slows the emptying of the stomach. This means food stays in the stomach longer, keeping you feeling full for a more extended period.
- Enhances Insulin Sensitivity: For individuals with type 2 diabetes, tirzepatide improves how the body responds to insulin, which can also contribute to better weight regulation.
These combined effects make tirzepatide one of the most effective medications currently available for weight loss.
Clinical Trials and Weight Loss Results
Tirzepatide has shown impressive results in clinical trials. In the SURMOUNT-1 trial, a study specifically focusing on weight loss in people with obesity or overweight, participants who received tirzepatide lost an average of 15% to 22.5% of their body weight, depending on the dose. For someone weighing 200 pounds, this could mean losing 30 to 45 pounds, which is a substantial amount.
In the trials:
- Most participants lost at least 5% of their body weight, a key benchmark for health improvements.
- Many individuals achieved even higher levels of weight loss, approaching results typically seen with bariatric surgery.
- Weight loss occurred gradually over the course of the treatment, with noticeable changes within the first 12 weeks and continued progress over a year.
Why Does Weight Loss Matter for Sleep Apnea?
Obesity is one of the most significant risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a condition where the airway becomes blocked during sleep. Excess fat tissue, especially around the neck and throat, can narrow the airway and make it harder to breathe. When a person loses weight:
- Neck Circumference Decreases: A reduction in fat around the throat can widen the airway and reduce the likelihood of blockages during sleep.
- Abdominal Fat Shrinks: Excess fat in the abdomen puts pressure on the lungs and diaphragm, making it harder to breathe deeply. Losing this fat improves breathing mechanics.
- Inflammation Reduces: Obesity is linked to higher levels of inflammation, which can worsen sleep apnea. Weight loss reduces inflammation, potentially improving symptoms.
Studies have shown that even a modest weight loss of 5-10% of total body weight can significantly improve the severity of sleep apnea. Given tirzepatide’s ability to produce far greater weight loss, it holds tremendous promise for people with this condition.
Other Benefits of Weight Loss With Tirzepatide
In addition to improving sleep apnea symptoms, weight loss achieved with tirzepatide can lead to a wide range of health benefits:
- Improved Heart Health: Losing weight lowers blood pressure and cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease—a common concern for people with sleep apnea.
- Better Blood Sugar Control: For individuals with type 2 diabetes, tirzepatide not only helps with weight loss but also stabilizes blood sugar, preventing complications like neuropathy and kidney disease.
- Higher Energy Levels: Many people report feeling more energetic as they lose weight, which can encourage physical activity, further improving overall health.
- Better Mental Health: Weight loss can boost self-esteem and reduce anxiety or depression, which are often linked to sleep disorders.
How Long Does It Take to See Results?
Patients using tirzepatide typically notice changes in their appetite and eating habits within the first few weeks. Weight loss, however, is a gradual process. Most people see the most significant changes after several months, with ongoing progress as they continue treatment.
It is important to remember that weight loss is not the same for everyone. Factors like diet, physical activity, and adherence to the medication schedule can influence outcomes. Healthcare providers often monitor patients closely during treatment to ensure they’re on track.
Tirzepatide represents a powerful tool for helping people achieve meaningful weight loss, which can directly and indirectly improve health. For those with obesity-related conditions like sleep apnea, the weight loss induced by tirzepatide could lead to better breathing, fewer nighttime interruptions, and improved overall quality of life. However, it’s essential to combine tirzepatide with a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
Is Tirzepatide Effective for Treating Sleep Apnea?
Tirzepatide is a newer medication designed to help with weight loss, and it has shown remarkable results in clinical trials. Many people want to know if it can directly treat sleep apnea. While tirzepatide is not specifically approved for sleep apnea, it may help improve the condition by addressing one of its primary causes: obesity.
How Weight Impacts Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea, especially obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), is often linked to obesity. Excess fat around the neck and upper airway can narrow the breathing passages, making it harder to breathe during sleep. This narrowing increases the likelihood of airway collapse, which is the main problem in obstructive sleep apnea. Additionally, obesity can lead to lower lung volume and reduced oxygen levels, which worsen sleep apnea symptoms.
When someone loses weight, the fat in these areas decreases, and this can reduce the severity of sleep apnea. Studies show that even modest weight loss can significantly improve symptoms, such as snoring, daytime sleepiness, and pauses in breathing during sleep. For this reason, weight management is often one of the first recommendations for people with sleep apnea who are overweight.
How Tirzepatide Works for Weight Loss
Tirzepatide works by mimicking natural hormones in the body called GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide). These hormones play a role in appetite regulation, digestion, and blood sugar control. Tirzepatide helps reduce hunger, makes you feel full sooner, and slows the rate at which food leaves the stomach. This combination helps people eat less and lose weight over time.
