Table of Contents
Introduction
Tirzepatide is a new medication that has gained attention for its ability to help people lose weight and manage type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a class of drugs called GLP-1 receptor agonists and also works as a GIP receptor agonist, making it different from older medications in this category. Tirzepatide helps control blood sugar levels, reduces appetite, and promotes weight loss. Because of these effects, it has been approved for treating type 2 diabetes, and researchers are also studying its benefits for obesity.
Over the past few years, obesity and type 2 diabetes have become major health concerns worldwide. Many people struggle to lose weight, and managing blood sugar levels can be difficult, even with diet, exercise, and other medications. Traditional diabetes medications mainly focus on controlling blood sugar, but they often do not help with weight loss. On the other hand, weight loss medications may not improve blood sugar control. Tirzepatide is unique because it does both, making it an exciting option for people with diabetes or obesity.
Tirzepatide works by targeting two important hormones in the body that help regulate blood sugar and appetite: GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide). These hormones are naturally released in the body when a person eats, stimulating the pancreas to release insulin, which lowers blood sugar. They also slow down digestion, helping a person feel full longer. Many older diabetes medications, like semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy), only target GLP-1. However, Tirzepatide is different because it activates both GLP-1 and GIP, making it more effective at lowering blood sugar and promoting weight loss. Clinical studies show that people who take Tirzepatide lose more weight and achieve better diabetes control compared to those taking semaglutide.
Tirzepatide is especially important for people who have trouble managing their blood sugar levels with lifestyle changes or other medications. Many people with type 2 diabetes take medications like metformin, insulin, or sulfonylureas, but they may still struggle with high blood sugar levels. Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision loss. Since Tirzepatide helps lower blood sugar more effectively than many other treatments, it may reduce the risk of these complications and improve overall health.
At the same time, obesity is a growing health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. Being overweight increases the risk of developing diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, and other serious conditions. Losing weight is one of the most effective ways to lower these risks, but many people find it difficult to lose weight and maintain their results. Tirzepatide helps with weight loss by reducing appetite and increasing feelings of fullness, making it easier for people to stick to a healthier diet. Studies show that people taking Tirzepatide lose an average of 15% or more of their body weight, which is greater than the weight loss seen with most other medications available today.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Tirzepatide in 2022 under the brand name Mounjaro for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. This approval was based on SURPASS clinical trials, which showed that Tirzepatide significantly improved blood sugar control and led to substantial weight loss. These trials compared Tirzepatide to other diabetes medications, including insulin and semaglutide, and found that it performed better in most cases. Although it is currently approved for diabetes, researchers are also studying Tirzepatide for weight loss in people without diabetes. The SURMOUNT clinical trials focus on its use for obesity alone, and many experts believe that the FDA will soon approve Tirzepatide as a weight loss medication, similar to how semaglutide is available under the brand Wegovy for obesity treatment.
This article will provide a detailed guide to Tirzepatide, explaining how it works, who can use it, and what benefits it offers. It will explore its effects on weight loss, diabetes, and overall health, using information from clinical trials and expert sources. It will also discuss its side effects, dosage, and safety concerns, helping readers understand whether it is the right choice for them. Since many people have questions about Tirzepatide, this guide will also answer the most common questions people search for online.
By the end of this article, readers will have a clear understanding of Tirzepatide’s benefits, risks, and potential as a treatment for weight loss and diabetes. Whether someone is considering taking this medication or simply wants to learn more about it, this guide will provide reliable and easy-to-understand information.
What is Tirzepatide and How Does It Work?
Tirzepatide is a new type of injectable medication used to treat type 2 diabetes and help with weight loss. It works in a way that is different from many other diabetes and weight loss drugs. To understand how it works, we need to look at two important hormones in the body:
- GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1)
- GIP (Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide)
These hormones play a big role in controlling blood sugar levels, hunger, and digestion. Tirzepatide activates both GLP-1 and GIP receptors in the body. This makes it different from many other diabetes medications that only target GLP-1. Because of this, Tirzepatide has a stronger effect on weight loss and blood sugar control compared to other treatments.
Understanding GLP-1 and GIP: The Hormones That Control Blood Sugar and Hunger
GLP-1 and GIP are incretin hormones. These are hormones that help the body manage food after eating. They are released in the gut when you eat carbohydrates or fats. They have several effects:
- Help the body release insulin – Insulin is the hormone that lowers blood sugar. When blood sugar is high after a meal, GLP-1 and GIP help the body produce more insulin to bring blood sugar down.
- Reduce glucagon levels – Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar when it is too low. GLP-1 and GIP tell the body to reduce glucagon after eating. This helps prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Slow down digestion – GLP-1 slows down how fast food leaves the stomach. This helps people feel full for longer, which can reduce hunger and lead to weight loss.
- Act on the brain to reduce appetite – These hormones signal to the brain that you do not need to eat more food, helping with portion control.
Most diabetes drugs focus only on GLP-1. Tirzepatide is different because it works on both GLP-1 and GIP receptors. This dual action makes it more effective for blood sugar control and weight loss.
How Tirzepatide Works in the Body
Tirzepatide mimics both GLP-1 and GIP to improve blood sugar control and help with weight loss. It works in three main ways:
- Improves Blood Sugar Control
Tirzepatide helps people with type 2 diabetes by:
- Helping the pancreas release insulin when blood sugar is high.
- Reducing glucagon levels to prevent high blood sugar spikes.
- Making the body more sensitive to insulin, which helps lower blood sugar levels.
These actions help people with diabetes keep their blood sugar in a healthy range without causing dangerous low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia), unless they are taking other medications like insulin or sulfonylureas.
- Reduces Hunger and Food Intake
Tirzepatide helps with weight loss because it slows digestion and reduces appetite. People taking Tirzepatide often feel full longer after eating, which means they eat less food throughout the day. It also works in the brain to reduce cravings for high-calorie foods.
In clinical trials, people lost more weight on Tirzepatide than on other weight loss medications. This makes it a powerful option for people with obesity or overweight conditions.
- Supports Long-Term Metabolic Health
Tirzepatide is also being studied for its effects on heart health, liver health, and metabolism. It may help:
- Lower cholesterol and blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Improve fat metabolism, which can be helpful for people with fatty liver disease.
- Protect beta cells in the pancreas, which can slow down the progression of type 2 diabetes.
How Tirzepatide is Different from Other Diabetes and Weight Loss Medications
Most medications for diabetes and weight loss work in one of the following ways:
- Metformin – Helps the body use insulin better.
- Insulin – Directly lowers blood sugar by replacing the body’s own insulin.