In clinical trials, tirzepatide has helped patients lose an average of 15-20% of their body weight when combined with lifestyle changes like a healthy diet and regular exercise. This level of weight loss is much greater than what is typically seen with older weight-loss medications, making tirzepatide a groundbreaking option for people struggling with obesity.
Does Tirzepatide Directly Treat Sleep Apnea?
While tirzepatide is not specifically approved for treating sleep apnea, its ability to promote significant weight loss suggests that it could indirectly help reduce sleep apnea symptoms. Here are some key points to consider:
- Weight Loss as a Mechanism of Improvement:
- Excess weight is one of the strongest risk factors for sleep apnea. Losing weight can reduce the pressure on the airway and improve airflow during sleep.
- People who lose weight with tirzepatide may notice fewer apnea episodes per hour and a reduction in snoring.
- Metabolic and Hormonal Effects:
- Tirzepatide not only reduces weight but also improves blood sugar control and reduces inflammation. Poor blood sugar control and inflammation are linked to worse sleep quality and may contribute to sleep apnea.
- These metabolic improvements could provide additional benefits for people with sleep apnea, though more research is needed to confirm this.
- Improvement in Cardiovascular Health:
- Sleep apnea is associated with high blood pressure, heart disease, and other cardiovascular problems. Tirzepatide helps improve heart health by lowering blood pressure and cholesterol levels, which may have a positive effect on overall sleep apnea management.
What Does the Research Say?
There is currently limited direct research on tirzepatide and sleep apnea. Most studies on tirzepatide focus on its effects on weight loss and type 2 diabetes. However, based on what we know about weight loss and its impact on sleep apnea, there is reason to believe that tirzepatide could play a helpful role.
Some smaller studies and anecdotal reports suggest that weight loss achieved with tirzepatide may lead to fewer apnea events and improved sleep quality. Ongoing clinical trials are expected to provide more evidence in the future.
The Need for More Studies
While the early signs are promising, more research is needed to determine how much tirzepatide can help people with sleep apnea. Specifically, studies are needed to answer questions like:
- How much weight loss is required to see meaningful improvements in sleep apnea symptoms?
- Are there any direct effects of tirzepatide on airway muscles or breathing control?
- Does tirzepatide improve sleep quality beyond the effects of weight loss?
Tirzepatide is not a direct treatment for sleep apnea, but it may offer significant benefits by helping with weight loss. Losing weight can reduce the severity of sleep apnea and improve overall health. While the medication shows great promise, it is important for patients to continue using traditional sleep apnea treatments like CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) therapy alongside tirzepatide. Consulting a healthcare provider is essential to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses both weight loss and sleep apnea.
What Are the Risks and Side Effects of Tirzepatide?
When considering any medication, it is important to understand the risks and potential side effects. Tirzepatide, though effective for weight loss, is no exception. This section outlines the most common side effects, rare risks, and precautions for individuals considering tirzepatide, particularly those with sleep apnea or related conditions.
Common Side Effects of Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide is generally well-tolerated by most people, but some individuals may experience side effects. These are usually mild to moderate and often related to how the medication works on the digestive system. Here are some common side effects:
- Nausea: This is the most frequently reported side effect. It occurs because tirzepatide slows down how quickly the stomach empties, a process called gastric emptying. For most people, nausea decreases over time as their body adjusts to the medication.
- Diarrhea: Some individuals may experience diarrhea during the initial weeks of treatment. This is typically temporary and manageable with hydration and dietary adjustments.
- Vomiting: In some cases, tirzepatide can lead to vomiting, especially if the dosage is increased too quickly. Starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it as prescribed can help reduce this risk.
- Constipation: While diarrhea is common, some individuals may experience the opposite effect—constipation. This can occur as the medication changes how the digestive system processes food.
- Loss of Appetite: Tirzepatide often reduces hunger, which is a key reason it helps with weight loss. However, for some individuals, this reduced appetite can feel uncomfortable.
Less Common but Serious Risks
While rare, tirzepatide has been associated with some more serious risks that should be carefully monitored. These include:
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas, known as pancreatitis, is a potential but rare side effect of tirzepatide. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Patients with a history of pancreatitis should discuss this risk with their doctor before starting the medication.
- Gallbladder Issues: Weight loss, including that induced by tirzepatide, can increase the risk of gallstones. Symptoms of gallstones include sharp pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, and changes in digestion.
- Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia): Tirzepatide can lower blood sugar levels, especially when combined with medications like insulin or sulfonylureas. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include dizziness, sweating, confusion, and shakiness. Patients using these other medications may need dose adjustments to avoid dangerously low blood sugar levels.
- Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to tirzepatide. Symptoms could include rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Anyone experiencing these symptoms should seek immediate medical attention.
- Thyroid Tumors: Animal studies have shown an increased risk of thyroid tumors with drugs similar to tirzepatide, though this has not been confirmed in humans. Individuals with a family history of thyroid cancer or a condition called Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN2) should avoid using tirzepatide.
Precautions for Patients with Sleep Apnea
Patients with sleep apnea need to take special care when considering tirzepatide. While the medication itself does not directly impact sleep apnea, certain factors should be considered:
- Breathing Irregularities: Sleep apnea often causes irregular breathing during sleep. While tirzepatide is unlikely to worsen this directly, patients should monitor for any new symptoms.
- Concurrent Conditions: Many individuals with sleep apnea also have other conditions, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart disease. Tirzepatide can affect these conditions, especially blood sugar levels in diabetics, so close medical supervision is critical.
- Weight Loss Monitoring: Rapid weight loss can sometimes temporarily worsen sleep apnea symptoms, as the body adjusts to changes in fat distribution around the neck and airway. Patients using tirzepatide should work closely with their healthcare provider to ensure their sleep apnea is well-managed during treatment.
Minimizing Side Effects
To reduce the chances of experiencing side effects, follow these tips:
- Start with a Low Dose: Healthcare providers usually prescribe tirzepatide at a low dose, gradually increasing it over several weeks. This approach helps the body adjust to the medication and reduces side effects.
- Eat Smaller Meals: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help prevent nausea and digestive discomfort.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can ease symptoms like nausea, diarrhea, and constipation.
- Report Symptoms Early: If you experience severe or persistent side effects, contact your healthcare provider. They may adjust your dose or recommend other solutions.
Long-Term Safety of Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide is a relatively new medication, and ongoing studies are examining its long-term safety. Current evidence suggests that the benefits, particularly for weight loss and improved metabolic health, often outweigh the risks. However, individuals should regularly follow up with their healthcare provider to monitor for any emerging issues.
While tirzepatide offers significant potential for weight loss and improved health, it is not without risks. Understanding the common and rare side effects is essential for anyone considering this medication, especially those with sleep apnea. By working closely with a healthcare provider, most patients can use tirzepatide safely and effectively to support their health goals.
How to Use Tirzepatide Safely for Sleep Apnea Patients
Tirzepatide is a promising medication that has shown significant benefits for weight loss, which can help manage sleep apnea. However, to use tirzepatide safely, patients with sleep apnea should understand how the medication works, the correct dosages, and how to monitor their health while on it. Sleep apnea patients have unique needs, so it is important to consider specific precautions.
How Tirzepatide is Used for Weight Management
Tirzepatide is not yet approved directly for treating sleep apnea but is approved for managing type 2 diabetes under the brand name Mounjaro® and is being studied for obesity treatment. Patients using tirzepatide for weight loss often experience secondary health benefits, including potential improvements in sleep apnea symptoms. The medication is injected once weekly, which makes it convenient for long-term use.
The dosage of tirzepatide typically starts low to reduce the risk of side effects. For example:
- Patients may start with a dose of 2.5 mg weekly for four weeks.
- The dose is gradually increased to higher levels, such as 5 mg, 10 mg, or even 15 mg weekly, based on the individual’s tolerance and treatment response.
A doctor will determine the best dosage for a patient based on their weight, medical history, and other medications they are taking. This gradual approach helps reduce common side effects such as nausea or upset stomach.
Monitoring While on Tirzepatide
Using tirzepatide safely requires regular monitoring by a healthcare provider. Patients with sleep apnea should ensure that their condition is closely watched during treatment because of potential interactions between weight loss, apnea symptoms, and other therapies like CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure).
Here’s how monitoring is typically done:
- Weight Loss Progress: Regular check-ins with a doctor help track how much weight a patient is losing. Losing weight too quickly can lead to muscle loss or nutritional deficiencies, while slow progress may require adjustments to the tirzepatide dosage.
- Sleep Apnea Symptoms: Patients and their doctors should pay attention to how sleep apnea symptoms are changing as weight decreases. Improvements in sleep apnea can sometimes allow for a reduction in CPAP pressure settings or other adjustments.
- Blood Sugar Levels: For patients with diabetes or prediabetes, tirzepatide can significantly lower blood sugar. This is a benefit, but it also means patients must watch for signs of low blood sugar, such as dizziness or shakiness.
- Side Effects: Common side effects of tirzepatide include nausea, diarrhea, and reduced appetite. Severe side effects, like pancreatitis, are rare but need immediate medical attention. Sleep apnea patients must ensure their symptoms are not mistaken for medication side effects.
Special Considerations for Sleep Apnea Patients
Patients with sleep apnea often use devices like CPAP to manage their condition. It’s essential to continue using these treatments as prescribed, even while starting tirzepatide. Stopping CPAP prematurely can lead to worsening apnea symptoms and health risks.