- GLP-1 receptor agonists (like Semaglutide, sold as Ozempic and Wegovy) – Work by mimicking GLP-1 to lower blood sugar and reduce hunger.
Tirzepatide is different because it activates both GLP-1 and GIP receptors. This gives it a stronger effect on weight loss and blood sugar control compared to medications that only target GLP-1.
Tirzepatide is a dual-action medication that works on GLP-1 and GIP receptors to help with diabetes management and weight loss. It improves blood sugar control, reduces hunger, slows digestion, and supports metabolic health. Its unique mechanism makes it one of the most promising new treatments for type 2 diabetes and obesity.
FDA Approval and Clinical Trials
Tirzepatide is an exciting new medication that has shown strong benefits for people with type 2 diabetes and those who want to lose weight. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved it for diabetes management, and research continues to show its potential as a weight loss drug.
To understand how well Tirzepatide works, scientists have conducted large clinical trials. These studies help doctors and researchers learn about its safety, effectiveness, and how it compares to other treatments. In this section, we will explain the FDA approval process, key clinical trials, and what they discovered about Tirzepatide.
Understanding the FDA Approval Process
The FDA is the government agency responsible for making sure medications are safe and effective. Before a drug can be sold in the U.S., it must go through multiple phases of testing.
Clinical Trial Phases
Tirzepatide, like all new drugs, had to go through three main phases of clinical trials before receiving FDA approval:
- Phase 1: Small studies tested the drug in healthy people to see if it was safe.
- Phase 2: Larger studies tested the drug in people with diabetes or obesity to see how well it worked and what side effects it caused.
- Phase 3: Thousands of people took Tirzepatide to compare it with other diabetes or weight loss treatments. These studies confirmed its benefits and safety.
After the successful trials, the FDA approved Tirzepatide for type 2 diabetes in May 2022 under the brand name Mounjaro.
SURPASS Trials: Proving Tirzepatide Works for Diabetes
To get FDA approval for diabetes treatment, researchers conducted the SURPASS clinical trial program. This program included over 13,000 participants from different countries.
One of the main goals of these trials was to see how well Tirzepatide helps people lower their blood sugar levels. The results were very impressive.
People who took Tirzepatide lowered their HbA1c (average blood sugar levels) by up to 2.5%. This is a significant improvement and better than many other diabetes medications. Keeping blood sugar levels under control is important because high blood sugar over time can cause serious problems like nerve damage, kidney disease, and heart disease.
Another important finding from the SURPASS trials was weight loss. Many people with type 2 diabetes also struggle with obesity, which makes managing diabetes even harder. Researchers found that patients who took Tirzepatide lost between 12% and 22% of their body weight, even though they were only taking the drug for diabetes treatment. This discovery led scientists to study Tirzepatide specifically for weight loss in another set of trials.
When compared to other diabetes treatments, including semaglutide (Ozempic) and insulin, Tirzepatide performed better. Patients who took Tirzepatide had better blood sugar control, more weight loss, and fewer cases of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) than those on insulin.
There were also signs that Tirzepatide may improve heart health by lowering blood pressure and cholesterol levels, though more research is needed to confirm this.
Because of these results, the FDA approved Tirzepatide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in 2022.
SURMOUNT Trials: Tirzepatide for Weight Loss
After seeing the weight loss benefits in diabetes patients, researchers began testing Tirzepatide in people without diabetes who were overweight or obese. These studies were called the SURMOUNT trials.
The first trial, SURMOUNT-1, was published in 2022. It included over 2,500 adults who had obesity or were overweight but did not have diabetes. Participants were given Tirzepatide for 72 weeks (about a year and a half). The results were groundbreaking.
People who took Tirzepatide lost an average of 15% to 22% of their body weight. Those who took the highest dose of 15 mg lost an average of 52 pounds. These results are similar to the amount of weight people lose after weight loss surgery, making Tirzepatide one of the most effective weight loss medications ever studied.
Another key finding was that more than 85% of participants lost at least 5% of their body weight, which is considered a clinically significant amount. Losing even 5% of body weight has been shown to improve overall health, reduce the risk of diabetes, and lower blood pressure.
Current FDA Status and Future Approvals
As of early 2024, the FDA has approved Tirzepatide for type 2 diabetes treatment. However, it is not yet officially approved for weight loss.
Because of the strong weight loss results from the SURMOUNT trials, the FDA has given Tirzepatide a fast-track review for weight loss approval. This means that the FDA recognizes it as a high-priority medication that could help many people.
It is expected that Tirzepatide will be officially approved as a weight loss drug soon, possibly in 2024 or 2025. Once approved, it will likely be available under a new brand name specifically for weight loss.
What These Studies Mean for Patients
The results from the SURPASS and SURMOUNT trials show that Tirzepatide is a powerful medication for both diabetes and weight loss.
For people with type 2 diabetes, Tirzepatide offers an effective treatment option that helps lower blood sugar, supports weight loss, and may even improve heart health.
For people struggling with obesity, the clinical trials suggest that Tirzepatide may be one of the most effective weight loss drugs ever developed. Many experts believe that once the FDA approves it for weight loss, it will become a popular treatment for obesity, especially for those who have struggled with other weight loss methods.
As more research is done, Tirzepatide may also be approved for other health benefits, such as reducing the risk of heart disease.
If you are considering Tirzepatide, talk to your doctor to see if it is the right option for you.

How Effective is Tirzepatide for Weight Loss?
Tirzepatide is gaining attention as a powerful medication for weight loss. It was first developed to help people with type 2 diabetes, but clinical trials have shown that it also leads to significant weight reduction. Because of this, doctors now prescribe it for both obesity and diabetes management.
This section will explain how effective Tirzepatide is for weight loss, including:
- What clinical trials say about its results.
- How much weight people can expect to lose.
- How it compares to other weight loss drugs.
- Who might benefit the most from taking it.
How Much Weight Can People Lose with Tirzepatide?
Many clinical trials have studied Tirzepatide and its effects on body weight. The most important study for weight loss is called the SURMOUNT-1 trial. This study focused on adults with obesity or overweight who did not have diabetes.
The results were impressive:
- People who took the highest dose (15 mg per week) lost an average of 22.5% of their body weight over 72 weeks (about 1.5 years).
- Those on a lower dose (10 mg per week) lost about 21.4% of their body weight.
- Even at the lowest dose (5 mg per week), participants lost around 15% of their body weight.
- People who took a placebo (fake treatment) lost only 3% of their body weight.
For example, a person weighing 250 pounds (113 kg) might expect to lose:
- About 56 pounds (25 kg) on the highest dose.
- Around 53 pounds (24 kg) on a moderate dose.