Tirzepatide’s weight-loss effects may reduce the severity of sleep apnea over time, but the timeline for improvement varies. Patients must be patient and avoid expecting immediate results. It can take several months to see significant weight loss and related benefits.
Additionally, sleep apnea patients may need extra support to manage:
- Medication Adjustments: Those taking medications for high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart disease may need their doses adjusted as their weight decreases and their metabolic health improves.
- Nutritional Needs: Losing weight with tirzepatide often reduces appetite, so patients should work with a dietitian to ensure they are still getting enough essential nutrients.
Safety Tips for Long-Term Use
- Stick to the Plan: Always use tirzepatide exactly as prescribed. Do not skip doses or take more than the recommended amount.
- Report Changes to a Doctor: If sleep apnea symptoms worsen, or if side effects become severe, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight loss medications work best when combined with healthy lifestyle changes. Patients should focus on eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining good sleep hygiene.
Who Should Avoid Tirzepatide?
Tirzepatide may not be suitable for everyone. Patients should avoid tirzepatide if they:
- Have a history of pancreatitis.
- Are allergic to any ingredients in the medication.
- Have a family history of thyroid cancer (a rare risk associated with similar medications).
Tirzepatide offers hope for many patients with sleep apnea by addressing one of the root causes—excess weight. However, it must be used with caution under medical supervision. By understanding how to take tirzepatide safely and monitoring progress closely, patients can maximize its benefits while minimizing risks. Always work closely with a healthcare provider to ensure the treatment aligns with your overall health needs.
Does Tirzepatide Improve Sleep Quality?
Tirzepatide, a medication primarily approved for type 2 diabetes and weight loss, is generating interest for its potential effects on sleep quality. Although it is not directly indicated to treat sleep apnea or sleep disorders, tirzepatide indirectly influences sleep by promoting significant weight loss and improving overall metabolic health. This section explores how these changes might positively affect sleep quality, particularly for people with sleep apnea.
How Weight Loss Impacts Sleep Quality
Weight loss is closely linked to improvements in sleep quality, especially for people with sleep apnea. Obesity is a major risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a condition where the airway becomes partially or fully blocked during sleep. Excess weight around the neck and throat narrows the airway, making it more likely to collapse during relaxation at night.
By reducing body fat, particularly in the upper airway region, weight loss can:
- Decrease the frequency of apnea events (periods of stopped breathing).
- Improve oxygen levels during sleep.
- Reduce snoring, a common symptom of OSA.
Tirzepatide works by helping people lose significant amounts of weight. In clinical trials, patients using tirzepatide lost an average of 15-22% of their body weight, depending on the dose. For people with sleep apnea, such dramatic weight loss can translate into fewer symptoms, better oxygenation, and overall improved sleep.
The Role of Metabolic Health in Sleep Quality
Sleep and metabolism are deeply interconnected. Poor metabolic health, characterized by conditions like insulin resistance, high blood sugar, and inflammation, can disrupt sleep patterns. People with obesity often experience hormonal imbalances, such as elevated cortisol (stress hormone) and reduced melatonin (sleep hormone), which make it harder to fall and stay asleep.
Tirzepatide targets these underlying issues by improving metabolic health. As a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, tirzepatide helps:
- Lower blood sugar levels.
- Reduce systemic inflammation.
- Normalize hormone levels that regulate hunger, stress, and sleep.
For instance, better blood sugar control can prevent nighttime blood sugar fluctuations that may wake people up. Additionally, reducing inflammation can improve the overall quality of restorative sleep.
Hormonal Effects of Tirzepatide That May Support Better Sleep
Tirzepatide’s hormonal effects extend beyond weight loss and metabolic improvements. GLP-1 receptor agonists, including tirzepatide, influence brain regions that regulate appetite, mood, and sleep. By modulating these pathways, tirzepatide may promote better sleep in the following ways:
- Appetite Regulation: Better appetite control prevents late-night snacking, which can disrupt sleep by causing indigestion or high blood sugar.
- Stress Reduction: Tirzepatide’s ability to lower cortisol levels can create a more relaxed state, making it easier to fall asleep.
- Improved Satiety: Feeling full for longer periods can prevent sleep disturbances caused by hunger.
Patient Experiences and Research Evidence
Although there is no direct research yet on tirzepatide’s effects on sleep quality, anecdotal reports and clinical observations suggest that patients using tirzepatide often experience improved sleep. This is likely due to a combination of reduced weight, stabilized blood sugar, and improved overall health.
Studies on other GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as semaglutide (marketed as Wegovy® or Ozempic®), have shown potential improvements in sleep quality through similar mechanisms. As tirzepatide offers even greater weight loss compared to semaglutide, it is reasonable to hypothesize that the benefits to sleep may be comparable or even greater.