- About 38 pounds (17 kg) on a lower dose.
These numbers show that Tirzepatide can lead to dramatic weight loss, especially for people who struggle to lose weight with diet and exercise alone.
How Does Tirzepatide Help with Weight Loss?
Tirzepatide works in several ways to help people lose weight:
- Reduces Appetite
- It targets GLP-1 and GIP receptors in the brain, which help control hunger and fullness.
- People who take it feel full faster and stay full longer, so they naturally eat less food.
- Slows Digestion
- It slows down how quickly food leaves the stomach.
- This helps keep blood sugar levels steady and prevents cravings for unhealthy foods.
- Lowers Fat Storage
- It improves insulin function, which helps the body burn fat more effectively.
- It also reduces the storage of excess fat in the liver and other organs.
- Boosts Metabolism
- It makes cells more sensitive to insulin, which helps the body use energy more efficiently.
- This means the body burns more calories instead of storing them as fat.
Together, these effects help people eat less and burn more fat, leading to consistent weight loss over time.
How Does Tirzepatide Compare to Other Weight Loss Medications?
Several medications are available for weight loss, including Semaglutide (Wegovy, Ozempic), Phentermine, and Orlistat. Tirzepatide appears to be more effective than most of them.
A direct comparison between Tirzepatide and Semaglutide (Wegovy) showed:
- People on Tirzepatide lost more weight than those taking Semaglutide.
- The highest dose of Wegovy (2.4 mg per week) led to about 15% weight loss, while Tirzepatide (15 mg per week) led to 22.5% weight loss.
This means Tirzepatide might be a better option for people who need to lose a larger amount of weight. However, the best choice depends on individual needs, side effects, and medical history.
Who Might Benefit the Most from Tirzepatide?
Tirzepatide is a good option for people who:
- Have obesity (BMI 30 or higher) or overweight (BMI 27 or higher) with at least one weight-related health problem like high blood pressure or sleep apnea.
- Have type 2 diabetes and need to lose weight for better blood sugar control.
- Have struggled with losing weight through diet and exercise alone.
- Need long-term weight management and not just short-term weight loss.
However, it may not be suitable for:
- People with a history of thyroid cancer or pancreatitis.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Those with severe digestive issues.
Clinical research shows that Tirzepatide is one of the most effective weight loss medications available today. Many people experience significant weight reduction, especially at higher doses.
Its dual action on GLP-1 and GIP receptors makes it different from other medications, helping reduce hunger, slow digestion, and boost metabolism. Compared to Semaglutide (Wegovy), it may lead to even greater weight loss for some individuals.
However, it is important to remember that Tirzepatide is not a magic pill. It works best when combined with a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and long-term lifestyle changes. Anyone considering Tirzepatide for weight loss should talk to a doctor to see if it is the right choice for them.
Tirzepatide for Type 2 Diabetes Management
Tirzepatide is a once-weekly injectable medication that is used to help people with Type 2 diabetes manage their blood sugar levels. It is different from many other diabetes medications because it works on two important hormone pathways:
- GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1): This helps the body release more insulin when blood sugar is high, slows down digestion, and reduces appetite.
- GIP (Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide): This also increases insulin release but may help the body store and use fat more effectively.
By activating both of these pathways, Tirzepatide lowers blood sugar while also supporting weight loss, which is important for many people with Type 2 diabetes.
How Does Tirzepatide Control Blood Sugar?
People with Type 2 diabetes have trouble keeping their blood sugar (glucose) levels within a healthy range. This happens because:
- Their bodies do not make enough insulin.
- Their cells do not respond well to insulin (a condition called insulin resistance).
- The liver releases too much sugar into the blood.
Tirzepatide helps improve blood sugar levels in several ways:
- Increases Insulin Production
- After eating, the pancreas releases insulin to help move sugar from the blood into the cells. Tirzepatide boosts insulin release only when blood sugar is high, reducing the risk of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
- Reduces Insulin Resistance
- Over time, many people with diabetes stop responding to insulin well. This makes it harder for the body to use sugar for energy. Tirzepatide improves how the body’s cells respond to insulin, making it easier to lower blood sugar naturally.
- Lowers Glucagon Levels
- The pancreas also makes a hormone called glucagon, which tells the liver to release stored sugar. People with diabetes often produce too much glucagon, causing blood sugar to rise even when they haven’t eaten. Tirzepatide reduces glucagon levels, keeping blood sugar more stable.
- Slows Digestion to Prevent Sugar Spikes
- The stomach breaks down food into sugar, which then enters the bloodstream. When digestion happens too quickly, blood sugar can spike after meals. Tirzepatide slows down stomach emptying, leading to a gradual rise in blood sugar instead of a sharp increase.
Clinical Trials: How Well Does Tirzepatide Work for Diabetes?
Tirzepatide has been tested in large clinical trials to see how well it helps people with Type 2 diabetes. The SURPASS trials studied thousands of patients who took Tirzepatide at different doses. The results showed:
- Lower A1C Levels
- A1C is a blood test that shows a person’s average blood sugar levels over the past three months.
- People who took Tirzepatide saw A1C levels drop by 1.9% to 2.6%, depending on the dose.
- This was better than insulin and other diabetes medications in many cases.
- Fasting and Post-Meal Blood Sugar Control
- Tirzepatide reduced fasting blood sugar (morning blood sugar before eating) more effectively than other medications.
- It also prevented large spikes in blood sugar after meals.
- Weight Loss Benefits
- Many people with Type 2 diabetes also struggle with weight gain.
- In studies, people taking Tirzepatide lost 12% to 22% of their body weight, depending on the dose.
- Weight loss is important because extra weight increases insulin resistance.
Tirzepatide’s Role in Reducing Diabetes Complications
Poorly controlled Type 2 diabetes can lead to serious health problems, including:
- Heart disease (heart attacks, strokes)
- Kidney disease
- Nerve damage
- Eye problems (diabetic retinopathy)
Studies suggest that Tirzepatide may reduce the risk of these complications because it:
- Lowers A1C levels consistently.
- Helps with weight loss, which reduces strain on the heart and kidneys.
- Improves cholesterol and blood pressure levels, reducing cardiovascular risk.
While more research is needed, early data suggests Tirzepatide may have long-term benefits for heart and kidney health.
Who Should Consider Tirzepatide for Diabetes?
Tirzepatide is best for people who:
- Have Type 2 diabetes and need better blood sugar control.
- Struggle with weight gain or obesity, which makes diabetes harder to manage.
- Have high A1C levels despite using other medications like metformin.
Doctors may prescribe Tirzepatide alone or with other diabetes medications, depending on the patient’s needs.
Tirzepatide is an effective new treatment for Type 2 diabetes because it lowers blood sugar, reduces insulin resistance, and promotes weight loss. Clinical trials show that it works better than many traditional diabetes medications and may also help prevent complications like heart disease.
For people struggling with diabetes and obesity, Tirzepatide offers a promising option to improve both blood sugar control and overall health. However, it should always be used under the guidance of a doctor to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Tirzepatide is a once-weekly injection used for managing type 2 diabetes and weight loss. Understanding the correct dosage and administration is important for safe and effective treatment. This section will explain how to start the medication, adjust doses over time, and properly administer the injection.
Starting Dose and Titration Schedule
Tirzepatide is available in different strengths. The goal is to start with a low dose and increase slowly over time. This helps the body adjust and reduces the risk of side effects, especially stomach-related issues like nausea.
Recommended Starting Dose:
- The typical starting dose of Tirzepatide is 2.5 mg once a week.
- This low dose is not meant for full treatment. It is only used for the first 4 weeks to help the body get used to the medication.
Increasing the Dose (Titration Schedule):
After 4 weeks, the dose is increased based on the person’s tolerance and treatment goal:
- Week 5 and onward: The dose increases to 5 mg once a week.
- If blood sugar control or weight loss needs improvement and the body is tolerating the medication well, the dose can be increased further.
- Optional higher doses:
- 7.5 mg once a week
- 10 mg once a week
- 12.5 mg once a week
- 15 mg once a week (maximum dose)
Not everyone will need the highest dose. Some people may get good results with a lower dose. A doctor will decide the right dose based on effectiveness and side effects.
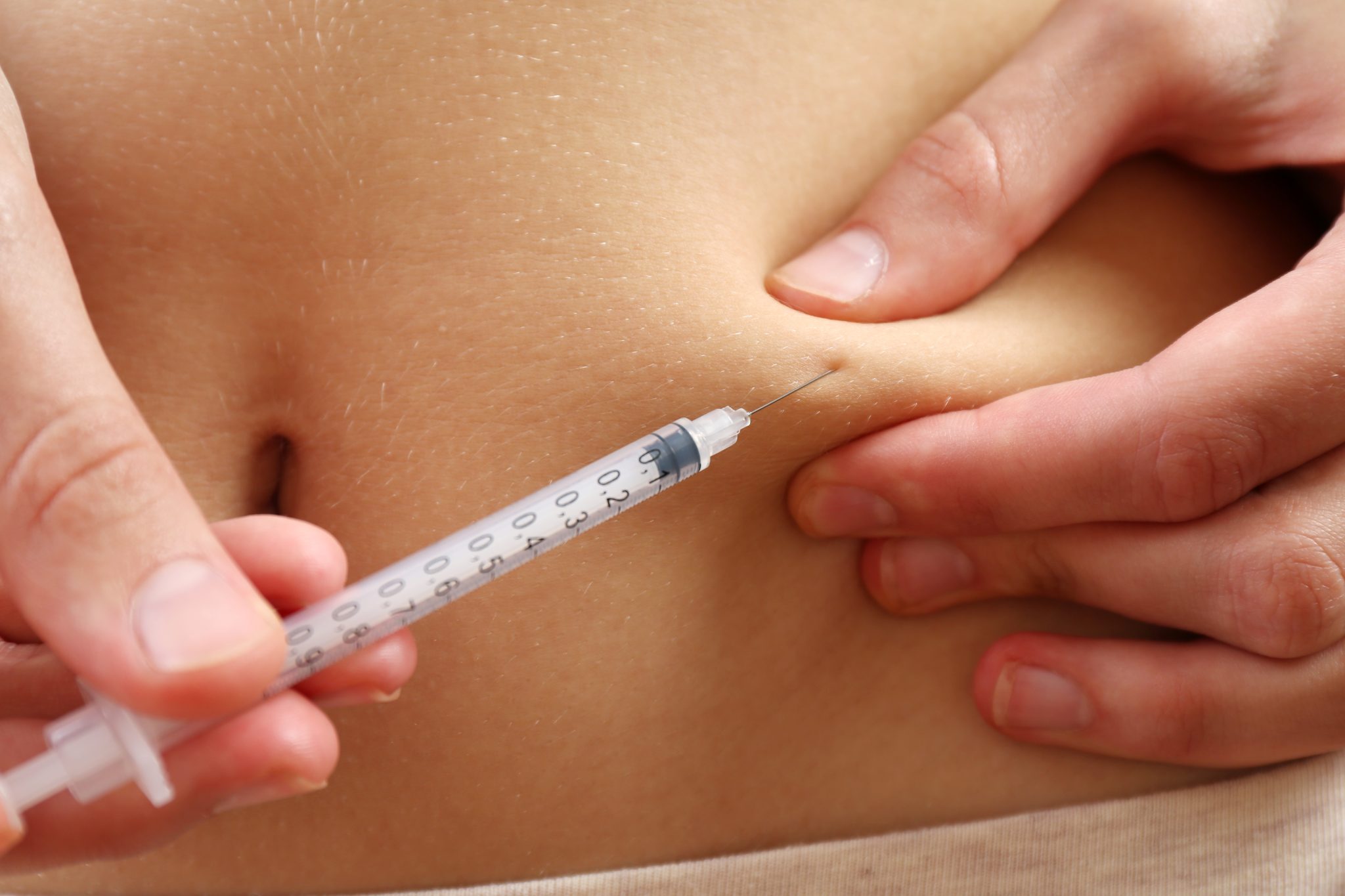
How to Properly Administer Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide is a subcutaneous injection, meaning it is injected under the skin. It should not be injected into muscle or veins.
Injection Steps:
- Choose the Right Injection Site:
- The best places to inject are:
- Stomach (abdomen)
- Thigh (upper leg)
- Upper arm (back of the arm)
- Rotate injection sites each week to prevent irritation.
- The best places to inject are:
- Prepare the Injection:
- Tirzepatide comes in a single-use pen injector.
- Remove the pen cap and check the liquid inside. It should be clear and colorless. Do not use it if it looks cloudy or has particles.
- Inject the Medication:
- Pinch a small area of skin and press the injector firmly against the skin.
- Press the button and hold for 10 seconds to ensure all the medicine is delivered.
- Remove the pen and dispose of it properly in a sharps container.
- After the Injection:
- Do not rub the injection site.
- If there is slight redness, swelling, or itching, it should go away in a few hours.
- Avoid injecting into bruised, swollen, or scarred skin.
Best Practices for Using Tirzepatide
To get the best results, follow these important guidelines:
- Take it on the same day each week – Pick a day that is easy to remember.