Sleep Apnea-Specific Improvements
For individuals with sleep apnea, tirzepatide may have added benefits:
- Reduced Dependence on CPAP Therapy: Weight loss can lower the severity of OSA, potentially reducing the need for continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy.
- Fewer Nighttime Awakenings: Apnea events often cause people to wake up gasping for air. As tirzepatide helps reduce these events through weight loss, patients may enjoy uninterrupted sleep.
- Better Daytime Alertness: Improved nighttime breathing and sleep quality result in less daytime fatigue, which is a common symptom of sleep apnea.
The Need for More Research
While the indirect effects of tirzepatide on sleep are promising, more studies are needed to confirm its role in improving sleep quality. Current clinical trials focus on tirzepatide’s impact on weight loss and diabetes, with limited data on its effects on sleep disorders like apnea. Future research could provide more targeted insights.
Practical Takeaways
For now, patients considering tirzepatide should view it as a weight-loss and diabetes management tool rather than a direct treatment for sleep apnea or other sleep disorders. However, the improvements in weight, metabolic health, and hormone regulation can contribute to better overall sleep, making tirzepatide a valuable part of a comprehensive approach to health.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Complement Tirzepatide for Sleep Apnea?
While tirzepatide shows promise in helping with weight loss and indirectly improving sleep apnea, it is not a standalone solution. Combining tirzepatide with lifestyle changes can maximize its benefits and provide long-term improvements in sleep apnea and overall health. In this section, we will explore several lifestyle changes that can complement the use of tirzepatide, focusing on a holistic approach to managing sleep apnea.
- Importance of a Comprehensive Treatment Plan
Sleep apnea is a complex condition often requiring multiple approaches for effective management. While tirzepatide can aid weight loss, it cannot directly treat the airway obstruction that defines sleep apnea. To address the condition fully, individuals should pair medication with proven therapies like CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure), positional therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Combining these strategies ensures a well-rounded approach to reducing the severity of sleep apnea.
- Diet and Nutrition: Supporting Weight Loss and Better Sleep
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in weight management and improving overall health. Even while on tirzepatide, making dietary changes can amplify weight loss and enhance metabolic health. Here are a few key points to consider:
- Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods: Choose fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential nutrients while keeping calorie intake in check.
- Reduce Inflammatory Foods: Limiting processed foods, refined sugars, and high-fat meals can reduce inflammation, which is often associated with obesity and sleep apnea.
- Avoid Heavy Meals Before Bed: Eating large meals close to bedtime can worsen sleep apnea symptoms by increasing acid reflux and disrupting sleep.
Consulting with a registered dietitian can help create a personalized nutrition plan that aligns with tirzepatide treatment.
- Regular Exercise: Improving Sleep and Supporting Weight Loss
Physical activity is another cornerstone of managing sleep apnea and achieving weight loss goals. Exercise strengthens muscles, improves cardiovascular health, and supports overall weight management. For individuals with sleep apnea, regular exercise can also improve sleep quality and reduce daytime fatigue.
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling help burn calories and reduce body fat, directly impacting sleep apnea symptoms.
- Strength Training: Building muscle boosts metabolism and can improve body composition, helping sustain weight loss achieved with tirzepatide.
- Consistency: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, as recommended by health experts.
Even light physical activities like stretching or yoga can help improve sleep and overall well-being.
- Sleep Hygiene: Creating an Environment for Better Sleep
While tirzepatide may help improve sleep indirectly by reducing weight, adopting good sleep hygiene practices can further enhance sleep quality. These habits can make a big difference, especially for individuals with sleep apnea:
- Stick to a Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Keep the bedroom dark, quiet, and cool. Use blackout curtains or white noise machines if necessary.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: Avoid electronic devices at least an hour before bedtime, as blue light can interfere with melatonin production.
- Avoid Stimulants: Caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol can disrupt sleep, so limit their use, especially in the evening.
Good sleep hygiene ensures that the sleep gained is restorative, even in the presence of sleep apnea.
- CPAP Therapy: Working Alongside Tirzepatide
For individuals with moderate to severe sleep apnea, CPAP therapy remains one of the most effective treatments. CPAP uses a machine to deliver steady air pressure, preventing airway collapse during sleep. While tirzepatide may reduce the severity of sleep apnea by promoting weight loss, CPAP can provide immediate relief of symptoms like loud snoring, frequent awakenings, and daytime sleepiness.
Using CPAP consistently alongside tirzepatide and lifestyle changes ensures a comprehensive approach to managing sleep apnea.