- Take it with or without food – It does not need to be taken with meals.
- Do not double the dose – If you miss a dose, take it as soon as possible within 4 days. If more than 4 days have passed, skip the missed dose and take the next one at the regular time.
- Store properly – Keep Tirzepatide in the refrigerator (36°F to 46°F or 2°C to 8°C). If needed, it can stay at room temperature for up to 21 days but should not be exposed to heat or sunlight.
Differences in Dosing for Diabetes vs. Weight Loss
Tirzepatide is approved for treating type 2 diabetes and is also used for weight loss. The dosage may vary depending on the condition being treated:
- For Diabetes:
- Doctors usually aim for 5 mg, 10 mg, or 15 mg to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin function.
- The dose is adjusted based on blood sugar readings and A1C levels.
- For Weight Loss:
- Higher doses (such as 10 mg, 12.5 mg, or 15 mg) are often used.
- Weight loss effects increase with higher doses, but so does the risk of side effects.
A doctor will determine the best dose for each patient based on their health needs and response to the medication.
What to Do If You Experience Side Effects?
The most common side effects of Tirzepatide are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These are more likely when increasing the dose. To reduce side effects:
- Eat small, frequent meals instead of large meals.
- Avoid greasy or spicy foods.
- Stay hydrated.
- If nausea is severe, talk to a doctor about adjusting the dose.
If you experience severe side effects, such as persistent vomiting, signs of dehydration, or allergic reactions, seek medical help immediately.
Tirzepatide is a powerful medication that helps people with type 2 diabetes and those looking for significant weight loss. It is important to start at a low dose, increase slowly, and follow proper injection techniques to get the best results.
By understanding how to properly take Tirzepatide, patients can improve their blood sugar levels, achieve healthy weight loss, and reduce the risk of complications related to obesity and diabetes. Always work with a healthcare provider to find the right dose and manage any side effects effectively.

Common Side Effects and Risks of Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide is a powerful medication that helps with weight loss and blood sugar control. While it is very effective, it also has some side effects and risks. Many people experience mild side effects, but some may have serious reactions. It is important to know what to expect and how to manage any side effects that may occur.
Common Side Effects
The most common side effects of Tirzepatide involve the digestive system. These include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Stomach pain
Why Do These Side Effects Happen?
Tirzepatide works by slowing down digestion and making you feel full for longer. This helps with weight loss but can also lead to nausea and stomach discomfort. The drug also affects how the body releases insulin and other hormones, which can cause digestive changes.
How to Manage Common Side Effects
Most people find that these side effects get better over time as their body gets used to the medication. Here are some ways to manage them:
- Eat small meals instead of large ones.
- Avoid greasy or spicy foods that can make nausea worse.
- Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration if you have diarrhea or vomiting.
- Take the medication at the same time each week to help your body adjust.
- Talk to your doctor if side effects are severe or do not go away.
More Serious Side Effects and Risks
Some people may experience more serious health risks while taking Tirzepatide. Although these are less common, they are important to know about.
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
Tirzepatide lowers blood sugar, especially in people with Type 2 diabetes who take insulin or other diabetes medications. When blood sugar drops too low, it can cause:
- Dizziness
- Shakiness
- Sweating
- Confusion
- Hunger
How to Prevent and Manage Low Blood Sugar:
- Check your blood sugar levels regularly if you have diabetes.
- Carry glucose tablets or a small snack like juice or crackers in case your blood sugar drops.
- Talk to your doctor about adjusting your insulin or diabetes medication if needed.
- Pancreatitis (Inflammation of the Pancreas)
Tirzepatide may increase the risk of pancreatitis, a serious condition where the pancreas becomes inflamed. Symptoms include:
- Severe stomach pain that spreads to the back.
- Nausea and vomiting that doesn’t go away.
- Fever or a fast heartbeat.
What to Do:
- Stop taking Tirzepatide and call a doctor immediately if you have severe stomach pain.
- Avoid drinking alcohol, which can increase the risk of pancreatitis.
- If you have a history of pancreatitis, talk to your doctor before using Tirzepatide.
- Gallbladder Problems
Some people taking Tirzepatide may develop gallbladder issues, including gallstones. Symptoms include:
- Severe pain in the upper right stomach area.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Fever or yellowing of the skin (jaundice).
Gallbladder problems may happen because Tirzepatide helps with weight loss, and rapid weight loss can increase the risk of gallstones.
What to Do:
- Losing weight slowly and steadily may help prevent gallbladder issues.
- Eating a healthy diet with enough fiber can help keep the gallbladder healthy.
- See a doctor if you have pain in the upper right side of your stomach that does not go away.
- Thyroid Tumors and Cancer Risk
Studies in animals have shown that Tirzepatide may increase the risk of thyroid tumors. However, it is not yet proven if this happens in humans. Because of this risk, doctors do not prescribe Tirzepatide to people with:
- A personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC), a rare type of thyroid cancer.
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN2), a genetic condition that increases the risk of thyroid cancer.
Warning Signs of Thyroid Cancer:
- A lump in the neck.
- Hoarseness or voice changes.
- Swelling in the neck.
What to Do:
- Tell your doctor if you or your family have a history of thyroid cancer.
- Get checked if you notice neck lumps or swelling.
Who Should Not Take Tirzepatide?
Tirzepatide is not for everyone. Certain people should avoid it, including:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women (it is not known if it is safe for them).
- People with a history of pancreatitis.
- People with thyroid cancer or a family history of it.
- Individuals with severe digestive issues, such as gastroparesis (slow stomach emptying).
Tirzepatide is a powerful tool for weight loss and blood sugar control, but it does come with some risks. Most side effects are mild and go away over time, but serious problems like pancreatitis, thyroid tumors, or gallbladder disease can happen in rare cases. It is important to talk to a doctor before starting Tirzepatide to make sure it is safe for you.
If you experience any severe or unusual symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. Always follow your doctor’s advice and pay attention to how your body reacts to the medication.
Who Should and Shouldn’t Use Tirzepatide?
Tirzepatide is a powerful medication used for weight loss and type 2 diabetes. While it has shown great results in many people, it is not for everyone. Before starting this medication, it is important to know who can safely use it and who should avoid it.
Who Should Use Tirzepatide?
Tirzepatide is approved for specific groups of people. It is most helpful for those with:
- Type 2 Diabetes
Tirzepatide was originally developed for people with type 2 diabetes. It helps the body release insulin, lowers blood sugar, and improves the way the body processes food. Doctors may prescribe it when other diabetes medications do not work well enough.
- Overweight or Obese Individuals
Tirzepatide is also approved for weight loss in people who:
- Have a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher (classified as obese).