- Positional Therapy: Adjusting Sleep Position
In many cases, sleep apnea symptoms worsen when sleeping on the back. This position can cause the tongue and soft tissues in the throat to block the airway. Positional therapy involves techniques to encourage side sleeping, which helps keep the airway open. Common strategies include:
- Using specialized pillows or positional devices.
- Sewing a tennis ball into the back of a pajama top to discourage back sleeping.
While tirzepatide addresses weight, positional therapy provides an immediate, non-invasive way to alleviate symptoms.
- Stress Management: Supporting Overall Health
Chronic stress can interfere with weight loss and worsen sleep quality, creating a cycle that may exacerbate sleep apnea. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques can complement tirzepatide’s benefits and improve overall health. Examples include:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like deep breathing and guided meditation can promote relaxation and better sleep.
- Time Management: Reducing overcommitment can help minimize stress and improve focus on health goals.
- Regular Relaxation Activities: Hobbies, reading, or spending time in nature can lower stress levels.
Managing stress is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and improving sleep apnea symptoms.
- Long-Term Behavior Changes: Ensuring Sustainability
For tirzepatide to be effective in the long term, it must be part of sustainable lifestyle changes. Crash diets or temporary exercise routines are unlikely to provide lasting results. Focus on small, manageable changes that can be maintained over time. Building healthy habits ensures that weight loss achieved with tirzepatide is preserved, reducing the likelihood of sleep apnea symptoms returning.
By integrating these lifestyle changes with tirzepatide, individuals with sleep apnea can achieve better health outcomes. While the medication can provide a significant boost in weight loss, addressing diet, exercise, sleep hygiene, and stress offers a more comprehensive path to relief from sleep apnea symptoms. Working with healthcare professionals to tailor these strategies to individual needs ensures the best possible results.
What Are the Long-Term Implications of Tirzepatide Use for Sleep Apnea?
Tirzepatide, a breakthrough medication initially developed to help with weight loss and diabetes management, has shown promising results in addressing sleep apnea symptoms, especially in people who are overweight or obese. Its long-term implications for sleep apnea are multifaceted and can significantly affect health outcomes if used appropriately.
Potential for Sustained Weight Loss
One of the most important benefits of tirzepatide is its ability to promote substantial weight loss over time. Research shows that losing weight can lead to marked improvements in sleep apnea. Excess weight, especially around the neck and upper body, can make it harder to breathe during sleep by narrowing the airway. Tirzepatide helps people shed weight by reducing appetite and regulating blood sugar levels. This can result in a decrease in the amount of fat stored around the airway, allowing for better airflow and less obstruction during sleep.
Maintaining weight loss is often a challenge for people who rely solely on lifestyle changes, but tirzepatide can help maintain long-term weight management when combined with healthy eating and regular exercise. By keeping the weight off, individuals with sleep apnea may continue to experience better sleep quality and reduced symptoms, potentially even eliminating the need for devices like CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) in some cases.
Long-Term Health Outcomes
Using tirzepatide over a long period may have additional health benefits beyond weight loss. Sleep apnea is associated with several serious health conditions, including:
- Heart Disease: Sleep apnea increases the risk of high blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms, and other cardiovascular issues. Tirzepatide’s ability to improve weight and metabolic health can reduce these risks.
- Diabetes: People with sleep apnea are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes due to insulin resistance. Tirzepatide directly addresses insulin resistance and helps control blood sugar levels, which can benefit those managing both conditions.
- Stroke and Brain Health: Sleep apnea can lead to decreased oxygen levels in the blood, which may contribute to an increased risk of stroke and cognitive decline. Long-term weight loss with tirzepatide might mitigate these risks by improving oxygen levels during sleep and overall circulation.
In the long run, these health improvements may lead to a higher quality of life, reduced healthcare costs, and fewer complications for individuals suffering from both obesity and sleep apnea.
Balancing Medication with Other Treatments
While tirzepatide offers numerous benefits, it’s important to remember that it is not a standalone cure for sleep apnea. For many people, sleep apnea treatment includes a combination of strategies, such as CPAP therapy, positional therapy, or oral appliances. Tirzepatide can work alongside these treatments to improve symptoms more effectively.
For example, if someone with severe sleep apnea uses CPAP therapy, losing weight with tirzepatide might allow them to lower the pressure settings on their machine, making the treatment more comfortable and easier to use. In some cases, losing enough weight may lead to a significant reduction in the severity of sleep apnea, allowing patients to transition to less intensive therapies.
Challenges and Considerations
Long-term use of any medication comes with potential risks and challenges. Tirzepatide is generally well-tolerated, but some people may experience side effects, such as nausea or gastrointestinal discomfort. These side effects often lessen over time, but patients should stay in regular contact with their healthcare providers to monitor their progress and address any concerns.
Another consideration is cost. Tirzepatide can be expensive, and insurance coverage may vary depending on its approved uses. Patients may need to explore financial assistance programs or discuss alternative payment options with their healthcare provider.