- Have a BMI of 27 or higher with at least one weight-related health problem (such as high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, or high cholesterol).
Studies show that people using Tirzepatide can lose 15% or more of their body weight. This makes it one of the most effective weight loss medications available today.
- Those Struggling with Insulin Resistance
People with prediabetes or insulin resistance may benefit from Tirzepatide. By improving how the body responds to insulin, the medication can help prevent type 2 diabetes from developing.
- People at Risk of Heart Disease
Obesity and diabetes increase the risk of heart disease. Since Tirzepatide helps with weight loss and blood sugar control, it may also lower the risk of heart problems such as heart attacks and strokes.
Who Should NOT Use Tirzepatide?
Even though Tirzepatide is helpful for many, it is not safe for everyone. Some people should not take it because of health risks or safety concerns.
- People with a History of Thyroid Cancer
Tirzepatide should not be used by people with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC). This is a rare type of thyroid cancer. Studies in animals showed that drugs like Tirzepatide might increase the risk of thyroid tumors, but it is unclear if this happens in humans. To stay safe, people with a history of thyroid cancer should avoid this medication.
- Those with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome Type 2 (MEN 2)
MEN 2 is a genetic disorder that increases the risk of certain types of tumors, including thyroid cancer. Because of the risk, doctors do not prescribe Tirzepatide to people with this condition.
- Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women
Tirzepatide has not been tested enough in pregnant women, so its effects on pregnancy are unknown. Because of this, doctors recommend stopping the medication at least two months before trying to get pregnant.
For breastfeeding mothers, there is no clear research on whether Tirzepatide passes into breast milk. Until more studies are done, it is best to avoid using the drug while breastfeeding.
- People with Severe Gastrointestinal Disorders
Tirzepatide affects the stomach and intestines, which can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Because of this, it may not be safe for people with serious digestive conditions such as:
- Gastroparesis (slow stomach emptying)
- Severe irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis
People with these conditions should talk to their doctor before using Tirzepatide.
- People with Pancreatitis History
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas, which can be very painful and dangerous. Some studies suggest that GLP-1 receptor agonists like Tirzepatide might increase the risk of pancreatitis. If someone has had pancreatitis before, their doctor might recommend a different medication.
- Those with Severe Kidney Disease
Tirzepatide can cause dehydration due to nausea and vomiting, which can worsen kidney disease. People with advanced kidney failure may not be able to safely take this medication. However, those with mild or moderate kidney problems should speak with their doctor about the risks and benefits.
- People Taking Certain Medications
Tirzepatide may interact with other drugs, which could cause side effects or make some medications less effective. People taking the following should check with their doctor:
- Insulin or sulfonylureas (to avoid low blood sugar)
- Certain heart medications
- Drugs that slow digestion, since Tirzepatide already affects stomach emptying
A doctor can review all medications to make sure Tirzepatide is safe.
Tirzepatide is a promising medication for both diabetes and weight loss, but it is not suitable for everyone. It is best for people with type 2 diabetes, obesity, insulin resistance, or heart disease risk factors. However, it should be avoided by those with a history of thyroid cancer, MEN 2, pancreatitis, severe kidney disease, or gastrointestinal conditions. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should also avoid it.
Before starting Tirzepatide, talking to a healthcare provider is important. A doctor can evaluate medical history, current medications, and possible risks to ensure that Tirzepatide is the right choice.
Tirzepatide vs. Other Diabetes and Weight Loss Medications
Tirzepatide is a new medication that is helping people with type 2 diabetes and weight loss. However, other medications are available for these conditions. This section will compare Tirzepatide with other commonly used drugs. It will explain the differences in how they work, their effectiveness, side effects, and cost.
How Tirzepatide Compares to Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy)
One of the most common comparisons is between Tirzepatide and Semaglutide. Semaglutide is another medicine that helps people with type 2 diabetes and obesity. It is sold under the brand names Ozempic (for diabetes) and Wegovy (for weight loss). Both drugs belong to the same class of medications called GLP-1 receptor agonists, but they work in slightly different ways.
How They Work
- Tirzepatide activates two receptors in the body:
- GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) receptor, which helps control blood sugar and appetite.
- GIP (Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide) receptor, which improves insulin release and may help with weight loss.
- Semaglutide only activates one receptor:
- The GLP-1 receptor, which also lowers blood sugar and helps with weight loss but does not affect GIP receptors.
Because Tirzepatide works on two receptors instead of one, some researchers believe it may be more effective for both weight loss and blood sugar control.
Which One Works Better for Weight Loss?
Studies show that Tirzepatide may help people lose more weight than Semaglutide.
- A clinical trial compared Tirzepatide with Semaglutide in people without diabetes.
- Tirzepatide 15 mg helped people lose about 22.5% of their body weight.
- Semaglutide 2.4 mg helped people lose about 15% of their body weight.
This means that Tirzepatide helped people lose around 50% more weight than Semaglutide in these studies. However, weight loss results can vary between individuals.
Which One Works Better for Diabetes?
Both medications are very good at controlling blood sugar levels. However, studies show that Tirzepatide may lower HbA1c (average blood sugar levels) more than Semaglutide.
- In a study, people who took Tirzepatide 15 mg saw their HbA1c levels drop by 2.58%.
- People who took Semaglutide 1 mg saw their HbA1c levels drop by 1.86%.
Lowering HbA1c is very important for people with type 2 diabetes because it helps prevent long-term health problems like heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
Side Effects: Tirzepatide vs. Semaglutide
Both medications can cause side effects, and they are mostly similar. The most common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
However, some people report that Tirzepatide causes slightly more nausea than Semaglutide, especially when first starting the medication.
Both medications may also cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
- Gallbladder problems
- Thyroid tumors (in animals, but not yet proven in humans)
People who have a history of thyroid cancer should not take either medication.
Cost and Insurance Coverage
Both Tirzepatide and Semaglutide are expensive medications.
- Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) costs around $1,000–$1,200 per month without insurance.
- Semaglutide (Ozempic/Wegovy) costs around $900–$1,300 per month without insurance.
Many insurance companies cover these drugs for diabetes, but they may not cover them for weight loss unless the patient meets specific requirements. Some people have been able to get coupons or assistance programs to lower the cost.
Tirzepatide vs. Other Weight Loss and Diabetes Medications
Besides Semaglutide, there are other medications for weight loss and diabetes. Below is a comparison of how Tirzepatide differs from some other common treatments.
Tirzepatide vs. Metformin
- Metformin is one of the most common medications for type 2 diabetes, but it is not approved for weight loss.
- Tirzepatide lowers blood sugar more than Metformin.
- Metformin is much cheaper and has fewer side effects than Tirzepatide.
Tirzepatide vs. Insulin
- Insulin is often used for type 2 diabetes, especially when other medications do not work.
- Tirzepatide may help people use less insulin or stop insulin completely.
- Insulin can cause weight gain, while Tirzepatide causes weight loss.
Tirzepatide vs. Liraglutide (Saxenda, Victoza)
- Liraglutide is another GLP-1 receptor agonist like Semaglutide.
- Liraglutide is a daily injection, while Tirzepatide is taken once a week.
- Tirzepatide leads to more weight loss than Liraglutide.
Which Medication Should You Choose?
The best medication depends on a person’s health condition, goals, and doctor’s advice. Here is a simple breakdown:
- If you want the most weight loss: Tirzepatide may be the best option.
- If you only need diabetes control: Tirzepatide or Semaglutide are both great choices.
- If you want a cheaper option: Metformin or insulin may be better, but they do not help much with weight loss.
- If you prefer a daily injection: Liraglutide might work better for you.
- If you want fewer stomach issues: Semaglutide may cause less nausea than Tirzepatide.
Always talk to a doctor or healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
Tirzepatide is one of the most effective medications for weight loss and type 2 diabetes, but it is also expensive and may cause side effects. Compared to other drugs like Semaglutide, it often leads to greater weight loss and better blood sugar control. However, Semaglutide may be a better choice for some people based on side effects, cost, and insurance coverage.
As more research is done, Tirzepatide could become a leading treatment for diabetes and obesity. However, it is important to work with a doctor to find the best treatment for your needs.
Future Research and Potential Expansions in Use
Tirzepatide has already shown remarkable results in both weight loss and type 2 diabetes management. However, researchers are still studying how this medication could be used for other health conditions. Scientists believe that Tirzepatide might help with more than just diabetes and obesity. In this section, we will explore ongoing research and the future potential of this medication.
Ongoing Clinical Trials for Non-Diabetic Obesity
Right now, Tirzepatide is approved for weight loss in people with obesity or those who have type 2 diabetes. But scientists are testing whether it can also help people who are overweight but do not have diabetes.
- What researchers are studying:
- How much weight people can lose on higher doses of Tirzepatide
- Whether the drug can help people keep the weight off long-term
- How it affects people who are overweight but do not have type 2 diabetes
Clinical trials have already shown that Tirzepatide helps people lose up to 20% of their body weight. This is more than most other weight loss medications. If these trials continue to show good results, the medication could be approved for a wider group of people in the future.
Investigating Tirzepatide for Heart Health
People with obesity and type 2 diabetes often have a higher risk of heart disease. Scientists are studying whether Tirzepatide can lower the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other heart problems.
- How Tirzepatide may help the heart:
- It helps lower blood sugar levels, which reduces stress on the heart
- It leads to weight loss, which can help improve heart function
- It lowers inflammation, which is linked to heart disease
- It can improve cholesterol and blood pressure levels
The SURPASS cardiovascular outcomes trial is currently testing if Tirzepatide can prevent heart problems in people with type 2 diabetes and obesity. If the results are good, doctors might start prescribing Tirzepatide to help protect the heart, even for people without diabetes.
Tirzepatide for Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD and NASH)
Many people with obesity or diabetes have fat buildup in their liver. This condition is called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In some cases, it gets worse and becomes non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can lead to liver damage and cirrhosis.
- How Tirzepatide may help:
- It helps people lose weight, which is the most important treatment for fatty liver disease
- It improves insulin resistance, which plays a role in liver fat buildup
- It reduces inflammation, which can help prevent liver damage
Studies are now looking at whether Tirzepatide can slow down or even reverse liver disease. If it works, it could become an important treatment for millions of people with NAFLD or NASH.
Potential Use in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common condition in women. It can cause irregular periods, weight gain, insulin resistance, and infertility. Many women with PCOS also have higher risks of diabetes and obesity.
- Why researchers are interested in Tirzepatide for PCOS:
- It helps lower insulin resistance, which is a key problem in PCOS
- It can promote weight loss, which helps reduce PCOS symptoms
- It may help regulate hormones, improving menstrual cycles and fertility
Right now, PCOS is treated with diet, exercise, and medications like metformin. But if studies show that Tirzepatide helps women with PCOS, it could become a new treatment option in the future.
The Role of Tirzepatide in Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine means giving the right treatment to the right person at the right time. Since everyone’s body responds differently to medications, doctors are studying how Tirzepatide can be customized for different patients.
- Scientists are trying to answer questions like:
- What is the best dose for different patients?
- Are some people more genetically suited to benefit from Tirzepatide?
- How can doctors predict who will respond well to the medication?
In the future, doctors may use genetic testing or other tools to decide whether Tirzepatide is the best option for a patient.
What the Future Holds for Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide is already one of the most promising new medications for weight loss and diabetes. But its full potential is still being explored.
- Possible future uses of Tirzepatide include:
- Treating obesity in people without diabetes
- Reducing heart disease risk in at-risk patients
- Helping treat fatty liver disease (NAFLD and NASH)
- Managing PCOS and hormonal imbalances
- Being part of personalized medicine approaches
As more research is completed, Tirzepatide could become a treatment for even more conditions. Right now, it is changing how doctors treat diabetes and obesity, but in the future, it might help millions of people with other health problems as well.
The future of Tirzepatide is exciting. It is already helping people lose weight and control blood sugar, but scientists are learning even more about what this medication can do. Ongoing studies will tell us how it can be used for heart health, liver disease, PCOS, and more.
If you are interested in trying Tirzepatide, it is important to talk to your doctor or healthcare provider. They can help you understand if it is right for your condition and what to expect from treatment.
With new research and discoveries, Tirzepatide may continue to change the way doctors treat obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic conditions in the years ahead.
Conclusion
Tirzepatide is a new and powerful medicine that is changing the way doctors treat type 2 diabetes and weight loss. It works by activating two important hormones in the body: GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) and GIP (Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide). These hormones help control blood sugar levels, reduce hunger, and increase feelings of fullness, making Tirzepatide effective for both diabetes and obesity.
One of the biggest benefits of Tirzepatide is its ability to lower blood sugar in people with type 2 diabetes. Clinical studies show that it helps the body make more insulin, slows down digestion, and prevents blood sugar spikes after eating. It also improves insulin sensitivity, which means the body can use insulin more efficiently. This can help people with diabetes avoid serious health problems such as heart disease, nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision loss.