Furthermore, it’s critical to ensure that weight loss achieved with tirzepatide is sustainable. Lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and good sleep hygiene, are essential for maintaining the benefits of the medication. Without these changes, there is a risk of regaining the lost weight once tirzepatide use is stopped.
Future Treatment Approaches
As research on tirzepatide continues, it’s possible that new treatment protocols will emerge that combine this medication with other therapies to provide even better outcomes for sleep apnea patients. For instance, studies might explore how tirzepatide interacts with other medications or treatments targeting airway health, inflammation, or metabolic regulation.
Additionally, researchers are likely to investigate the effects of tirzepatide on specific subgroups of patients with sleep apnea, such as those with mild symptoms, individuals who are not obese, or those with central sleep apnea. Understanding these nuances will help tailor treatment options to meet individual needs more effectively.
The long-term implications of using tirzepatide for sleep apnea are promising. By addressing the root cause of obesity and its related health problems, tirzepatide offers a pathway to improved sleep, better overall health, and a higher quality of life. However, it’s important to use this medication as part of a comprehensive treatment plan under the guidance of a healthcare provider. With ongoing research and careful monitoring, tirzepatide could play a key role in transforming how sleep apnea is managed in the future.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea is a serious condition that affects millions of people worldwide, often going undiagnosed. It can lead to a range of health problems, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and a reduced quality of life. One of the most common risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is obesity, as excess weight can lead to the narrowing or collapse of the airway during sleep. This makes weight loss an essential part of managing and improving sleep apnea. Tirzepatide, a medication primarily developed to aid in weight management, has shown promising results in helping people lose significant amounts of weight. As research continues, many are exploring how tirzepatide might also help improve conditions like sleep apnea.
Weight loss can have a profound effect on sleep apnea. Studies show that even a modest reduction in body weight can lead to measurable improvements in sleep apnea severity. This is because losing weight reduces fat around the neck and upper airway, making it easier to breathe during sleep. Weight loss can also improve lung function, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of related health issues. Tirzepatide plays a key role here because it is effective in helping people lose a significant percentage of their body weight. For individuals struggling with obesity, tirzepatide can provide a much-needed boost to achieve their weight loss goals, potentially leading to better sleep and fewer sleep apnea symptoms.
Tirzepatide works by targeting two key hormones: GLP-1 and GIP. These hormones play an important role in regulating appetite and blood sugar levels. By making people feel fuller for longer and reducing their appetite, tirzepatide helps reduce calorie intake. Clinical trials have shown that tirzepatide can lead to weight loss of over 15% of body weight in many individuals, with some losing even more. This is particularly important for people with sleep apnea, as significant weight loss can drastically reduce the severity of their condition. While tirzepatide is not specifically approved for treating sleep apnea, its ability to aid in weight loss may make it a valuable tool for managing this condition.
However, it is important to remember that tirzepatide is not a cure for sleep apnea. For many individuals, especially those with moderate to severe sleep apnea, weight loss alone may not fully resolve the condition. Treatments like continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy remain essential for maintaining an open airway during sleep. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as improving diet, increasing physical activity, and adopting good sleep hygiene can enhance the benefits of tirzepatide. A combined approach that includes medication, lifestyle adjustments, and standard treatments like CPAP is often the most effective strategy.
Using tirzepatide also comes with potential risks and side effects. Like any medication, it is important to use tirzepatide under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting, which may occur as the body adjusts to the medication. In rare cases, there may be more serious side effects, so regular monitoring is important. Patients with sleep apnea should work closely with their doctors to ensure that tirzepatide is safe for them, particularly if they have other health conditions like heart disease or diabetes.
Another consideration is that tirzepatide may indirectly improve sleep quality beyond its effects on weight loss. Obesity can disrupt hormonal balance and metabolism, which can lead to poor sleep. By improving metabolic health, tirzepatide might also help regulate sleep patterns, though more research is needed to confirm this effect. For now, the primary benefit of tirzepatide for sleep apnea lies in its ability to reduce body weight and lower related risks.
Looking ahead, tirzepatide could play an important role in the long-term management of sleep apnea, especially for people who struggle with obesity. Sustained weight loss not only reduces sleep apnea symptoms but also lowers the risk of other complications like high blood pressure and diabetes. With proper use, tirzepatide could help individuals maintain a healthier weight and improve their overall quality of life. However, it is important to recognize that weight management is a lifelong journey. Tirzepatide may provide a strong foundation, but long-term success requires ongoing commitment to a healthy lifestyle.
In conclusion, tirzepatide offers a promising pathway for individuals with obesity and sleep apnea to achieve significant weight loss and potentially improve their sleep apnea symptoms. While it is not a standalone treatment, its effects on weight and metabolic health make it a valuable addition to current sleep apnea management strategies. Combining tirzepatide with established therapies, lifestyle changes, and medical supervision can provide the best outcomes for those seeking to improve both their weight and their sleep health. As research continues, we will likely gain a deeper understanding of how tirzepatide can be used to support individuals with sleep apnea in achieving better health and quality of life.
Research Citations
Malhotra, A., Grunstein, R. R., Fietze, I., Weaver, T. E., Redline, S., Azarbarzin, A., Sands, S. A., Schwab, R. J., Dunn, J. P., Chakladar, S., Bunck, M. C., & Bednarik, J. (2024). Tirzepatide for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea and obesity. The New England Journal of Medicine, 391(12), 1193–1205. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2404881
Eli Lilly and Company. (2024, April 17). Tirzepatide reduced sleep apnea severity by up to nearly two-thirds in adults with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and obesity. Retrieved from https://investor.lilly.com/news-releases/news-release-details/tirzepatide-reduced-sleep-apnea-severity-nearly-two-thirds
University of California San Diego Health. (2024, June 21). Study identifies first drug therapy for sleep apnea. Retrieved from https://health.ucsd.edu/news/press-releases/2024-06-21-study-identifies-first-drug-therapy-for-sleep-apnea/
American Diabetes Association. (2024, June 21). Use of tirzepatide shown to improve sleep apnea and cardiovascular outcomes. Retrieved from https://diabetes.org/newsroom/press-releases/use-tirzepatide-shown-improve-sleep-apnea-and-cardiovascular-outcomes
American College of Cardiology. (2024, June 24). Tirzepatide for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea and obesity. Retrieved from https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/clinical-trials/2024/06/24/16/16/surmount-osa
Verywell Health. (2024, November 16). Why GLP-1 drugs may improve sleep apnea. Retrieved from https://www.verywellhealth.com/glp-1-drugs-and-sleep-apnea-8637353
News-Medical. (2024, June 26). New drug tirzepatide significantly improves sleep apnea and weight loss. Retrieved from https://www.news-medical.net/news/20240626/New-drug-tirzepatide-significantly-improves-sleep-apnea-and-weight-loss.aspx
The Wall Street Journal. (2024, April 17). Studies show Eli Lilly weight-loss drug helps with sleep apnea. Retrieved from https://www.wsj.com/articles/studies-show-eli-lilly-weight-loss-drug-helps-with-sleep-apnea-06fcc7c9
WebMD. (2024, April 17). Eli Lilly to ask FDA to approve weight loss drug for sleep apnea. Retrieved from https://www.webmd.com/sleep-disorders/sleep-apnea/news/20240417/eli-lilly-to-ask-fda-to-approve-weight-loss-drug-sleep-apnea
Nature Medicine. (2024, July 1). Transforming sleep apnea treatment with a metabolic drug. Retrieved from https://www.nature.com/articles/d41591-024-00051-z
Questions and Answers: Tirzepatide and Sleep Apnea
Tirzepatide is a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist used primarily for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. It helps regulate blood sugar and promotes weight loss.
Tirzepatide works by increasing feelings of satiety, slowing gastric emptying, and improving glucose metabolism, leading to reduced caloric intake and significant weight loss in many patients.
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. It can lead to poor sleep quality, daytime fatigue, and increased risks of cardiovascular diseases.
Yes, obesity is a significant risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), as excess weight can cause fat deposits around the upper airway, narrowing it and increasing the likelihood of airway obstruction during sleep.
Tirzepatide can indirectly improve sleep apnea symptoms by promoting weight loss, which reduces airway obstruction. However, more research is needed to confirm its direct effects on sleep apnea.
As of now, there are limited studies specifically addressing Tirzepatide’s direct impact on sleep apnea. Most benefits are observed through its ability to aid weight loss, which is a known treatment for sleep apnea.
The primary benefit is significant weight loss, which can decrease the severity of obstructive sleep apnea, improve breathing during sleep, and enhance overall health.
Common side effects of Tirzepatide include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue, which could potentially disrupt sleep quality, especially when starting the medication.
No, Tirzepatide is not a substitute for CPAP therapy. It may complement sleep apnea treatment by reducing weight, but CPAP remains the standard treatment for managing airway obstruction in moderate to severe sleep apnea.
Patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes or those struggling with significant weight-related health issues, including sleep apnea, may consider Tirzepatide under the guidance of a healthcare provider.

Dr. Judith Germaine
Dr. Jude (Germaine-Munoz) Germaine, MD is a family physician in Springfield, New Jersey. She is currently licensed to practice medicine in New Jersey, New York, and Florida. She is affiliated with Saint Josephs Wayne Hospital.