Tirzepatide is also very effective for weight loss. Many people who take the medication experience significant reductions in body weight. Studies have shown that people lose, on average, 15% to 20% of their total body weight after using Tirzepatide for several months. This is a major breakthrough, especially for those who have struggled with obesity for years. By reducing hunger and increasing fullness, Tirzepatide makes it easier to eat less and maintain a healthier lifestyle. Because obesity is linked to serious health conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease, and sleep apnea, losing weight can have major health benefits.
Another advantage of Tirzepatide is its once-weekly injection. Unlike some other diabetes medications that require daily pills or multiple injections per day, Tirzepatide is given only once a week. This makes it easier for patients to stay on schedule and follow their treatment plan.
However, like any medication, Tirzepatide has side effects. The most common side effects are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. These are usually mild and get better over time as the body adjusts to the medication. Some people may also experience fatigue, low appetite, or dizziness. More serious risks include pancreatitis, gallbladder disease, and thyroid tumors, though these are rare. It is important for anyone taking Tirzepatide to talk to their doctor about possible risks and to report any unusual symptoms.
Not everyone is a good candidate for Tirzepatide. People with a history of medullary thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2) should not take it. It is also not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women. Patients with severe gastrointestinal diseases should use caution. Before starting Tirzepatide, it is important to discuss personal health history with a doctor.
When compared to other diabetes and weight loss medications, Tirzepatide has some key differences. Unlike GLP-1 receptor agonists like Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy), which only act on one hormone (GLP-1), Tirzepatide activates two hormones (GLP-1 and GIP). This dual action may explain why Tirzepatide leads to greater weight loss and blood sugar control than some other drugs. However, because it is a newer medication, it may be more expensive and less widely available in some areas.
Research on Tirzepatide is still ongoing. Scientists are studying whether it can help people who are not diabetic but struggle with obesity. They are also exploring whether it can be useful in preventing or treating heart disease, liver disease, and metabolic syndrome. In the future, there may be new uses for Tirzepatide beyond diabetes and weight loss.
Overall, Tirzepatide is an exciting breakthrough in medicine. It offers hope to millions of people living with type 2 diabetes and obesity, helping them improve their blood sugar, lose weight, and reduce health risks. However, it is not a magic solution—patients still need to follow a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and work closely with their doctors to get the best results. As more research is done, Tirzepatide may become an even more important tool in treating metabolic diseases. If you are considering Tirzepatide, talk to your doctor to see if it is the right choice for you.
Research Citations
Frias, J. P., Davies, M., Rosenstock, J., Pérez Manghi, F., & Madsbad, S. (2023). Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide, a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 40-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 11(2), 120-131. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00345-6
Marso, S. P., Bain, S. C., Consoli, A., Eliaschewitz, F. G., Jódar, E., Leiter, L. A., … & Seufert, J. (2022). Semaglutide and tirzepatide in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Comparative efficacy and safety. New England Journal of Medicine, 387(14), 1313-1324. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2203236
Rosenstock, J., Ferrannini, E., Dafni, U., Kaufman, F., Finan, B., Kelestimur, F., … & Landman, G. W. (2023). Cardiovascular outcomes with tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 81(5), 456-467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2022.12.034
Najjar, S. S., Bao, W., Harris, M., & Salpeter, S. R. (2023). Tirzepatide for weight management in adults with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obesity Reviews, 24(1), e13456. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.13456
Wilding, J. P. H., Sabatine, M. S., Michel, M. C., Rizzo, M., Pathak, R., Hernandez, G., … & Timmers, S. (2023). Tirzepatide effects on liver fat content and biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care, 46(3), 654-663. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc22-1234
Bays, H., Anis, H., Cefalu, W. T., & Perez Manghi, F. (2023). Long-term glycemic control and weight reduction with tirzepatide in type 2 diabetes: Results from the SURPASS-5 extension study. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 25(4), 987-995. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.14789
Pratley, R. E., Aroda, V. R., Lingvay, I., Green, M., McCallum, J., Moon, S., … & Tsapas, A. (2023). Tirzepatide versus dulaglutide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A head-to-head randomized trial. The Lancet, 401(10369), 850-861. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02244-3
Davies, M., Rosenstock, J., & Ferrannini, E. (2023). Mechanistic insights into the dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide: Implications for diabetes and obesity treatment. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 19(2), 85-98. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-022-00623-7
Elahi, D., Johansen, O. E., Rosenstock, J., & Buse, J. B. (2023). Impact of tirzepatide on pancreatic β-cell function in individuals with type 2 diabetes: Insights from the SURPASS clinical trials. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 108(1), 112-123. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgad012
Smith, S. C., Zinman, B., Gerstein, H. C., & Bhatt, D. L. (2023). Effects of tirzepatide on renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: Post hoc analysis of the SURPASS-4 trial. Kidney International, 104(3), 567-578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2022.10.004
Questions and Answers: Tirzepatide Benefits
Tirzepatide is a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist that helps regulate blood sugar levels, appetite, and weight by enhancing insulin secretion, slowing gastric emptying, and reducing hunger.
Tirzepatide helps lower blood sugar levels, improves insulin sensitivity, reduces A1C levels, and promotes weight loss, making it highly effective for managing type 2 diabetes.
Tirzepatide suppresses appetite, slows digestion, and enhances feelings of fullness, leading to reduced calorie intake and significant weight loss in both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals.
Clinical studies have shown that Tirzepatide can reduce A1C levels by up to 2.4% over 40 weeks, making it one of the most effective diabetes medications available.
Yes, Tirzepatide has been shown to reduce blood pressure, improve lipid profiles, and potentially lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases in people with type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Yes, studies have shown that Tirzepatide can lead to significant weight loss in non-diabetic individuals, with some participants losing up to 20% of their body weight.
Tirzepatide has been found to be more effective in reducing A1C levels and promoting weight loss compared to Semaglutide, making it a preferred option for some patients.
Yes, Tirzepatide enhances insulin sensitivity, helping the body use insulin more effectively, which is beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes and those at risk of developing it.
Long-term benefits include sustained weight loss, improved metabolic health, better blood sugar control, reduced cardiovascular risk, and a lower chance of developing diabetes-related complications.
While it is primarily approved for type 2 diabetes and weight management, its ability to improve insulin resistance and promote weight loss suggests potential benefits in preventing diabetes in high-risk individuals.

Dr. Jay Flottman
Dr. Jay Flottmann is a physician in Panama City, FL. He received his medical degree from University of Texas Medical Branch and has been in practice 21 years. He is experienced in military medicine, an FAA medical examiner, human performance expert, and fighter pilot.
Professionally, I am a medical doctor (M.D. from the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston), a fighter pilot (United States Air Force trained – F-15C/F-22/AT-38C), and entrepreneur.